Petra - Katute
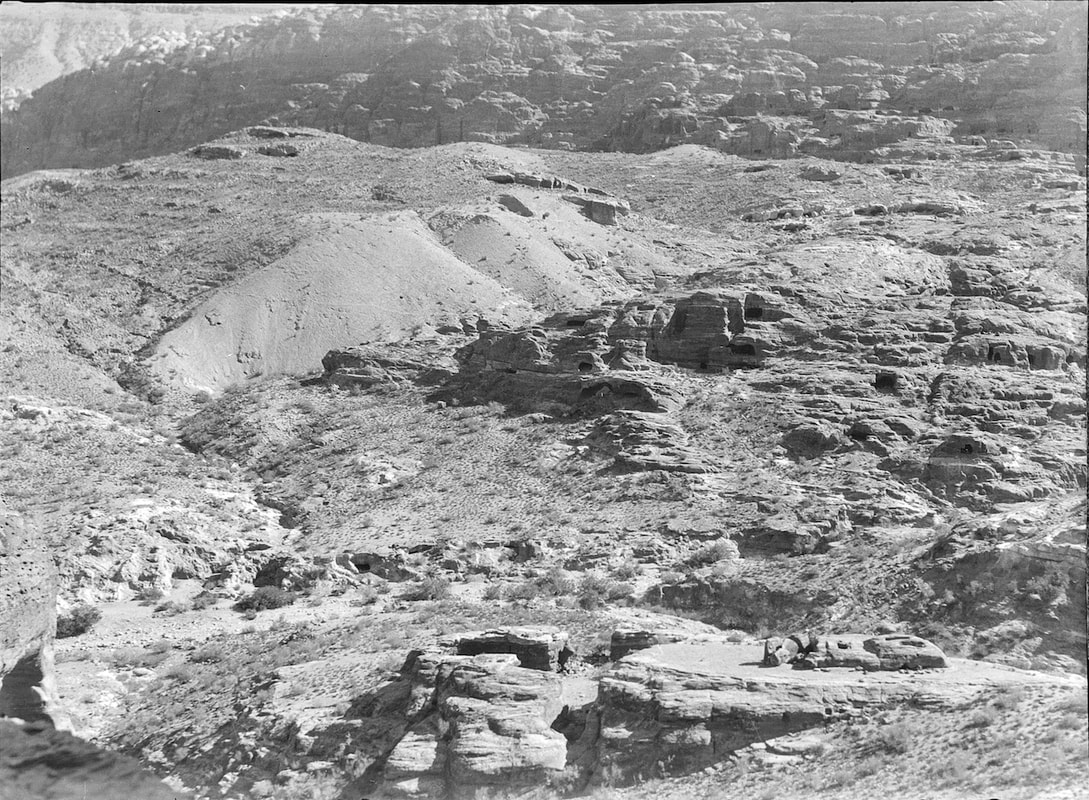 The rubbish dumps known as "Katoote"
The rubbish dumps known as "Katoote"
click on image to open a high res magnifiable image in a new tab
Copyright UCL Institute of Archaeology
| Transliterated Name | Source | Name |
|---|---|---|
| el-Katute | Arabic | يلءكاتوتي |
- from Chat GPT 5.2, 14 January 2026
- source: Parr (1960)
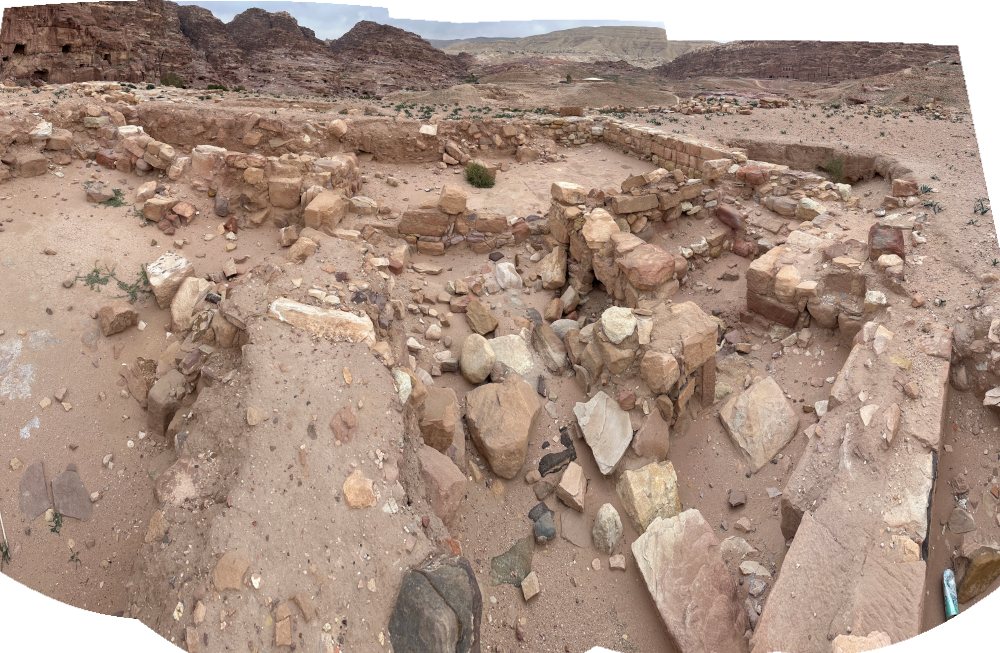
Although the precise function of the structure at el-Katute remains uncertain, its monumentality suggests a role beyond purely domestic use and points to participation in Petra’s broader civic, ceremonial, or administrative framework. The site therefore contributes to understanding the diversity and complexity of Petra’s urban fabric, particularly in areas outside the city’s most intensively studied monumental zones.
- from Petra - Introduction - click link to open new tab
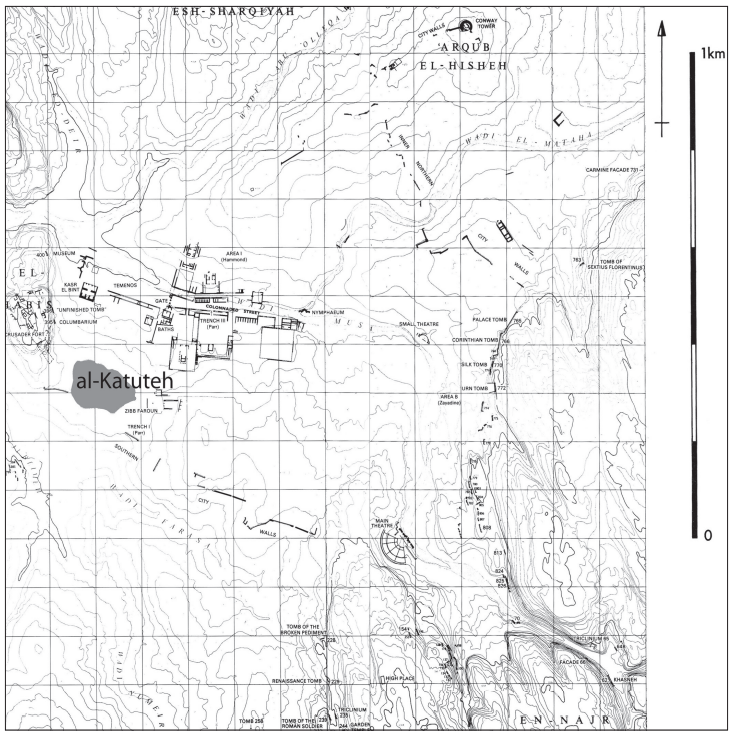
- Fig. 1 - Location Map from
Parr (1960)
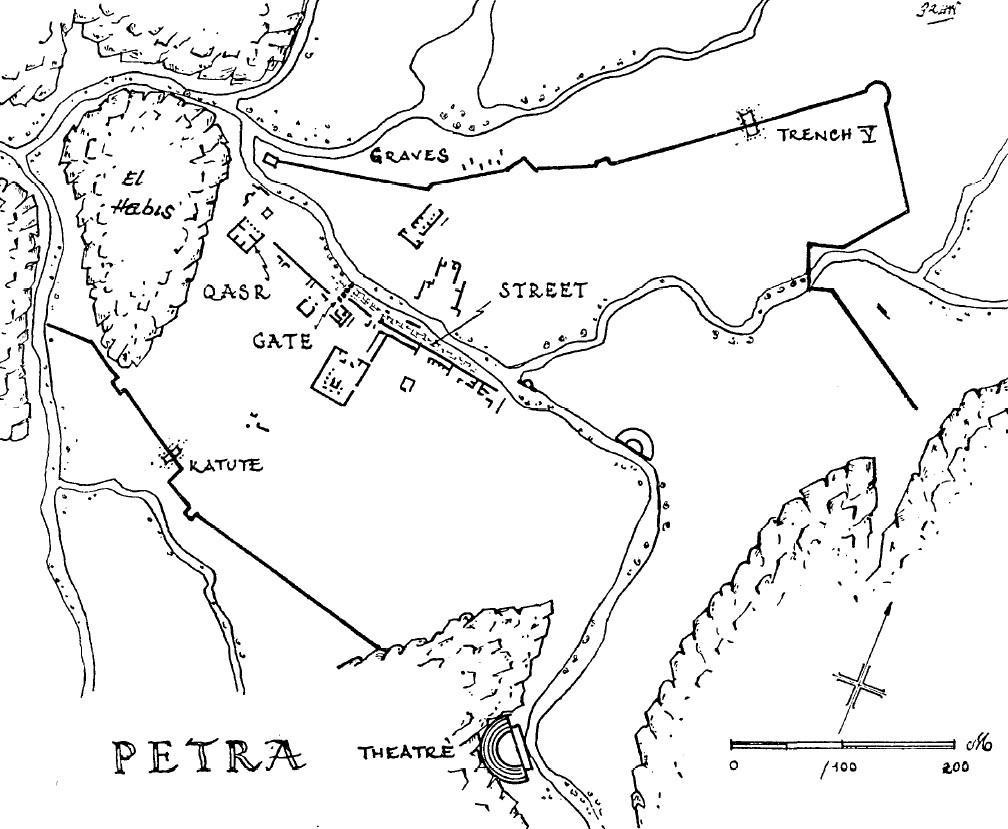
 Figure 1
Figure 1
JW:Map of Petra. Katute is middle left
Parr (1960) - Fig. 1a - Location Map from
Jordan et al. (2016)
- Fig. 1 - Location Map from
Parr (1960)

 Figure 1
Figure 1
JW:Map of Petra. Katute is middle left
Parr (1960) - Fig. 1a - Location Map from
Jordan et al. (2016)
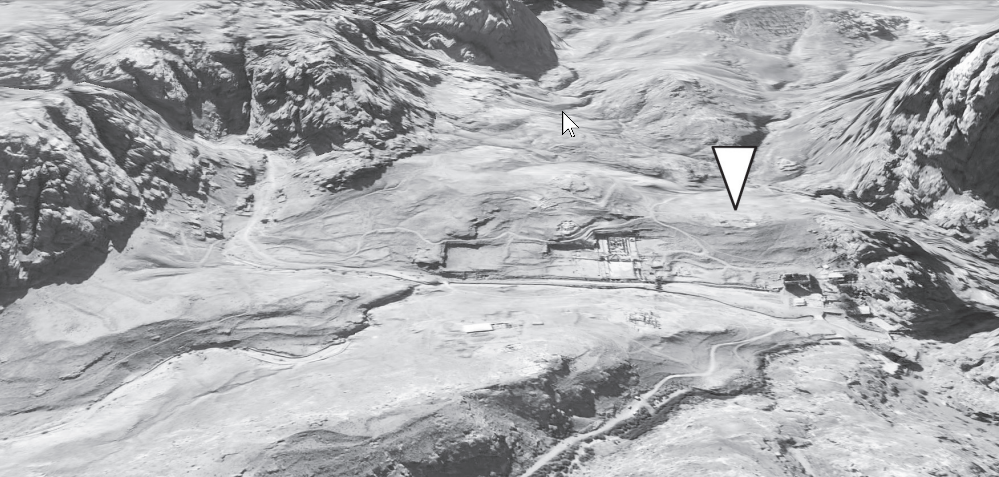
- Fig. 1b #1 Aerial View of
site from Jordan et al. (2016)
- Fig. 1b #2 Aerial View of
excavation areas from Jordan et al. (2016)
- Fig. 1b #3 Aerial View of
geophysical survey areas from Jordan et al. (2016)
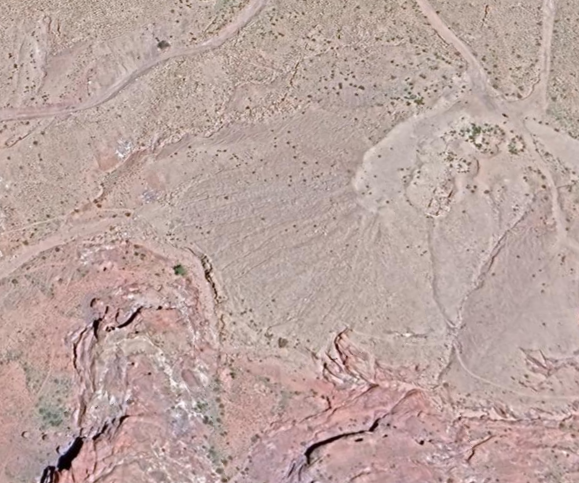
- Approximate location of Katute in Google Earth
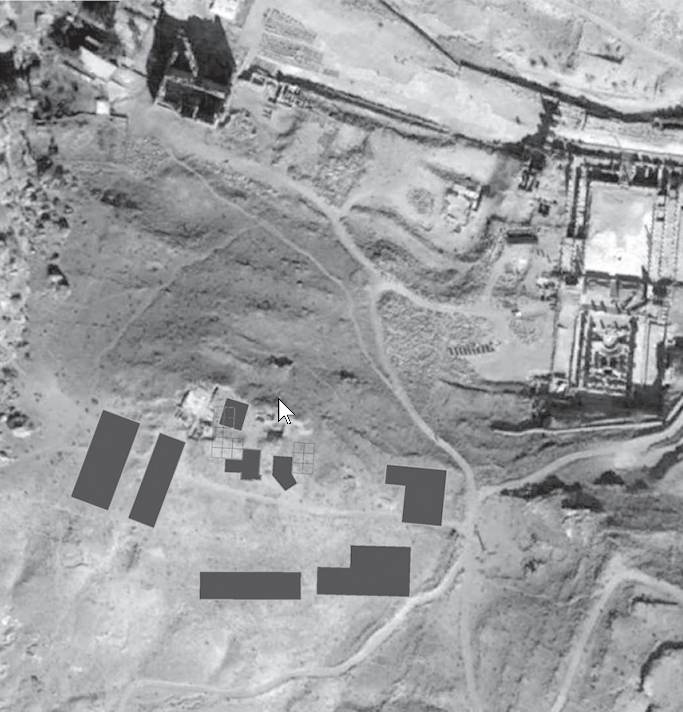
- Fig. 1b #1 Aerial View of
site from Jordan et al. (2016)
- Fig. 1b #2 Aerial View of
excavation areas from Jordan et al. (2016)
- Fig. 1b #3 Aerial View of
geophysical survey areas from Jordan et al. (2016)
- Approximate location of Katute in Google Earth
Parr (1960:129) reports a partial destruction of interior walls from a
building outside of the
"monumental structure" at Katute. A tentative 71 CE terminus ante quem for the date of destruction
is suggested from numismatics.
Parr, P. J. (1960:129), reported the following from excavations at Trench I in Katute:
Only in two restricted areas, both outside the building, have the original floors been reached, and until more evidence is forthcoming the date of its construction must remain uncertain. But from the secondary surfaces within the building, some of them laid down after the partial destruction of the interior walls, a series of coins gives a firm date for the latest occupation of the structure. Of eight coins so far studied, two are of Malichus II and Shaqilath II (c. A.D. 40-71), five are of Rabbel II and Gamilath (A.D. 71-106, but late in the period, since Gamilath is Rabbel's second consort), and one is of Rabbel with either Shaqilath or Gamilath, this being uncertain. The significance of these coins is increased when it is noted that four of Rabbel II and Gamilath come from the same layer of make-up beneath one of the secondary floors. There can be little doubt, therefore, that the building was in use at the end of the 1st century A.D., and probably right up until the Roman conquest of A.D. 106, though the apparent lack of Roman Imperial coins suggests that it soon feel out of use then. Judging from the fact that the secondary surfaces from which the coins come in some cases seal the first destruction levels of the building, a date in the first half of the 1st century A.D. for its construction is not, perhaps, unlikely. An earlier date than this for the rebuilding of the main wall is precluded by the discovery of a coin of Aretas IV and Shaqilath I (c. 9 B.C-A.D. 40) in a level immediately underlying the construction level associated with that rebuilding.
- from Parr (1960:129)
| Effect | Location | Image(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Displaced Walls | a building outside of the "monumental structure" at Katute | partial destruction of the interior walls- Parr (1960) |
- Earthquake Archeological Effects chart
of Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
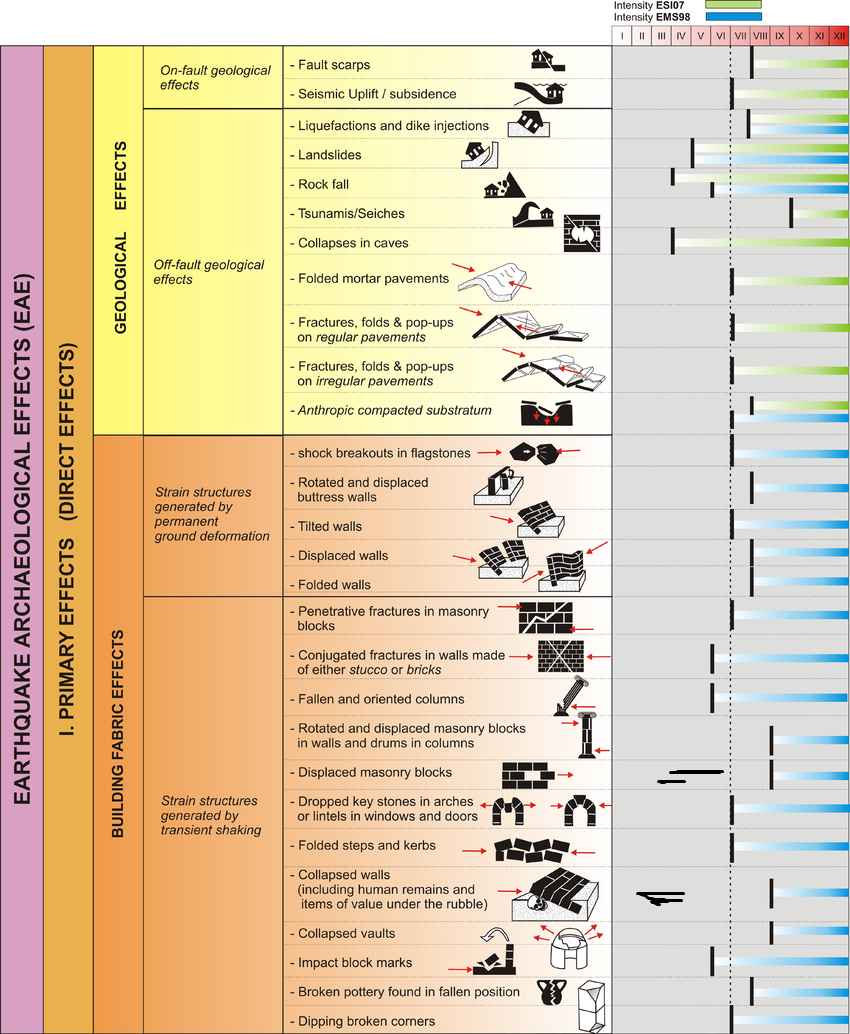
 Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
| Effect | Location | Image(s) | Description | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Displaced Walls | a building outside of the "monumental structure" at Katute | partial destruction of the interior walls- Parr (1960) |
VII + |
Jordan, David, Mahler, Uwe, Mustafa, Kocak, Berger, Frederick, and Thierry-Hildenbrand (2016)
Geophysical Prospection at Petra: Methodical Research within the 2012 al-Katutah Campaign
Studies in the History and Archaeology of Jordan 12, Department of Antiquities of Jordan
Koçak, M., Mahler, K.-U., Berger, F., Jordan, D., & Thierry-Hildenbrand, B. (2013)
. The 2012 al-Katutah excavations in Petra: Methods and preliminary results
. In N. I. Khairy & Th. M. Weber (Eds.), Studies on the Nabataean Culture 1 (pp. 47–58).
Amman, Jordan: The University of Jordan Press.
Parr, P. J. (1960). "Excavations at Petra, 1958–59." Palestine exploration quarterly 92(2): 124-135.
- from Wikipedia