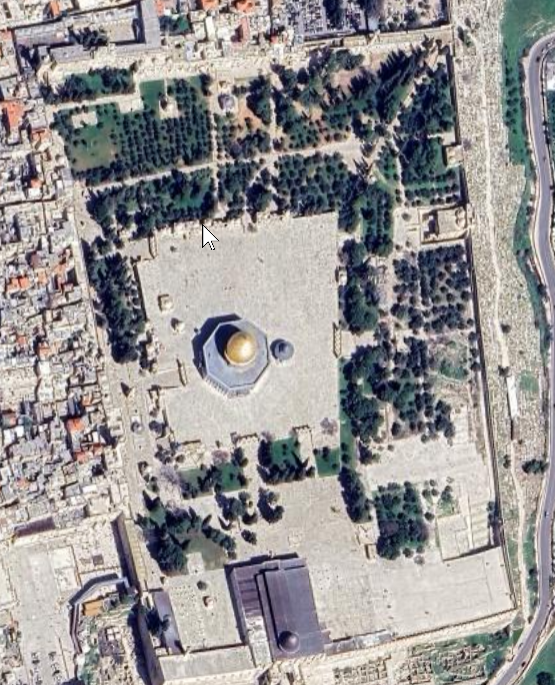
Jerusalem - Temple Mount
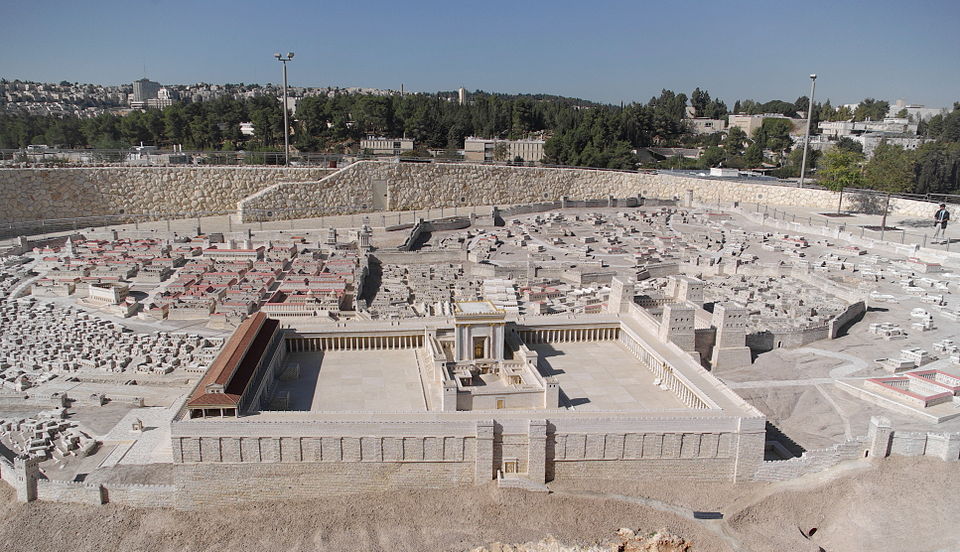 The Holyland Model of Jerusalem depicts Jerusalem during the late Second Temple period. The Temple Mount and Herod's Temple are shown in the middle. View from the east.
The Holyland Model of Jerusalem depicts Jerusalem during the late Second Temple period. The Temple Mount and Herod's Temple are shown in the middle. View from the east.
Click on image to open a high res version in a new tab
Berthold Werner - Wikipedia - Public Domian
| Transliterated Name | Language | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Temple Mount | | |
| Jerusalem's holy esplanade | | |
| Har haBayīt | Hebrew | הַר הַבַּיִת |
| Haram esh-Sharif | Arabic | الحرم الشريف |
Chat GPT Summary
- from Chat GPT 5.1, 11 December 2025
- from Temple Mount — Wikipedia
Following the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, the Temple Mount underwent several transformations under successive empires. During the early Islamic period, it became the site of the Dome of the Rock and the al-Aqsa Mosque, both of which remain major religious monuments today. The platform continues to be central to Judaism, Islam, and Christianity, and its archaeological landscapes—including subterranean passages, vaulted halls, and adjacent bridge structures such as Wilson’s Arch—reflect a long continuum of construction, destruction, renovation, and reinterpretation. Its religious, cultural, and political significance makes it one of the most sensitive and studied heritage sites in the world.
Jerusalem - Introduction Webpage
- from Jerusalem - Introduction - click link to open new tab
Maps and Aerial Views
Maps
General Maps
Normal Size
- Topographical map of
Jerusalem from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Topographical map of Jerusalem.
Topographical map of Jerusalem.
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of the Old City
and its environs from Stern et al (2008)

 Map of the Old City and its environs; numbers refer to excavation sites discussed in the text
Map of the Old City and its environs; numbers refer to excavation sites discussed in the text
Stern et al (2008)
Magnified
- Topographical map of
Jerusalem from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Topographical map of Jerusalem.
Topographical map of Jerusalem.
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of the Old City
and its environs from Stern et al (2008)

 Map of the Old City and its environs; numbers refer to excavation sites discussed in the text
Map of the Old City and its environs; numbers refer to excavation sites discussed in the text
Stern et al (2008)
Jerusalem in different periods
Normal Size
- Fig. 2 - Map of Iron Age Jerusalem
from Finkelstein et. al. (2011)

 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
Map of Jerusalem showing the possible location of the supposed mound on the Temple Mount, the City of David and the line of the Iron IIB-C city-wall.
Finkelstein et. al. (2011) - Map of Jerusalem at the
end of the First Temple period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem at the end of the First Temple period
Map of Jerusalem at the end of the First Temple period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem at the
end of the Second Temple period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem at the end of the Second Temple period
Map of Jerusalem at the end of the Second Temple period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Roman period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Roman period
Map of Jerusalem in the Roman period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Byzantine period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Byzantine period
Map of Jerusalem in the Byzantine period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Early Arab period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Early Arab period
Map of Jerusalem in the Early Arab period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Crusader period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Crusader period
Map of Jerusalem in the Crusader period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2)
Magnified
- Fig. 2 - Map of Iron Age
Jerusalem from Finkelstein et. al. (2011)

 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
Map of Jerusalem showing the possible location of the supposed mound on the Temple Mount, the City of David and the line of the Iron IIB-C city-wall.
Finkelstein et. al. (2011) - Map of Jerusalem at the
end of the First Temple period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem at the end of the First Temple period
Map of Jerusalem at the end of the First Temple period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem at the
end of the Second Temple period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem at the end of the Second Temple period
Map of Jerusalem at the end of the Second Temple period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Roman period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Roman period
Map of Jerusalem in the Roman period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Byzantine period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Byzantine period
Map of Jerusalem in the Byzantine period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Early Arab period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Early Arab period
Map of Jerusalem in the Early Arab period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2) - Map of Jerusalem in the
Crusader period from Stern et al (1993 v. 2)

 Map of Jerusalem in the Crusader period
Map of Jerusalem in the Crusader period
Stern et al (1993 v. 2)
Aerial Views
Normal Size
Crucifixion Quake - 26-36 CE
Discussion
363 CE Earthquake
Discussion
Crucifixion Quake - 26-36 CE
| Effect | Location | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2nd Temple |
|
363 CE Earthquake
| Effect | Location | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Temple Mount |
Descriptions
|
Crucifixion Quake - 26-36 CE
- Earthquake Archeological Effects chart
of Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
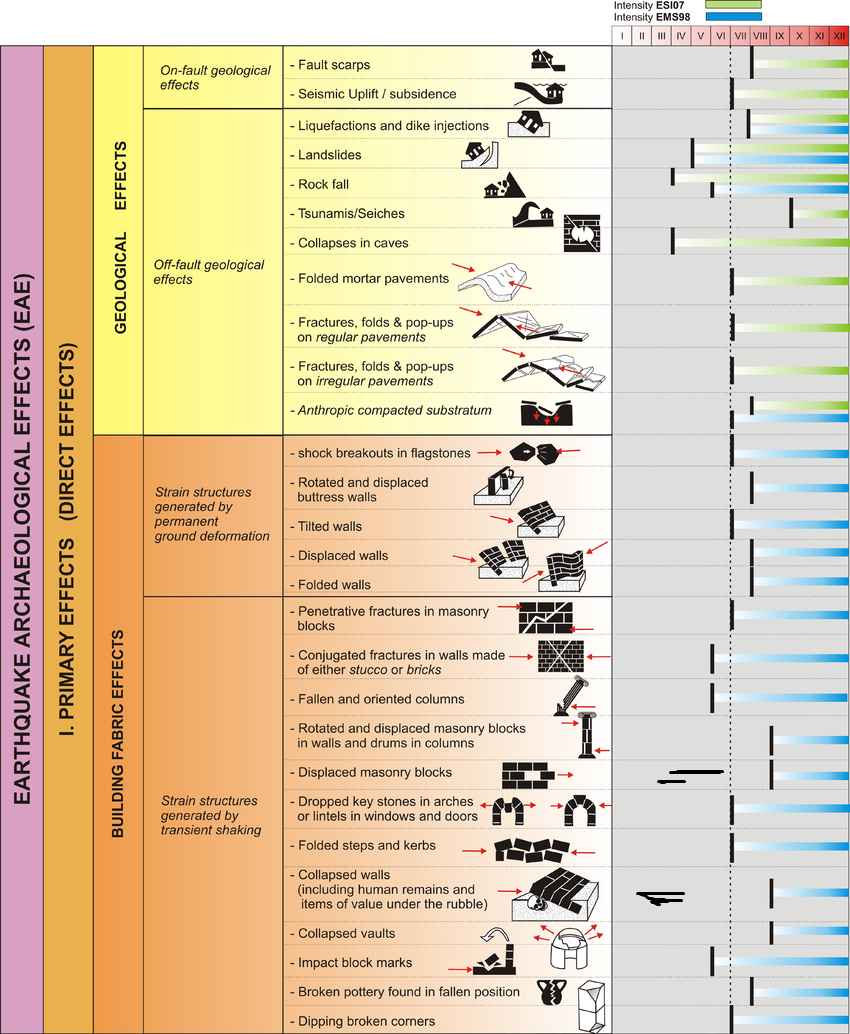
 Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
| Effect | Location | Image | Description | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2nd Temple |
|
|
363 CE Earthquake
- Earthquake Archeological Effects chart
of Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)

 Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
| Effect | Location | Image | Description | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Temple Mount |
Descriptions
|
|
References
Wikipedia pages
Temple Mount
kmz's
- download these files into Google Earth on your phone, tablet, or computer
- Google Earth download page
| kmz | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Right Click to download | Master Jerusalem kmz file | various |

