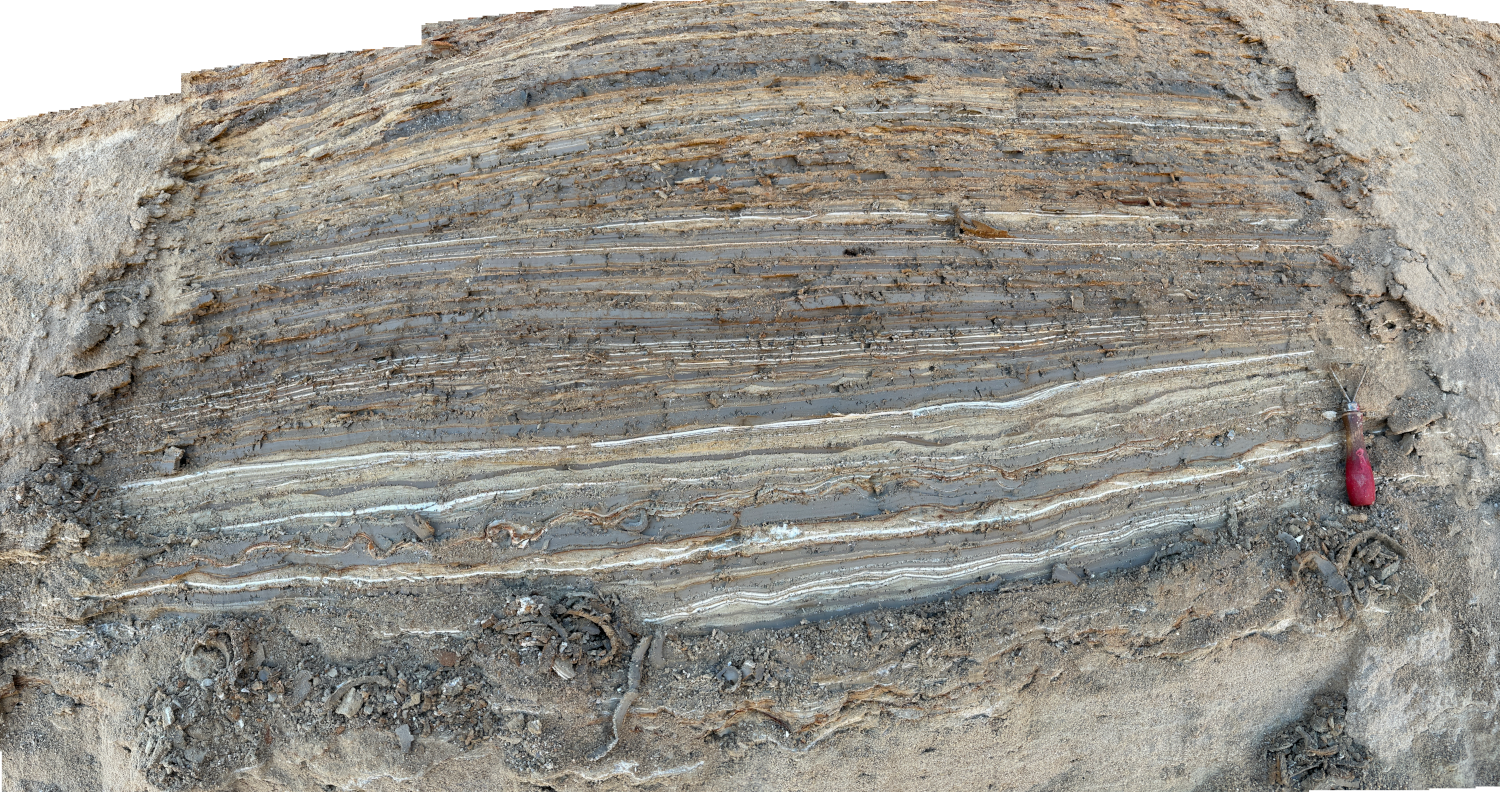
Nahal Ze'elim
 Aerial shot of Nahal Ze'elim from the east
Aerial shot of Nahal Ze'elim from the eastClick on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Panorama from Drone Photos by Jefferson Williams 11 Feb. 2023
- Map of Gullies where
Revital Bookman did her work in ZA-1

 Map of Gullies where Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) did her work
Map of Gullies where Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) did her work
Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) - Nahal Ze'elim outcrop areas in Google Earth
- Nahal Ze'elim outcrop area on govmap.gov.il
- Aerial View of Nahal Ze'elim outcrop area by Jefferson Williams
- DSW Site Map

 Dead Sea Works Site Map
Dead Sea Works Site Map
- Map of Gullies where
Revital Bookman did her work in ZA-1

 Map of Gullies where Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) did her work
Map of Gullies where Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) did her work
Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) - Aerial View of Nahal Ze'elim outcrop area by Jefferson Williams
- DSW Site Map

 Dead Sea Works Site Map
Dead Sea Works Site Map
 Figure 2
Figure 2The lithology and chronology of a composite section exposed in Ze'elim Plain. The section is described from two outcrops exposed in different gullies 300 m apart. The correlation between the outcrops is based on the sedimentary sequence, laminae counting, and 14C dates. Ages presented in 14C years B.P. Deformed units (mixed layers and liquefied sands) are marked by capital letters.
slight modification by Williams
Ken-Tor et al. (2001a)
 Figure 2
Figure 2The lithology and chronology of a composite section exposed in Ze'elim Plain. The section is described from two outcrops exposed in different gullies 300 m apart. The correlation between the outcrops is based on the sedimentary sequence, laminae counting, and 14C dates. Ages presented in 14C years B.P. Deformed units (mixed layers and liquefied sands) are marked by capital letters.
Ken-Tor et al. (2001a)
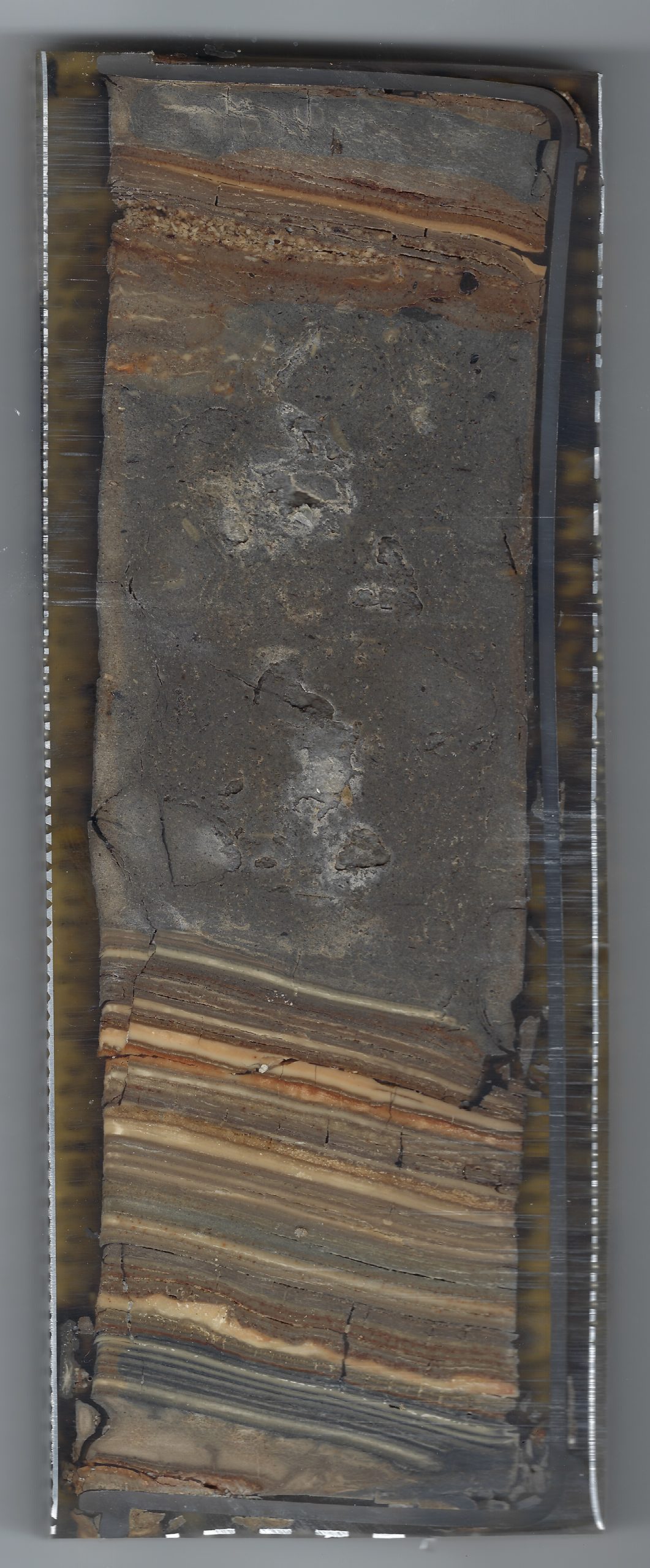
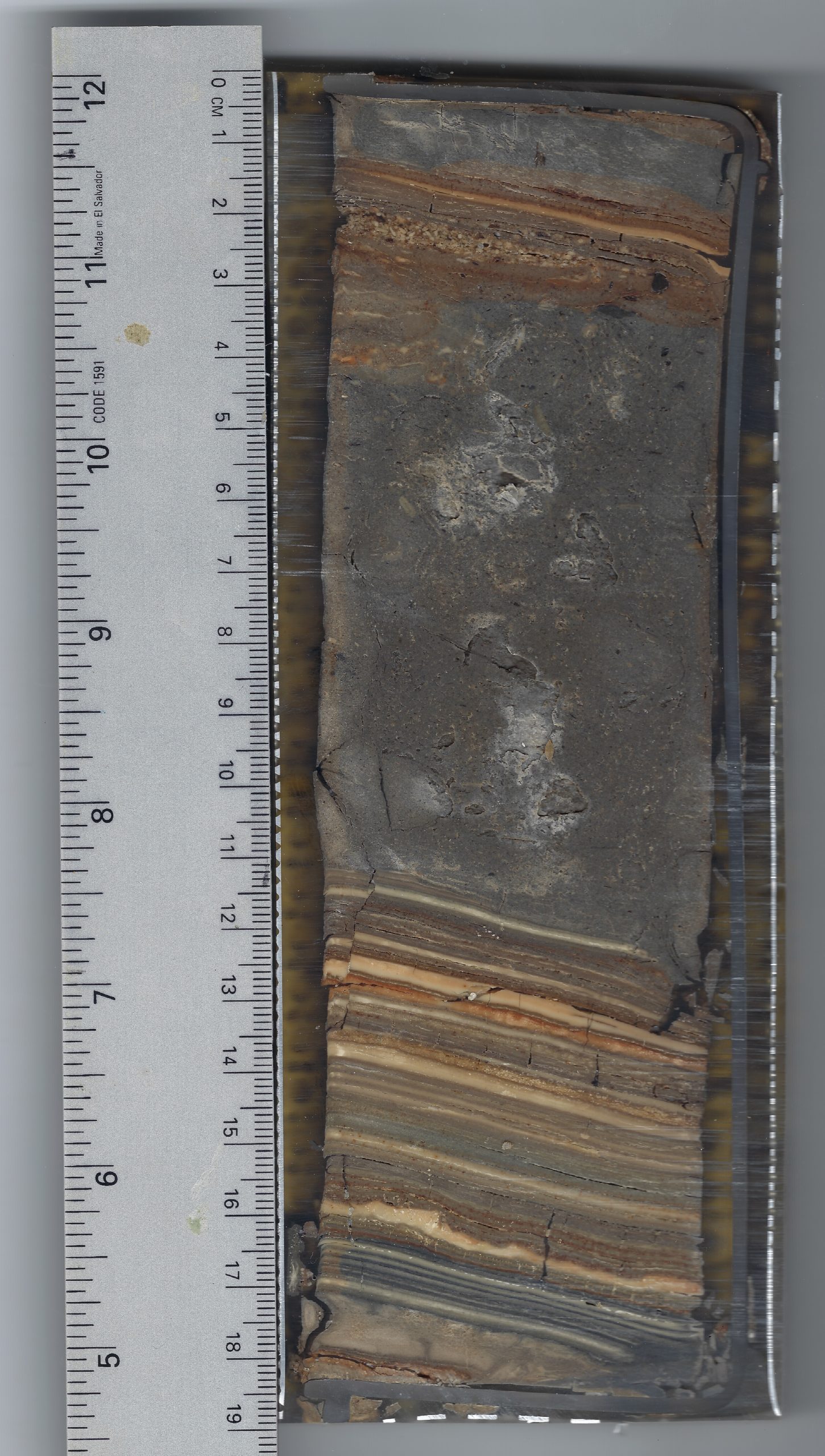
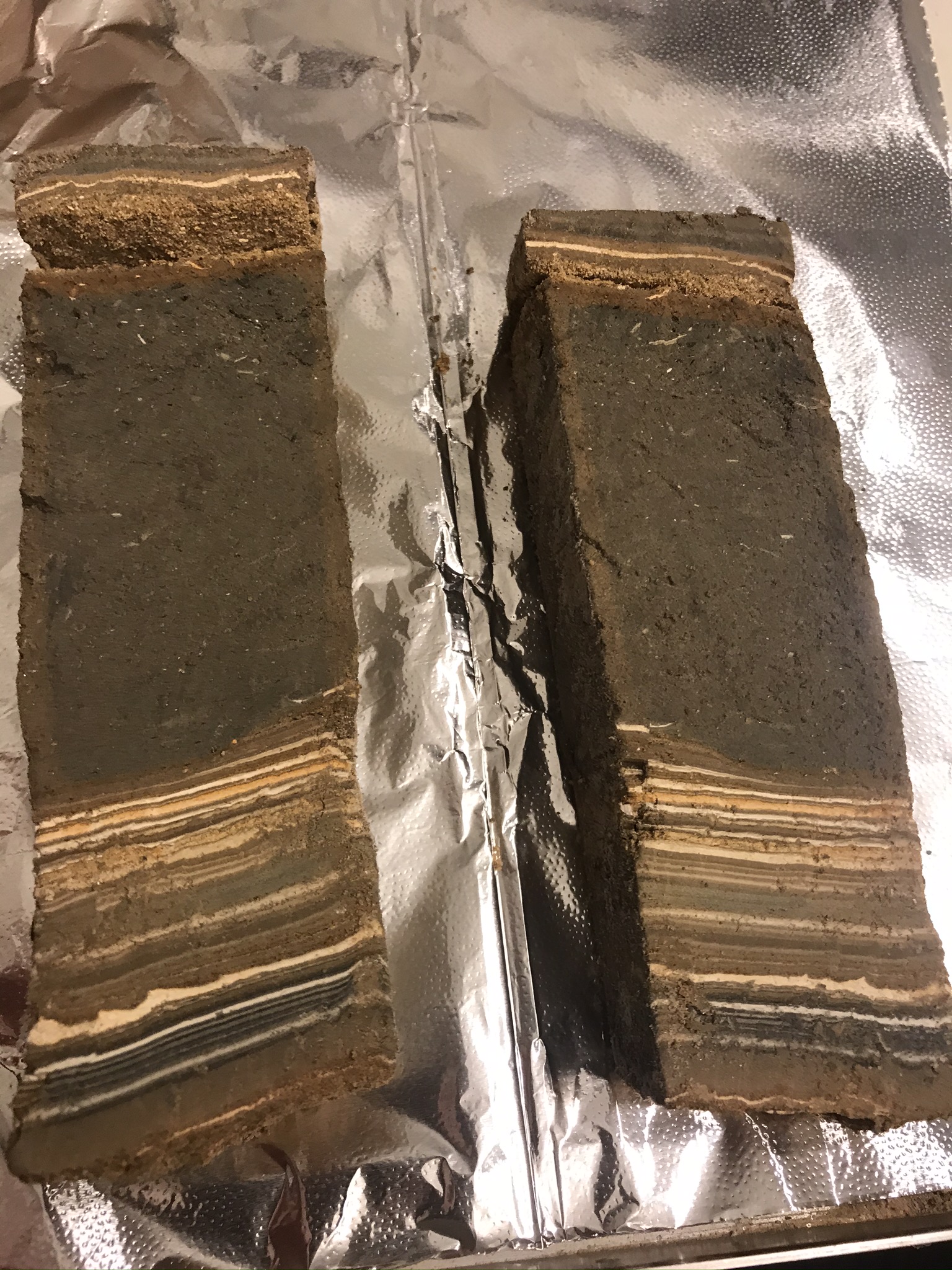
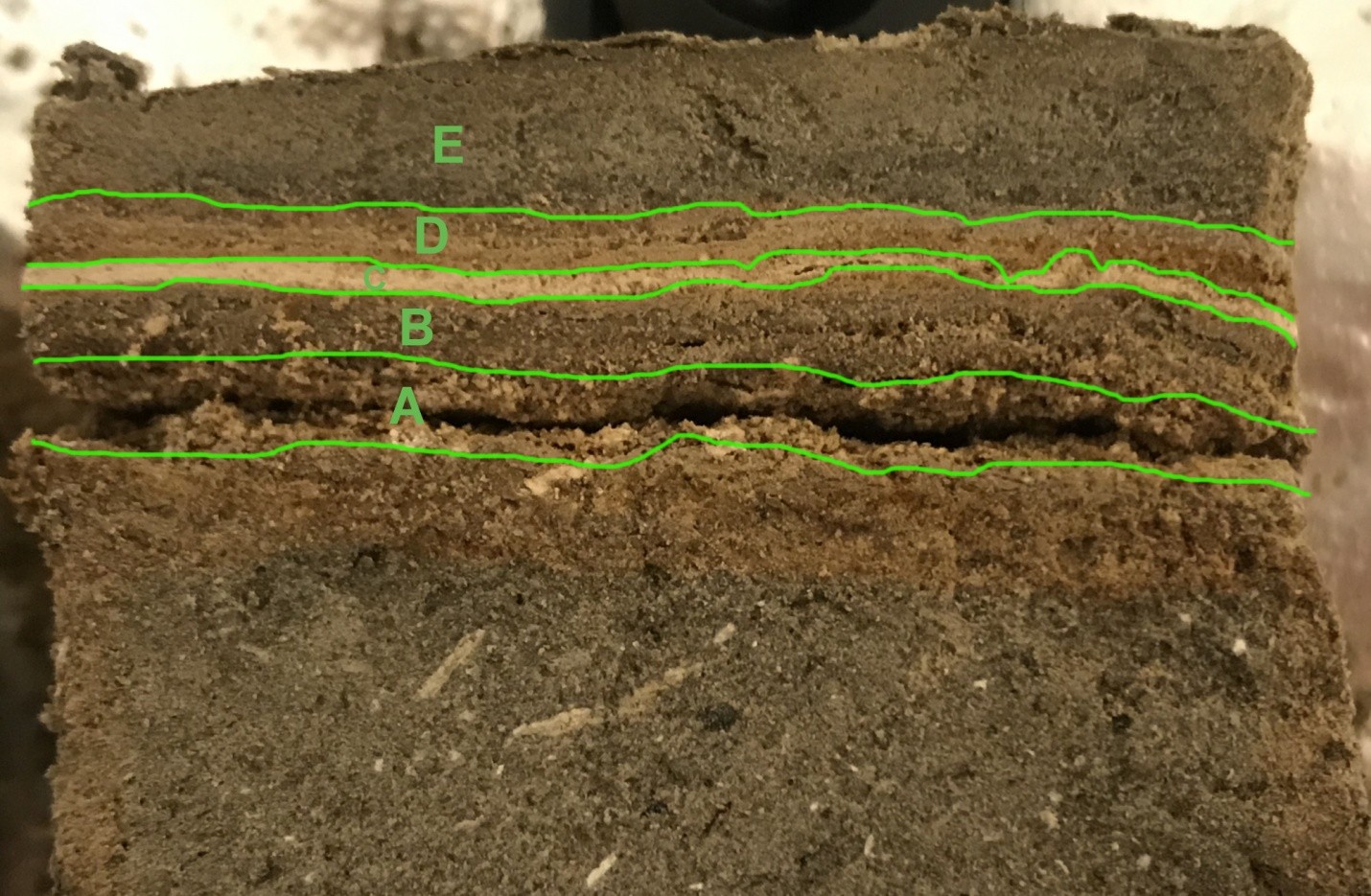
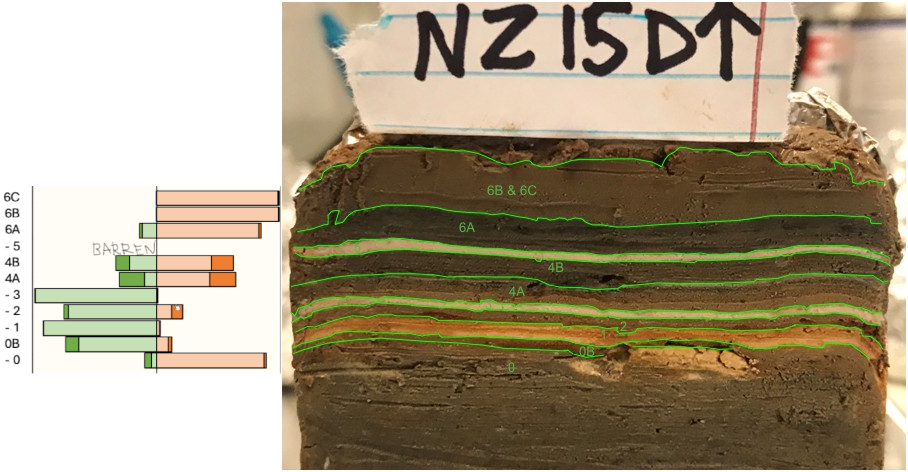
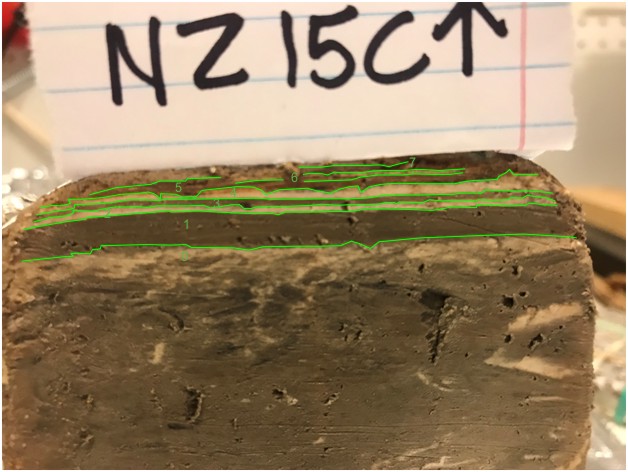
 Correlated Trench Logs used to produce composite ZA-1 litholog
Correlated Trench Logs used to produce composite ZA-1 lithologThe final lithosection of Bookman (nee Ken-Tor) is a composite lithologs derived from multiple sites as far as, I think, 300 meters apart. ZA-1 refers to the location where a large part of the composite lithosection was derived. More landward gullies were used to capture the most recent earthquakes - Events G (1834) and H (1927). Bookman referred to site ZA-1 as site 2.
Revital Bookman (nee Ken-Tor)
 Figure 8
Figure 8A modified age model for Ze'elim section studied in outcrop (Ken-Tor et al., 2001a) and drill core (Migowski et al., 2004). A-H denote events discussed in the text. The present model was constrained by two rules
(1) each event horizon (top of each intraclast breccia) matches a historical earthquake of notice
(2) each continuous deposition segment shows a uniform deposition rate.
Two outcomes support the model: Two of the breccia layers match pairs of earthquakes (64-31 B.C.; 1202-1210 A.D.) such that the earlier event horizon is within the breccia layer and the later event matches the top. With these assignments for the event horizons, the model gives a uniform rate of sedimentation of 0.5 cm/yr during the three periods separated by hiatuses.
Agnon et al (2006)
- from Kagan et al. (2011)
- these have been incorporated into the Master Seismic Events Tables for all sites

Ze'elim and Ein Feshka Seismites with Model Ages and Historic Event Correlation
- LS, local source, moderate earthquake, not appearing in the historical catalogs, may have produced these seismites
- Gully depth below fan delta surface
- Seismite type
A, Intraclast breccia layer
B, Microbreccia (“homogenite” to the naked eye)
C, liquefied sand
D, Folded laminae
E, Small offsets
Q, Questionable as seismite. See Table 1 and Figure 2. - Model ages of seismites extrapolated from deposition model (see section 5 for details)
- Fit of historical earthquake dates within 1σ or 2σ calibrated age ranges of seismites. Although model ages are tabulated here with 1 year precision for convenience, event fit considers the realistic precision of 10 years (see section 5.1)
- All other possible events within the age probability range (1σ or 2σ range) of the designated earthquake; 1068a refers to March 1068 A.D., and 1068b refers to May 1068 A.D. (see Table A1)
- Outside model range, extrapolated from model (Figure 4)
- Outside model range, estimated based on below and above radiocarbon ages (Figure 4)
- Alternately, this historic earthquake could have formed seismites below or above the one marked
Kagan et al (2011)
- from Kagan et al. (2011)
- these have been incorporated into the Master Seismic Events Tables for all sites
 Table 4
Table 4Multisite Comparison of Holocene Seismites from four lacustrine sediments sites along the Western Dead Sea Basin
Kagan et al (2011)
- from Kagan et al. (2011)
 Figure 7
Figure 7Recurrence intervals and cumulative number of breccias in time.
- Ein Feshkha (EFE)
- Ein Gedi (EG)
- Zeelim (ZA1 and ZA2)
- Diamonds represent breccias
- circled diamonds are the IBS (intrabasin seismites)
- Horizontal gray bars indicate periods of seismic quiescence
(left) the earlier period is recorded at EG and ZA, and (right) the younger quiescence period is recorded at all three sites. Horizontal lines connect IBS events at the three sites.
Kagan et al (2011)
 Table 2
Table 2The 14C Chronology of the Deformed Layers (Seismites)
Ken-Tor et al (2001a)
- Event B has been assigned to the 31 BCE Josephus Quake
- Event C has been assigned to the Jerusalem Quake which is currently dated to 26-36 CE
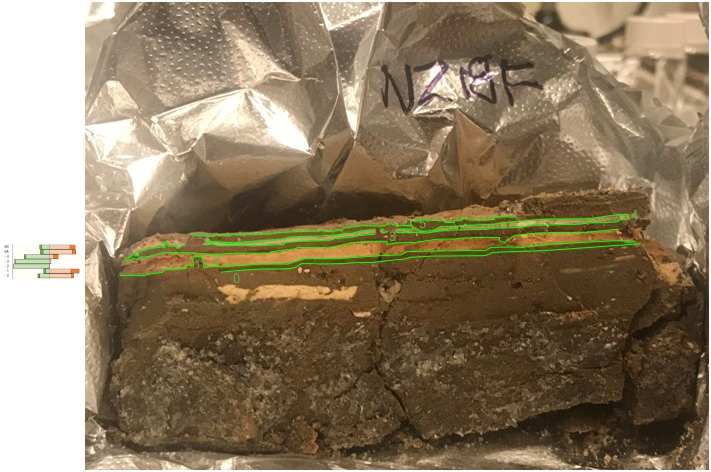
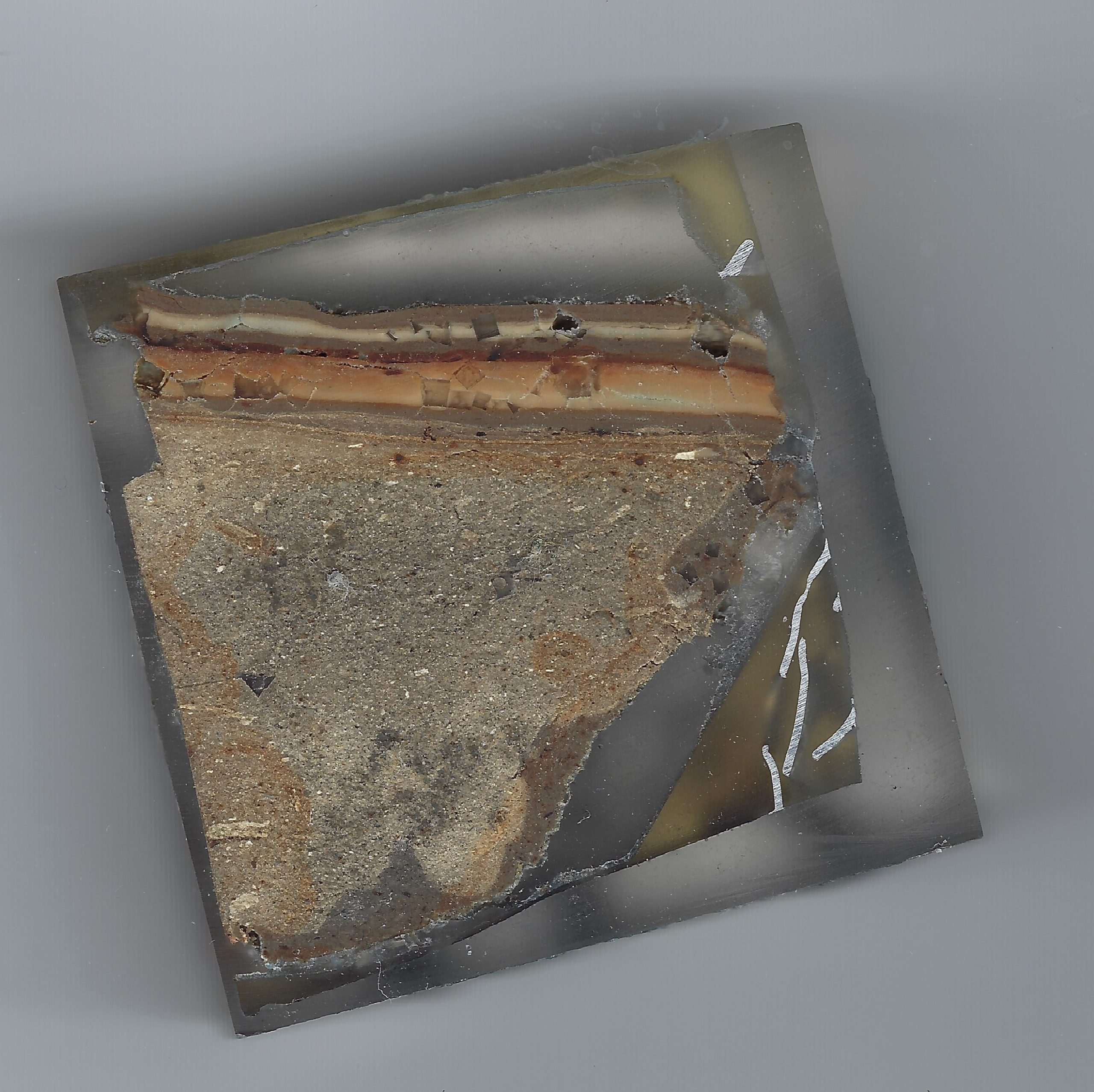
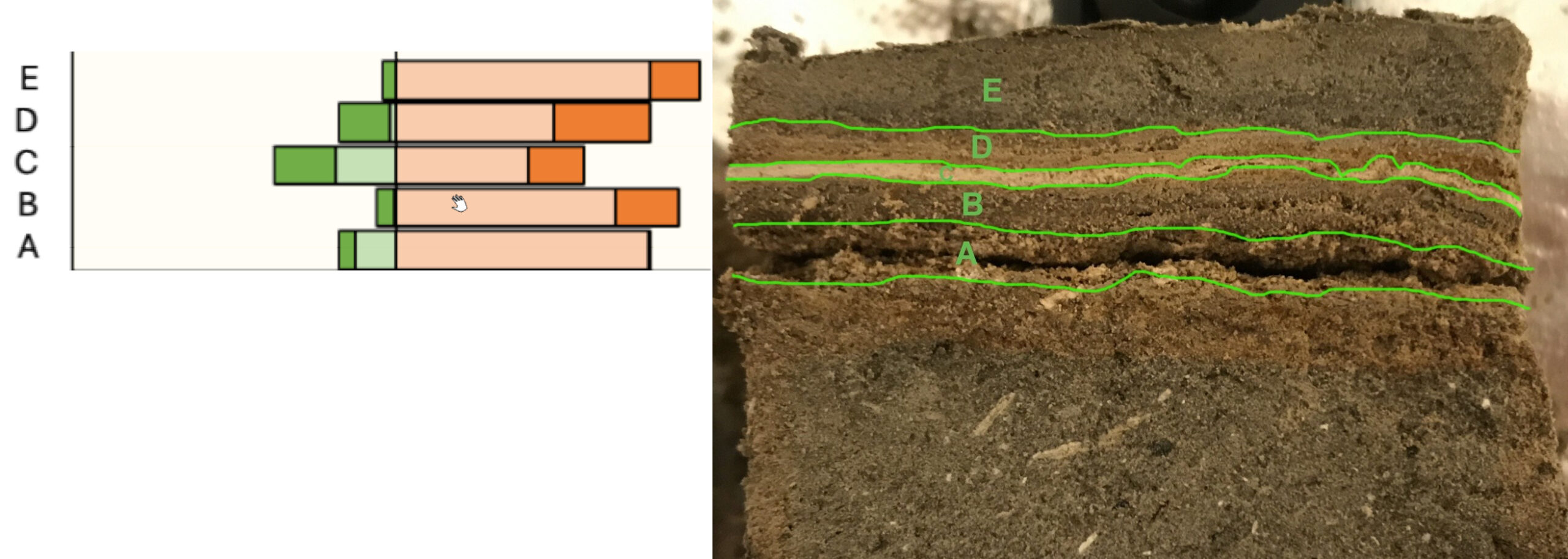
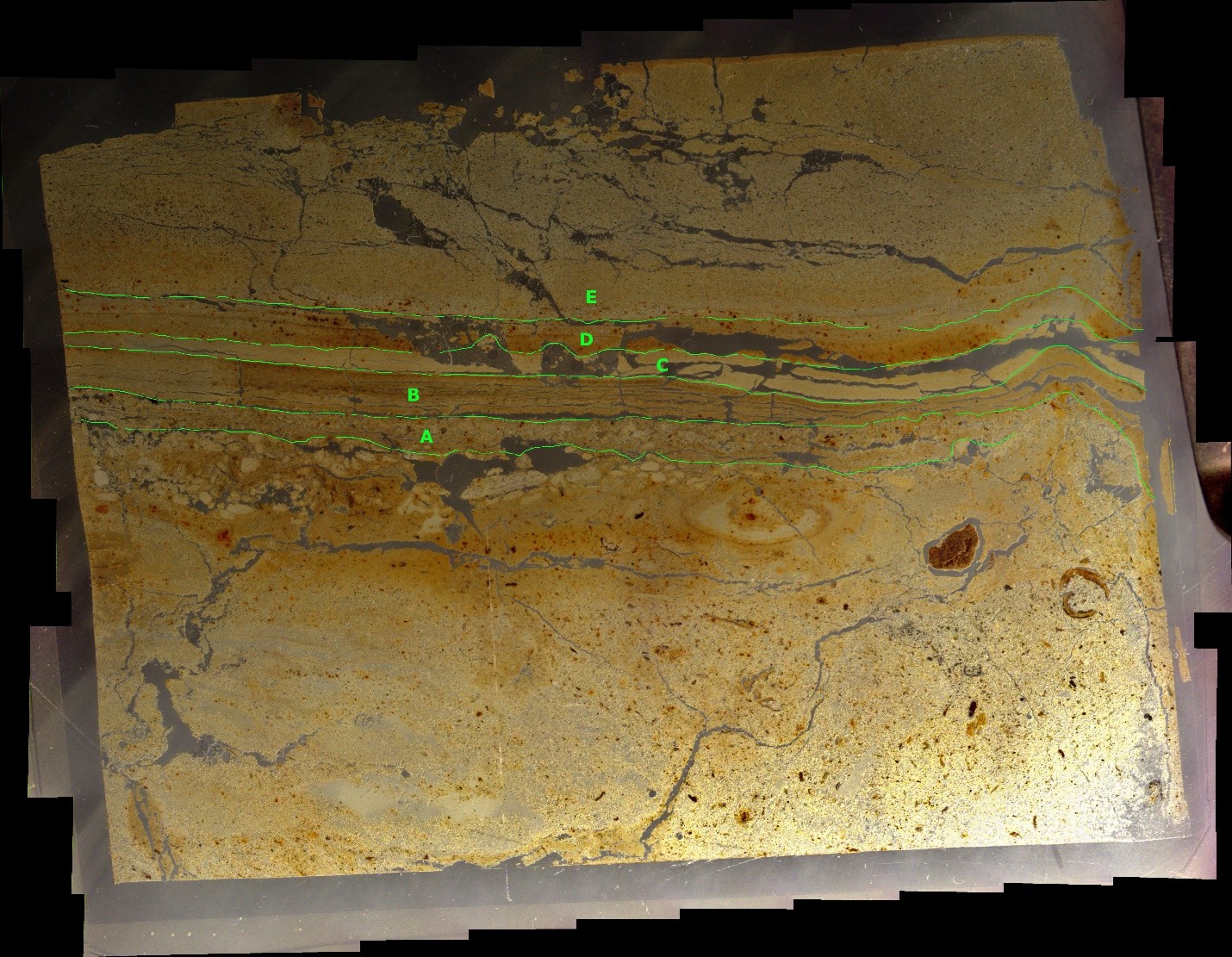
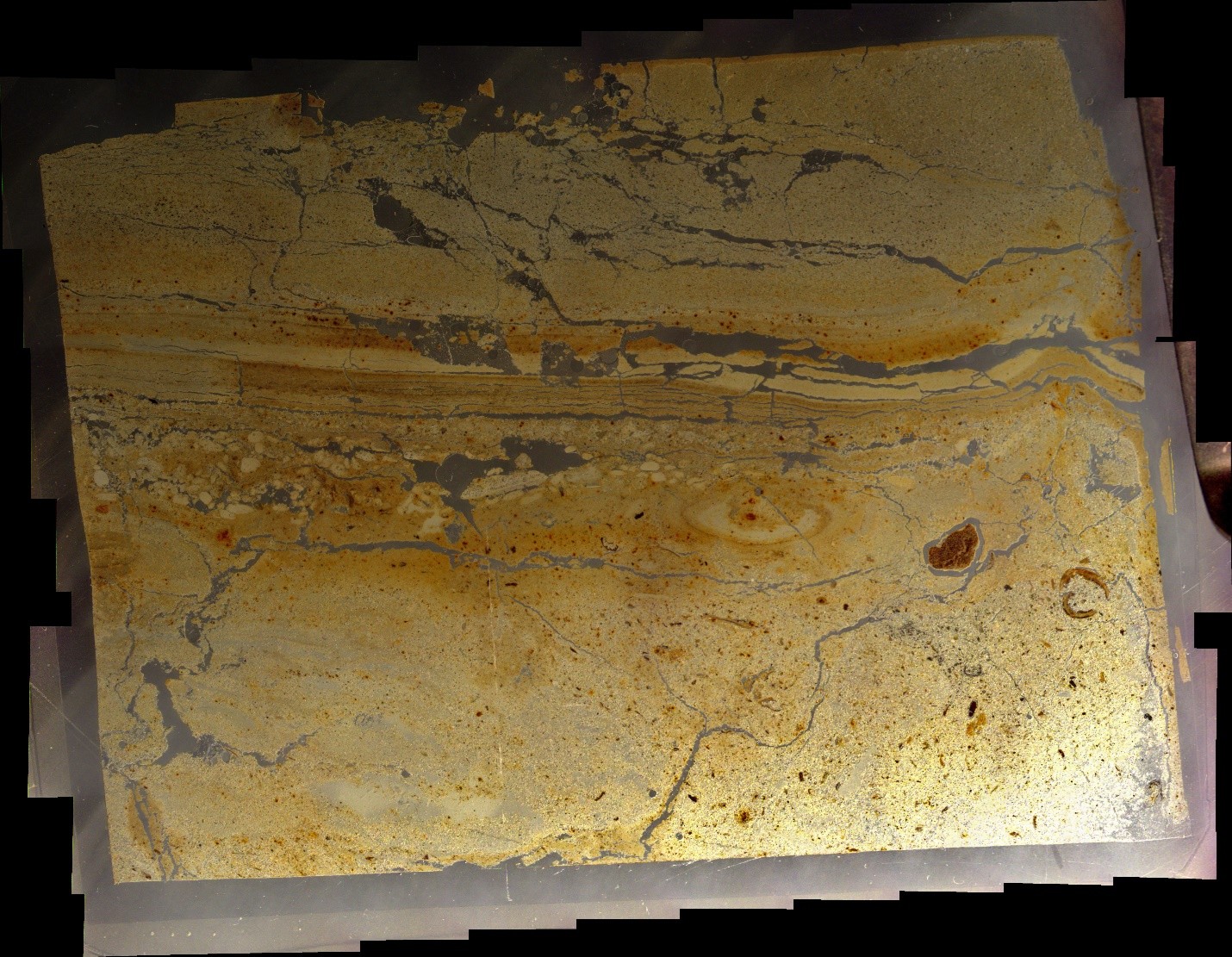
 Events B (Josephus Quake - 31 BCE) and C (Jerusalem Quake - 26-36 CE) at site ZA-1
Events B (Josephus Quake - 31 BCE) and C (Jerusalem Quake - 26-36 CE) at site ZA-1Photo by Jefferson Williams (2000)
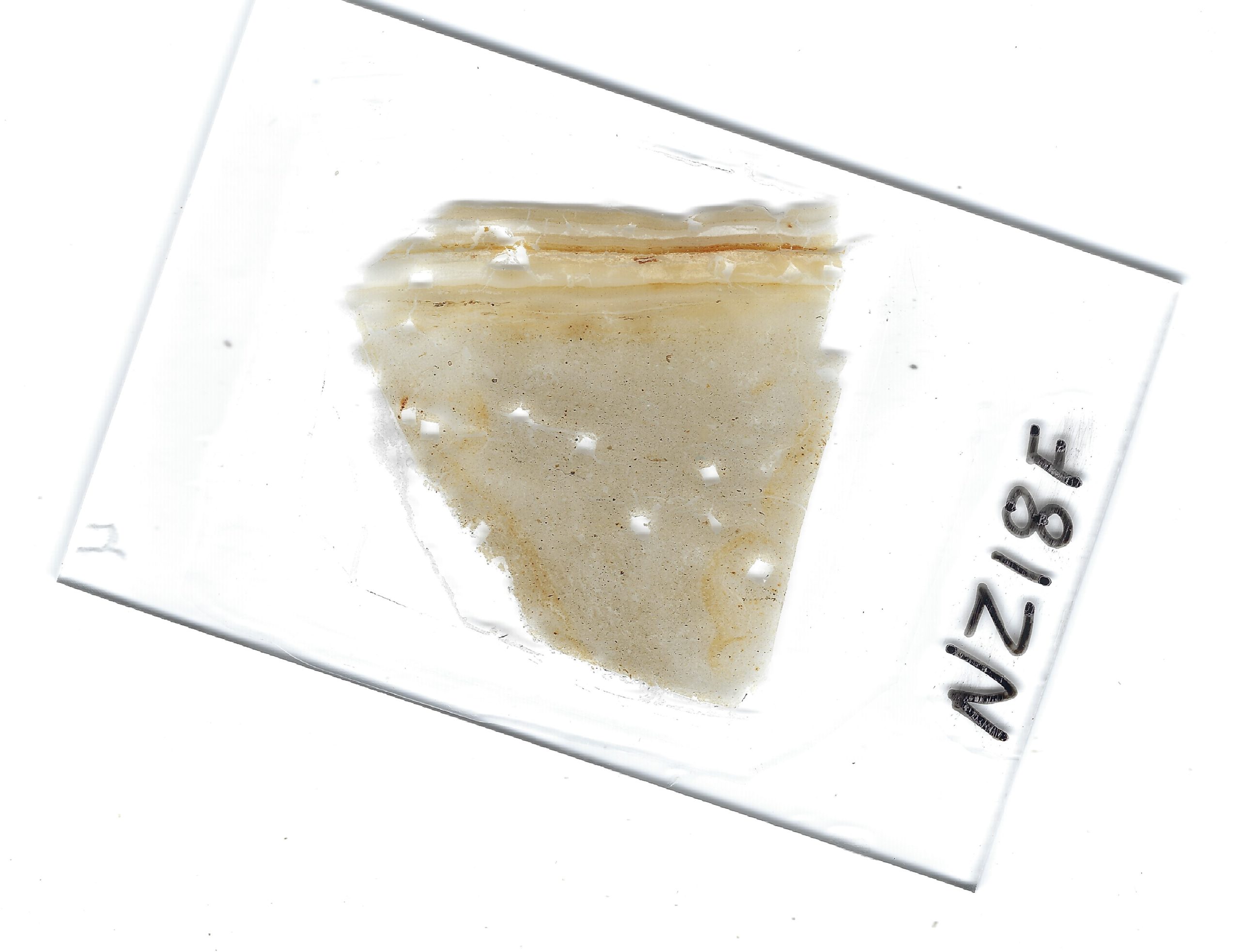
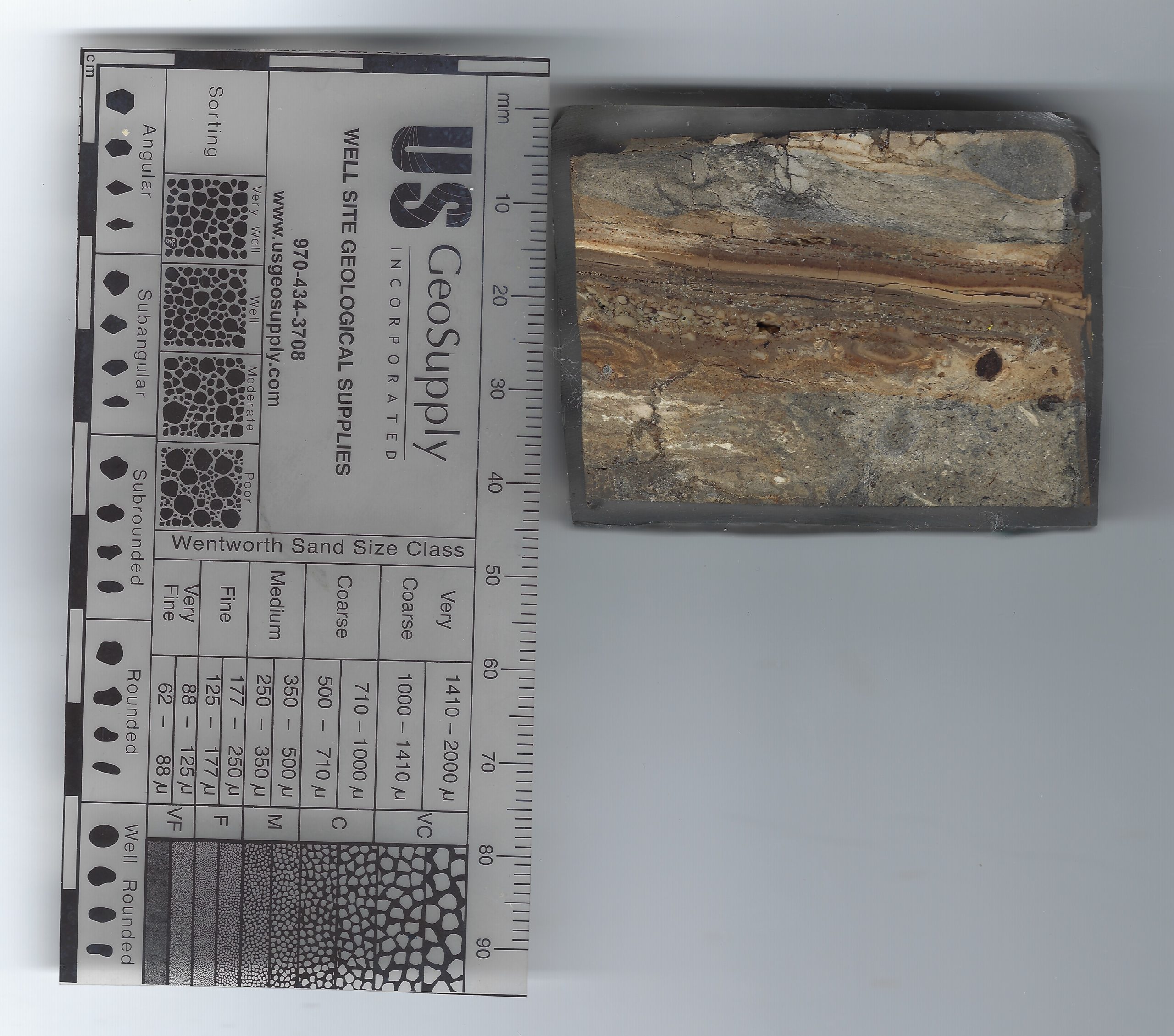
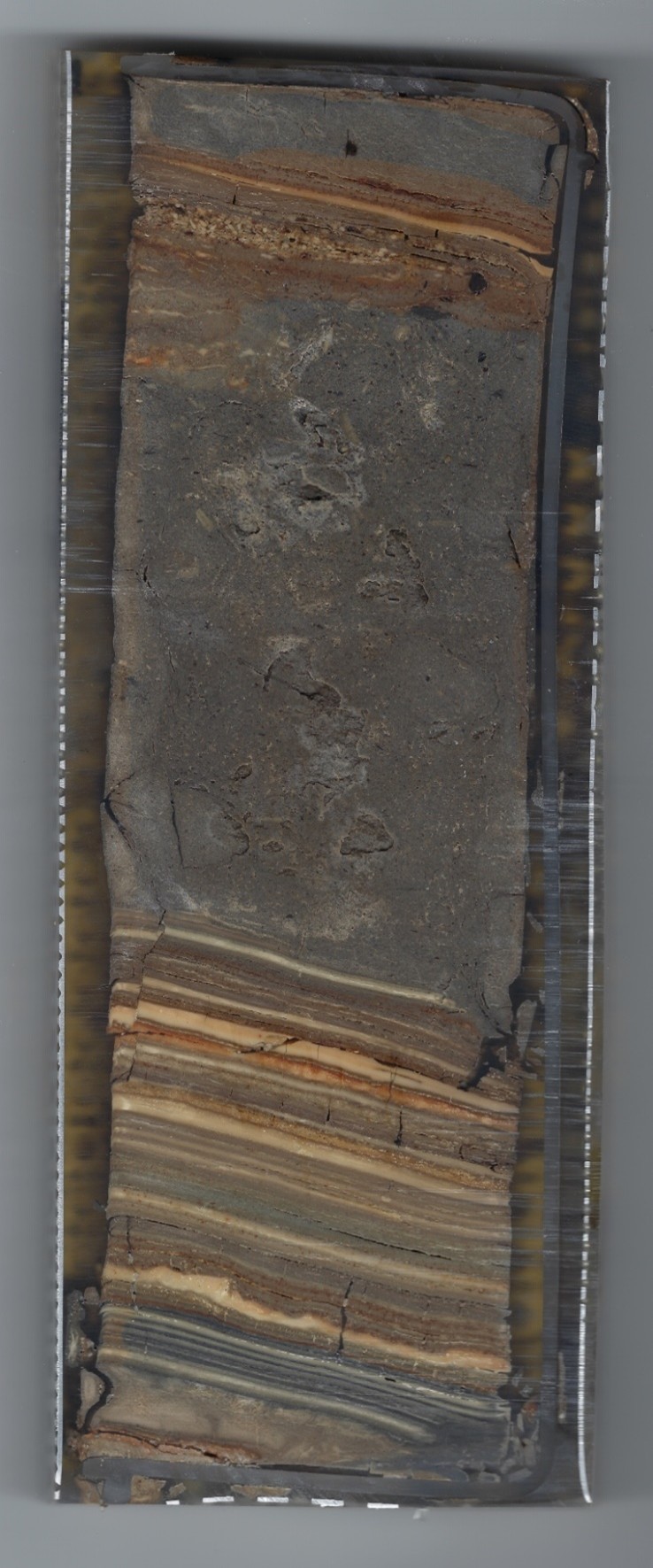
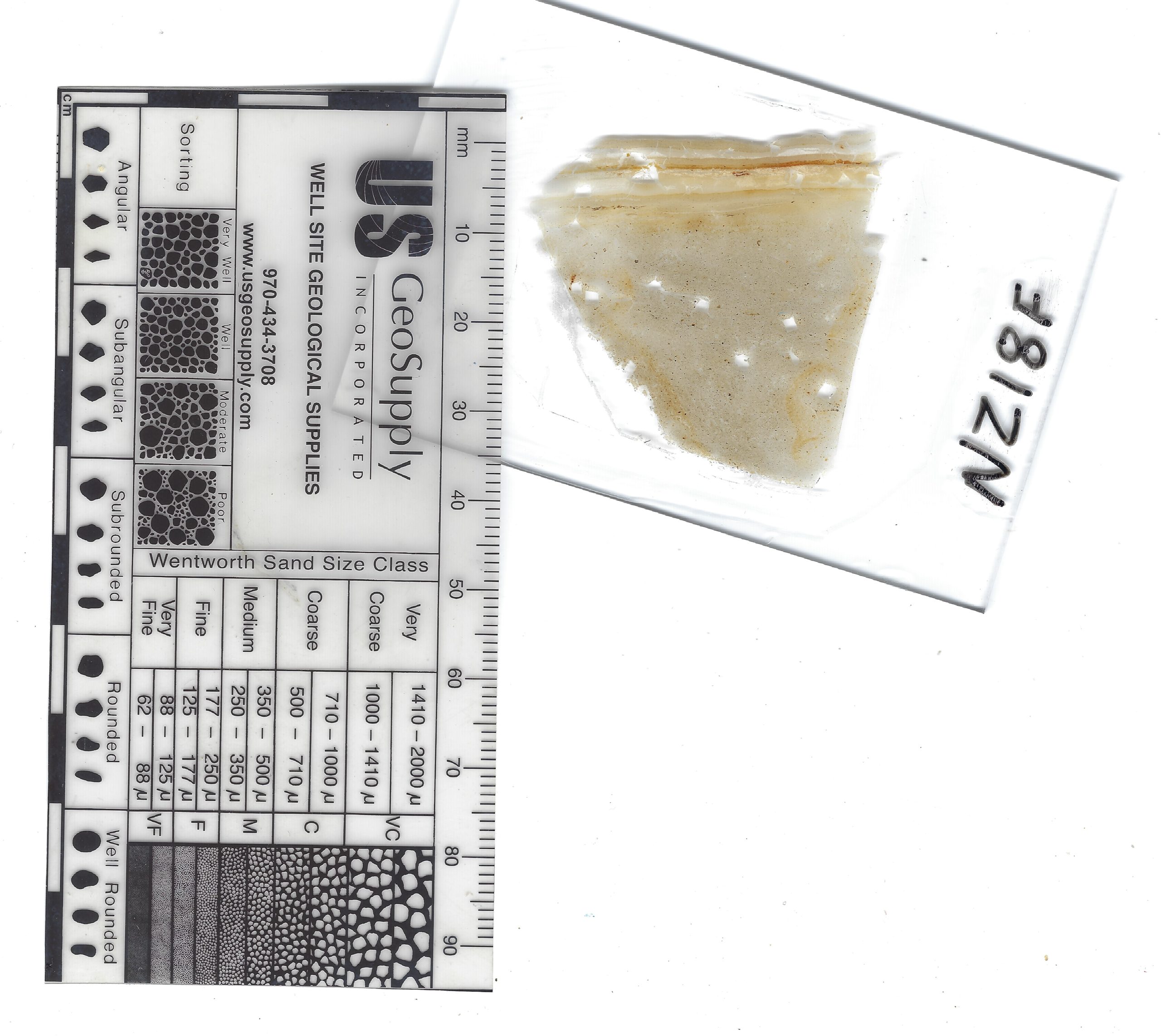
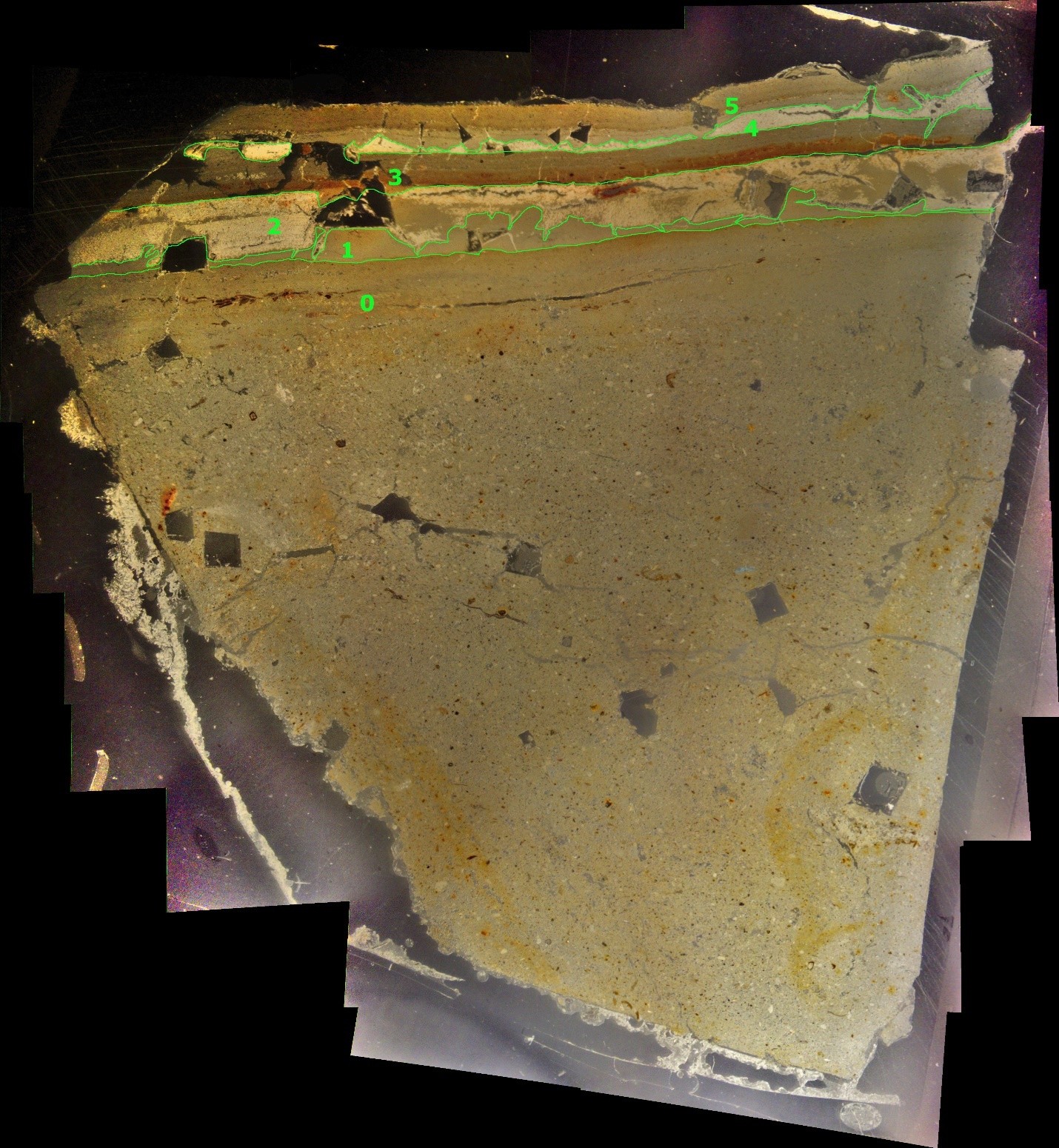
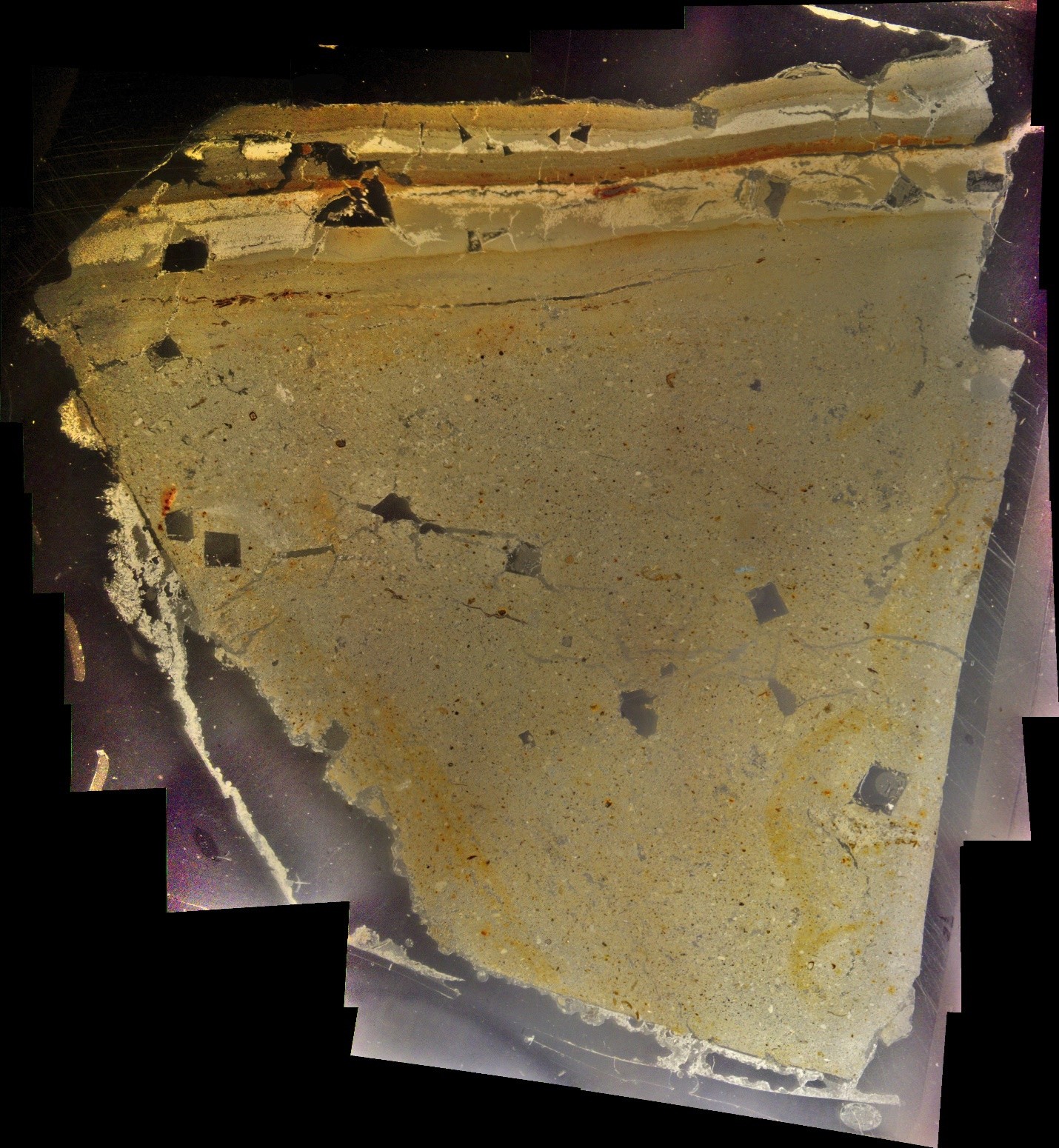
 Thin Section Slide from sample taken at site ZA-1
Thin Section Slide from sample taken at site ZA-1Jefferson Williams (2000)
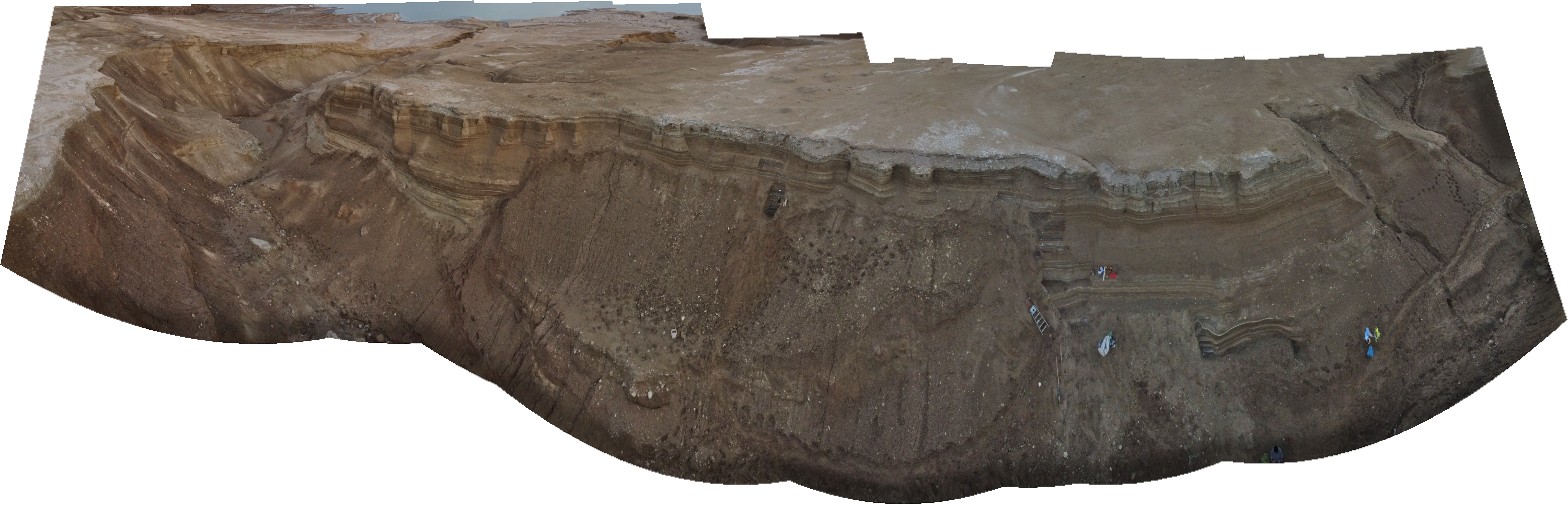
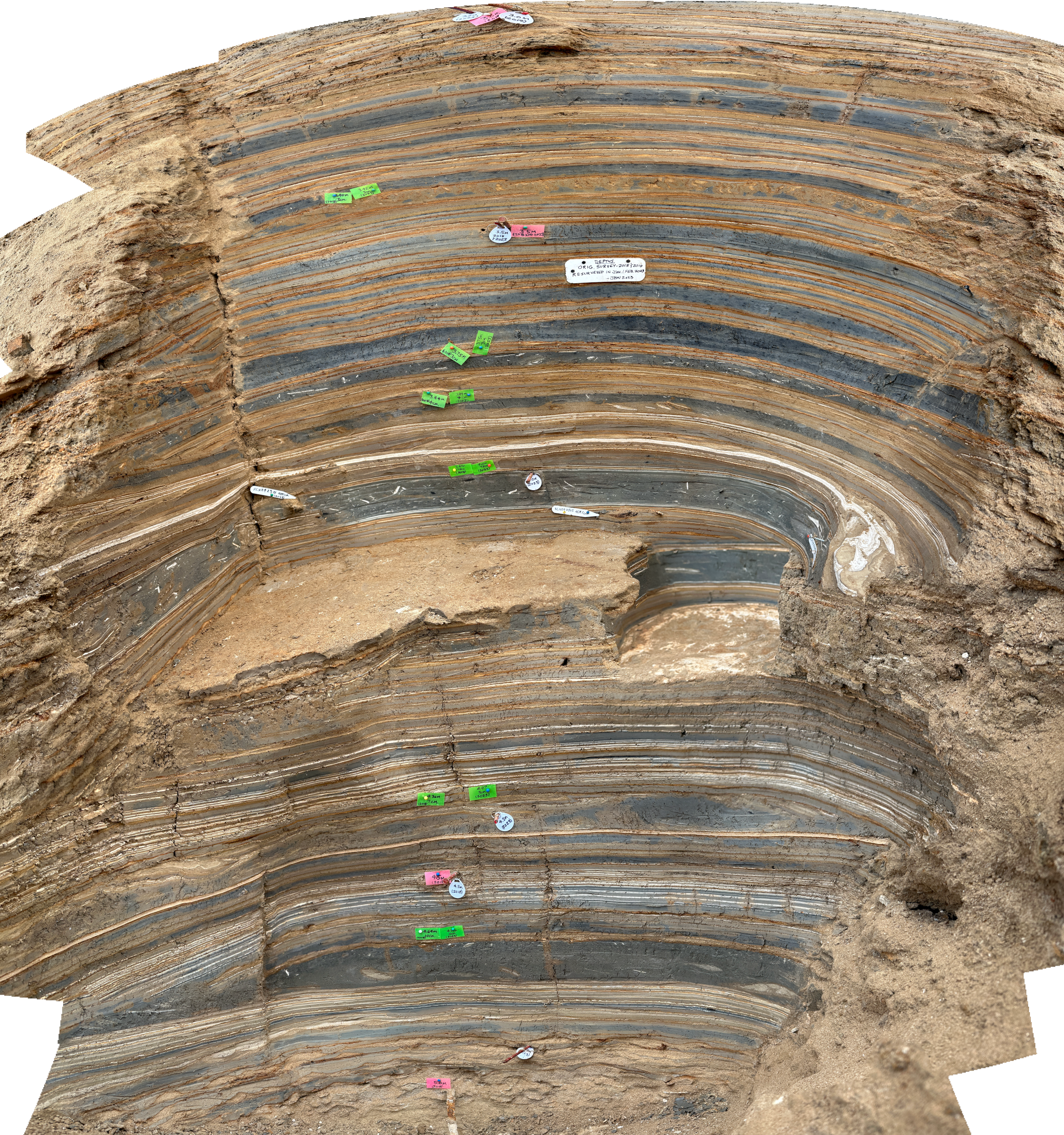
 Panorama of Site ZA-2 (South Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-2 (South Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos by Jefferson Williams 12 Feb. 2023
 Panorama of Site ZA-2 (South Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-2 (South Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos by Jefferson Williams 13 Feb. 2023
 Panorama of Site ZA-2 (South Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-2 (South Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos salvaged on iPhone by Jefferson Williams 22 Feb. 2023
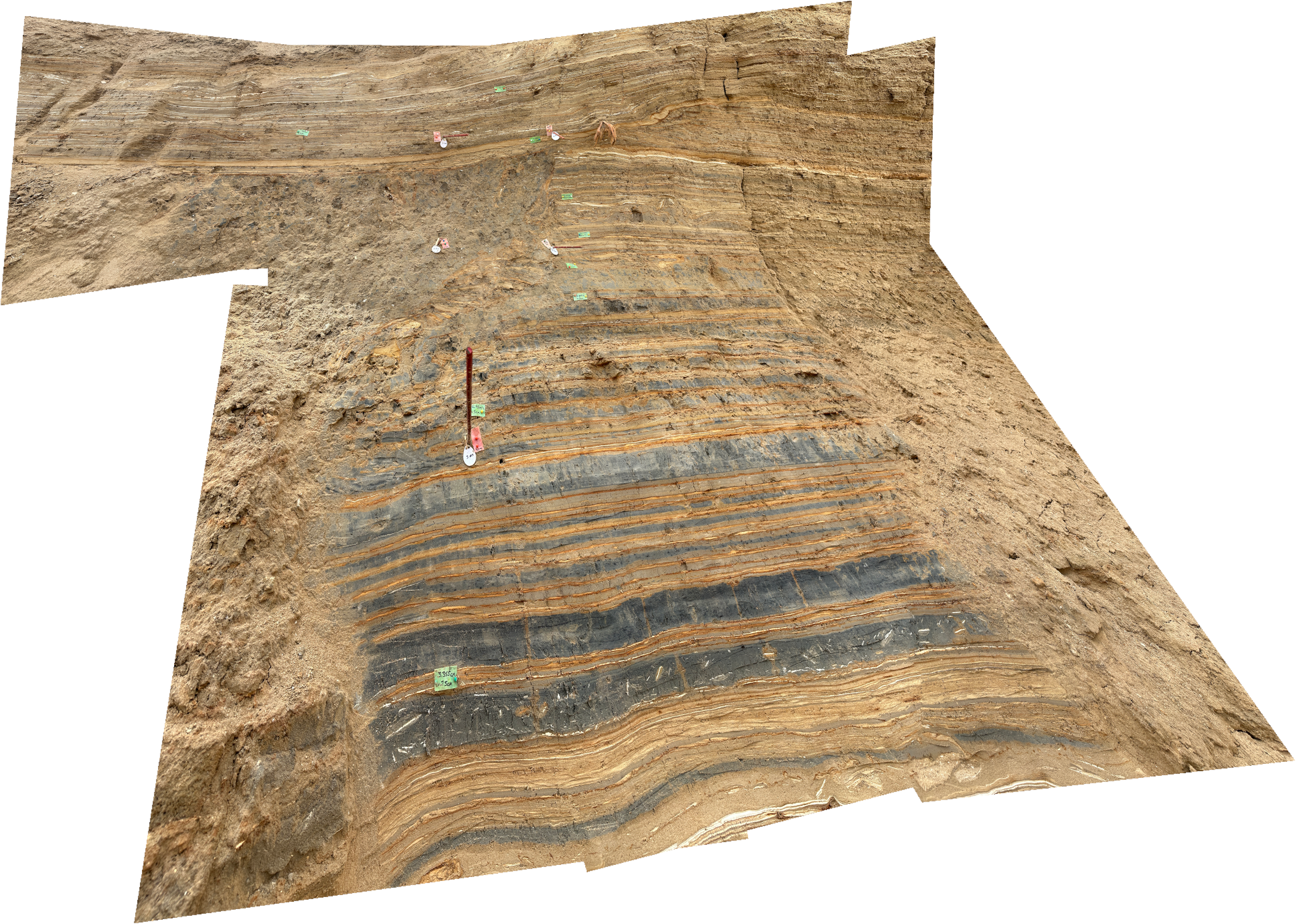
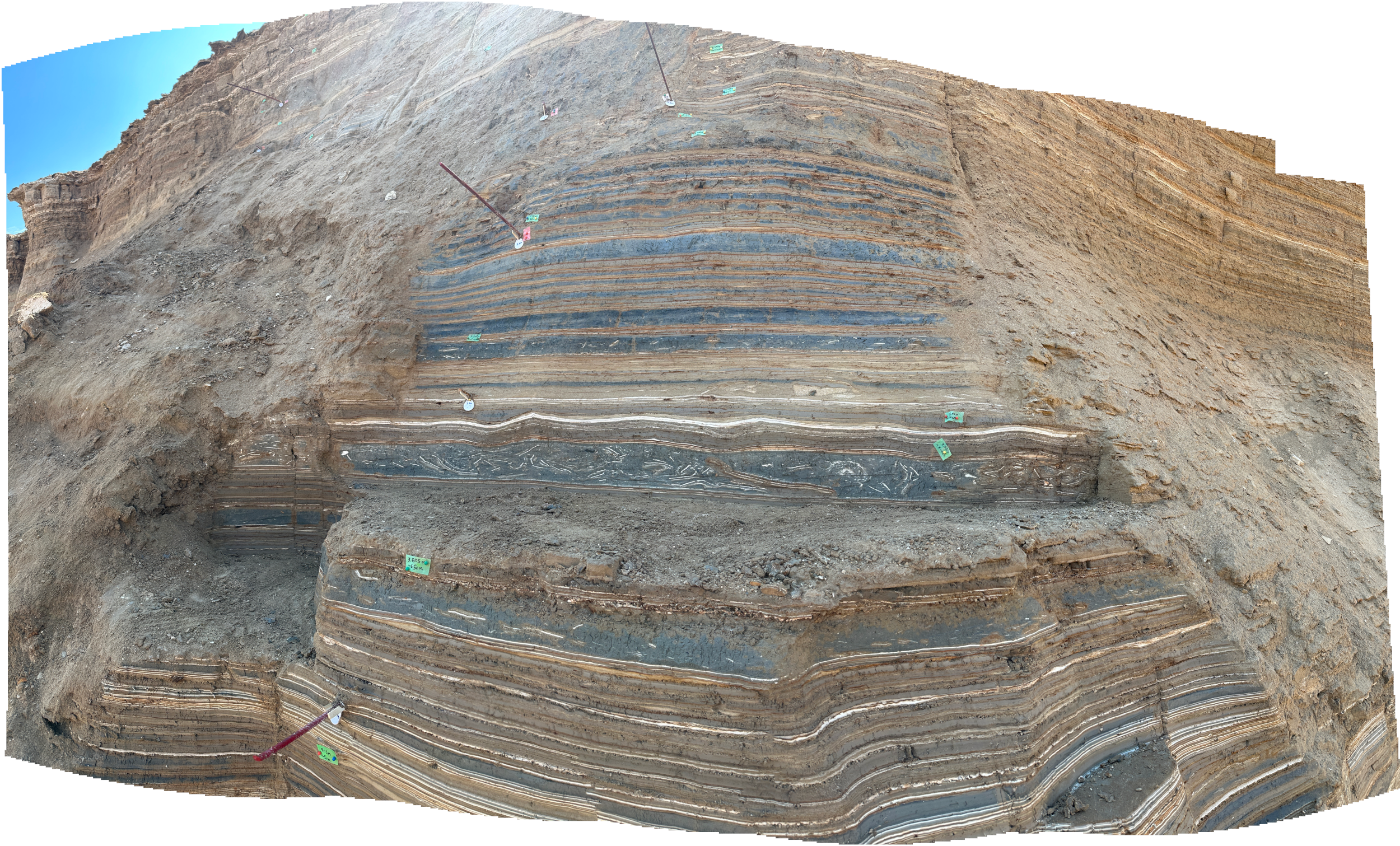
 Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos by Jefferson Williams 12 March 2023
 Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos by Jefferson Williams 12 Feb. 2023
 Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos by Jefferson Williams 13 Feb. 2023
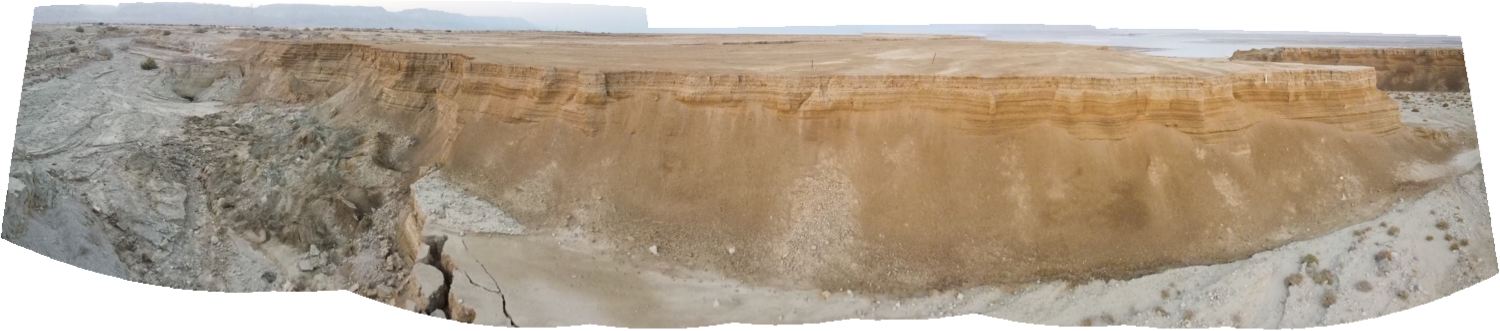 Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)
Panorama of Site ZA-3 (North Wall)Click on Image for high resolution magnifiable image
Drone photos salvaged from iPhone by Jefferson Williams 22 Feb. 2023
- from Kagan et al. (2011)
- these have been incorporated into the Master Seismic Events Tables for all sites

Ze'elim and Ein Feshka Seismites with Model Ages and Historic Event Correlation
- LS, local source, moderate earthquake, not appearing in the historical catalogs, may have produced these seismites
- Gully depth below fan delta surface
- Seismite type
A, Intraclast breccia layer
B, Microbreccia (“homogenite” to the naked eye)
C, liquefied sand
D, Folded laminae
E, Small offsets
Q, Questionable as seismite. See Table 1 and Figure 2. - Model ages of seismites extrapolated from deposition model (see section 5 for details)
- Fit of historical earthquake dates within 1σ or 2σ calibrated age ranges of seismites. Although model ages are tabulated here with 1 year precision for convenience, event fit considers the realistic precision of 10 years (see section 5.1)
- All other possible events within the age probability range (1σ or 2σ range) of the designated earthquake; 1068a refers to March 1068 A.D., and 1068b refers to May 1068 A.D. (see Table A1)
- Outside model range, extrapolated from model (Figure 4)
- Outside model range, estimated based on below and above radiocarbon ages (Figure 4)
- Alternately, this historic earthquake could have formed seismites below or above the one marked
Kagan et al (2011)
- from Kagan et al. (2011) Correction
- these have been incorporated into the Master Seismic Events Tables for all sites
 Table 4
Table 4Multisite Comparison of Holocene Seismites from four lacustrine sediments sites along the Western Dead Sea Basin
Kagan et al (2011)
 Table 4
Table 4Multisite Comparison of Holocene Seismites from four lacustrine sediments sites along the Western Dead Sea Basin
Kagan et al (2011)
- from Kagan et al. (2011)
- these have been incorporated into the Master Seismic Events Tables for all sites
 Table 4
Table 4Multisite Comparison of Holocene Seismites from four lacustrine sediments sites along the Western Dead Sea Basin
Kagan et al (2011)
- from Kagan et al. (2011)
 Figure 7
Figure 7Recurrence intervals and cumulative number of breccias in time.
- Ein Feshkha (EFE)
- Ein Gedi (EG)
- Zeelim (ZA1 and ZA2)
- Diamonds represent breccias
- circled diamonds are the IBS (intrabasin seismites)
- Horizontal gray bars indicate periods of seismic quiescence
(left) the earlier period is recorded at EG and ZA, and (right) the younger quiescence period is recorded at all three sites. Horizontal lines connect IBS events at the three sites.
Kagan et al (2011)
 Figure 4
Figure 4Stratigraphic section of Ze’elim (ZA2) and (right) age-depth deposition model derived by OxCal 4.1. The top 7.5 m are modeled, while the bottom of the section is presented as single calibrated dates. Probability density functions (histograms) on the graph give model ages for radiocarbon samples (details are given in Table 3). The histograms give the distributions for the single calibrated dates while the darker center part of each histogram take into account the stratigraphic information (see Bronk Ramsey [2008] for model specifics). The depth model curves are envelopes for the 95% (outer, lighter, approximately 2σ) and 68% (inner, darker, approximately 1σ) highest probability density ranges. The dashed line near the top is the extrapolation of the model upward, while the ellipse represents the uppermost seismite.
Kagan et al (2011)
 Figure 3.1.5
Figure 3.1.5Correlation of historic earthquakes to age-depth model.
Ze' elim Gully outcrop.
Squares indicate historic earthquake ages correlated to ages of seismites. Some historic earthquake dates are shown.
Kagan (2011)
 Figure 3
Figure 3ZA-3 outcrop section with main archaeological periods and elevations.
Kagan et al (2015)
- JW: This is north of ZA-3
 Fig. 1.2a
Fig. 1.2aGullies of the Zeʾelim fan delta cut into terraces created by the recession of the Dead Sea (Google Earth); the red circle marks the sampling location
Langgut and Finkelstein (2023)
 Fig. 1.2b
Fig. 1.2bThe Zeʾelim sediment section where we conducted our palynological and sedimentological investigations, with main archaeological periods and elevations; presented in meters below msl
(photo: Dafna Langgut)
Langgut and Finkelstein (2023)
| Description | Image | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Section Above Beach Ridge |
Photo by Jefferson Williams 10 Feb. 2023 |
Jefferson Williams |
| Eastern Section Below Beach Ridge Long Shot - Cleaned |
Long Shot Cleaned Photo by Jefferson Williams 10 Feb. 2023 |
Jefferson Williams |
| Eastern Section Below Beach Ridge Long Shot Less Clean but with Rulers and Scale |
Long Shot Less clean but with rulers and scales Photo by Jefferson Williams 14 Feb. 2023 |
Jefferson Williams |
| Eastern Section Below Beach Ridge Medium Shot Less Clean but with Rulers and Scale |
Medium Shot Less clean but with rulers and scales Photo by Jefferson Williams 14 Feb. 2023 |
Jefferson Williams |
| Eastern Section Below Beach Ridge Closeup on Woody Deposits with Ruler and Scales |
Closeup on Woody Deposits with rulers and scales Photo by Jefferson Williams 14 Feb. 2023 |
Jefferson Williams |
| Image | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 06 Feb. 2023 |
Entire Middle Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 03 Feb. 2023 |
Entire Middle Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 03 Feb. 2023 |
Bottom of Middle Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 03 Feb. 2023 |
Middle 01 of Middle Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 03 Feb. 2023 |
Middle 02 of Middle Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 03 Feb. 2023 |
Top of Middle Section | Jefferson Williams |
| Image | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 06 Feb. 2023 |
All 3 Western Sections | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 06 Feb. 2023 |
Entire Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Entire Western Section (view from below) |
Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Top Left of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Top Left and Top Right of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Above Top Middle of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Top Middle of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Mid Middle of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Bottom Middle of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 05 Feb. 2023 |
Bottom of Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
| Image | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 06 Feb. 2023 |
All 3 Western Sections | Jefferson Williams |
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 06 Feb. 2023 |
Entire Western Section Connector | Jefferson Williams |
| Image | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
|
Photo by Jefferson Williams 06 Feb. 2023 |
All 3 Western Sections | Jefferson Williams |

 Far Western Section at Site ZA-4
Far Western Section at Site ZA-4Photo by Jefferson Williams 10 Feb. 2023 |
Far Western Section | Jefferson Williams |
- JW: needs to be redone with a 44 cm. thickness for the 192/193 cm. seismite and a label of 419 or ~500 CE
 Bayesian Analysis of a section at Site ZA-4 version 004
Bayesian Analysis of a section at Site ZA-4 version 004Click on image to open in a new tab
Run using BACON and BACONQuake on Radiocarbon samples collected by JW in 2018 and 2023. Lake Level Curve from Bookman et al. (2004)
 Bayesian Analysis of a section at Site ZA-4 version 003
Bayesian Analysis of a section at Site ZA-4 version 003Click on image to open in a new tab
Run using BACON and BACONQuake on Radiocarbon samples collected by JW in 2018 and 2023. Lake Level Curve from Bookman et al. (2004)
 Bayesian Analysis of a section at Site ZA-4 version 002
Bayesian Analysis of a section at Site ZA-4 version 002Click on image to open in a new tab
Run using BACON and BACONQuake on Radiocarbon samples collected by JW in 2018 and 2023. Lake Level Curve from Bookman et al. (2004)
- BACONQuake
- Bacon("RC_NZ_Will_and_Will_2018_Combined_TopAndBottomAndOutlierOldSamplesRemoved",20,BCAD=FALSE,ask=FALSE)
- seismite_info_AllPossQuakes = read.table("SeismiteInfo_AllPossQuakes_ZA4_Will.csv", header = TRUE,sep = ",")
- seismite_info_Depths = read.table("SeismiteInfo_Depths_ZA4_Will.csv", header = TRUE,sep = ",")
- seismite_info_Picks = read.table("SeismiteInfo_Picks_ZA4_Will.csv", header = TRUE,sep = ",")
- LakeLevels = read.table("LakeLevelCurvesBookman2004_ZeelimA.csv", header = TRUE,sep = ",")
- Entire Middle Section
- Bottom Part of Middle Section
- BaconQuake Bayesian Analysis
| RC Depth (cm) |
Sample Depth (cm) |
Thickness (cm) |
Quake | Sample Name |
InSitu Image | Extracted Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 195 | 192 | ~44 | 419 CE | NZ423K |
|
||
| 195 | 192 | ~44 | 419 CE | NZ423K - resample |
|
Top Bottom |
|
| 240 | 251 (2018) 249 (2023) |
16 (2018) 16 (2023) |
363 CE | NZ423I | |||
| 380 | 400 (2023) 389 (2018) |
7.5 (2018) 7.5 (2023) |
~31 CE | NZ423A |
| RC Depth (cm) |
Sample Depth (cm) |
Thickness (cm) |
Quake | Sample Name |
InSitu Image | Extracted Image | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
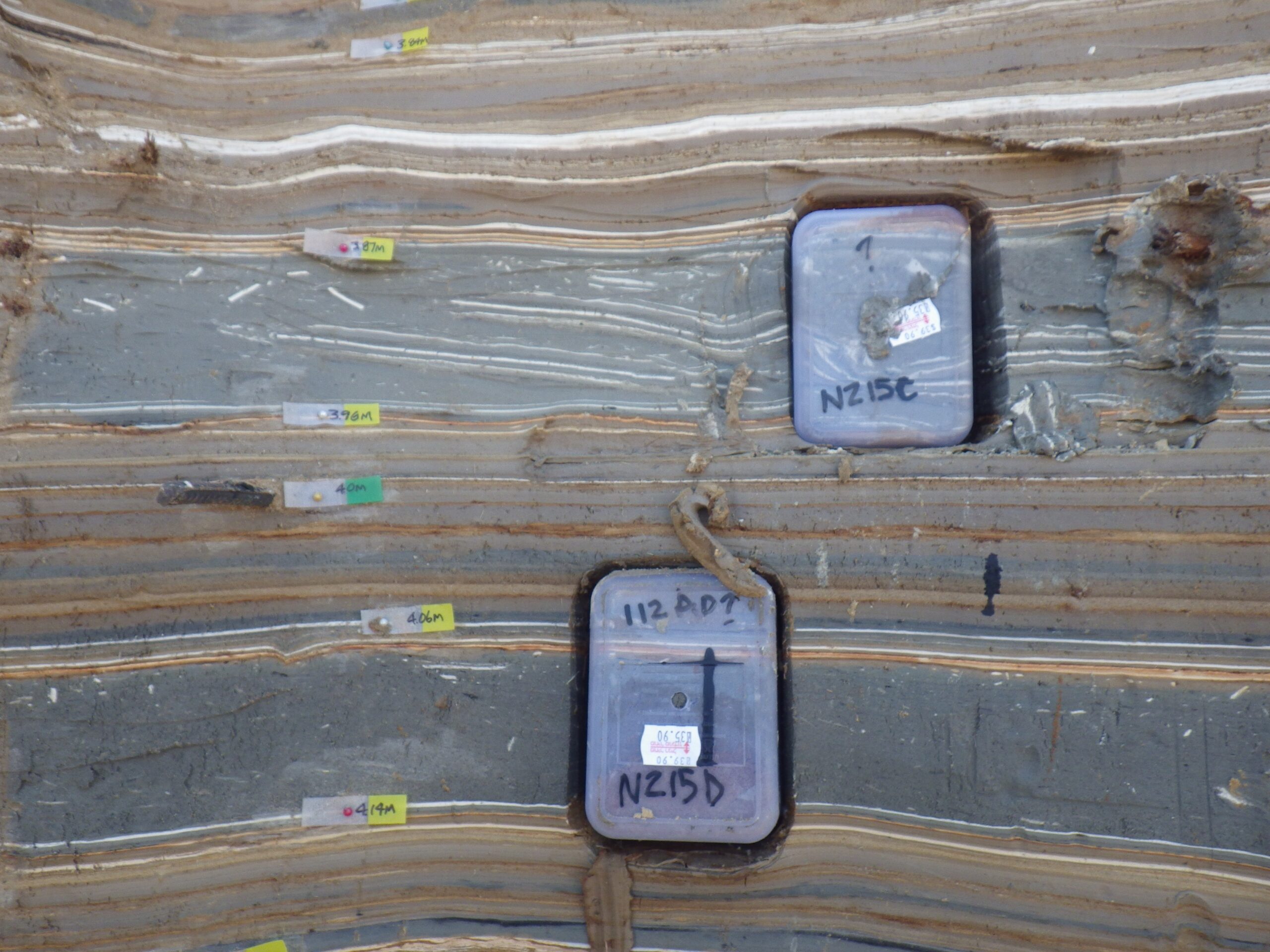
| 387 | 12 | NZ415C |
|
||||
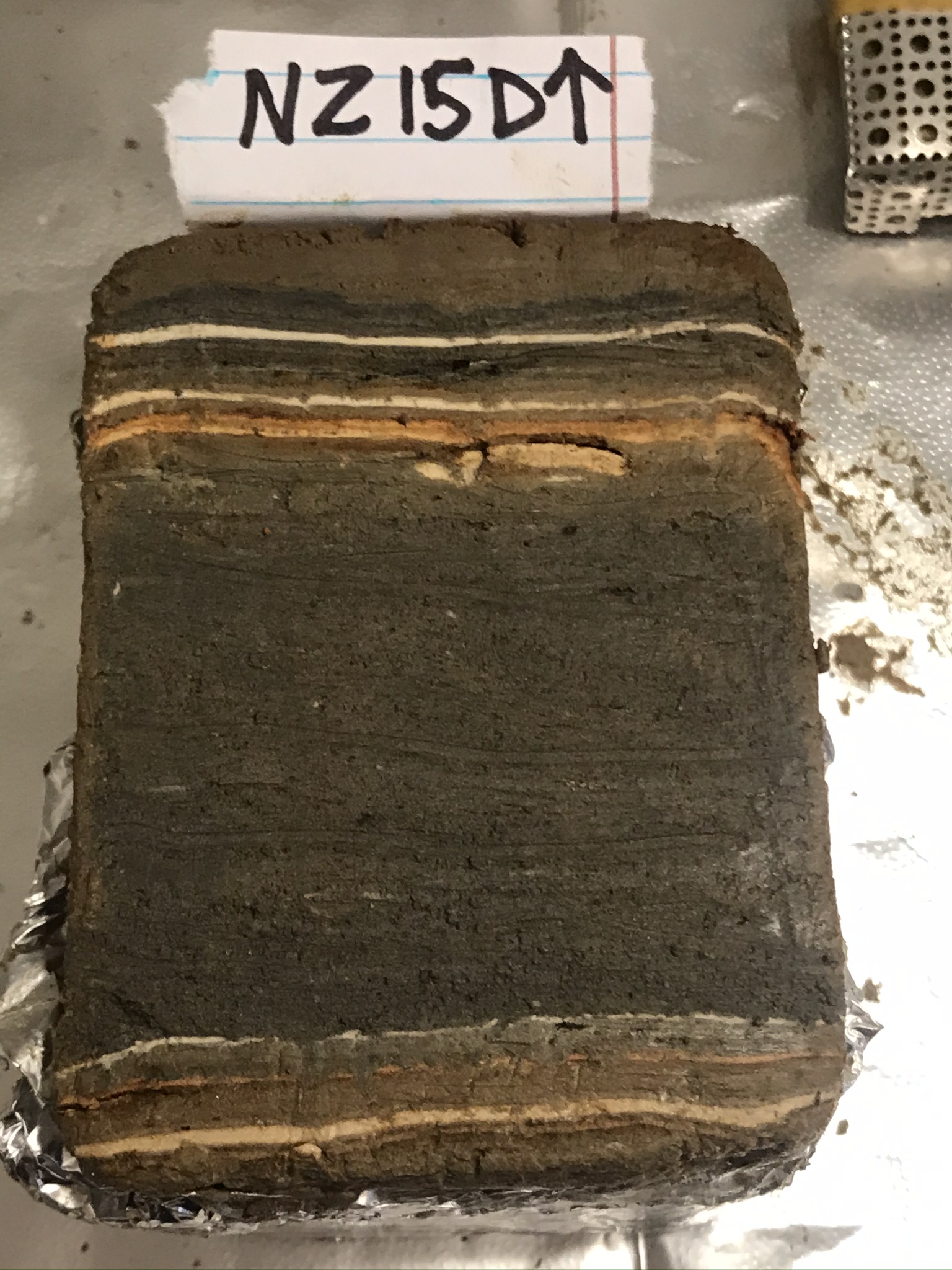
| 406 | 8 | NZ415D |
|
||||
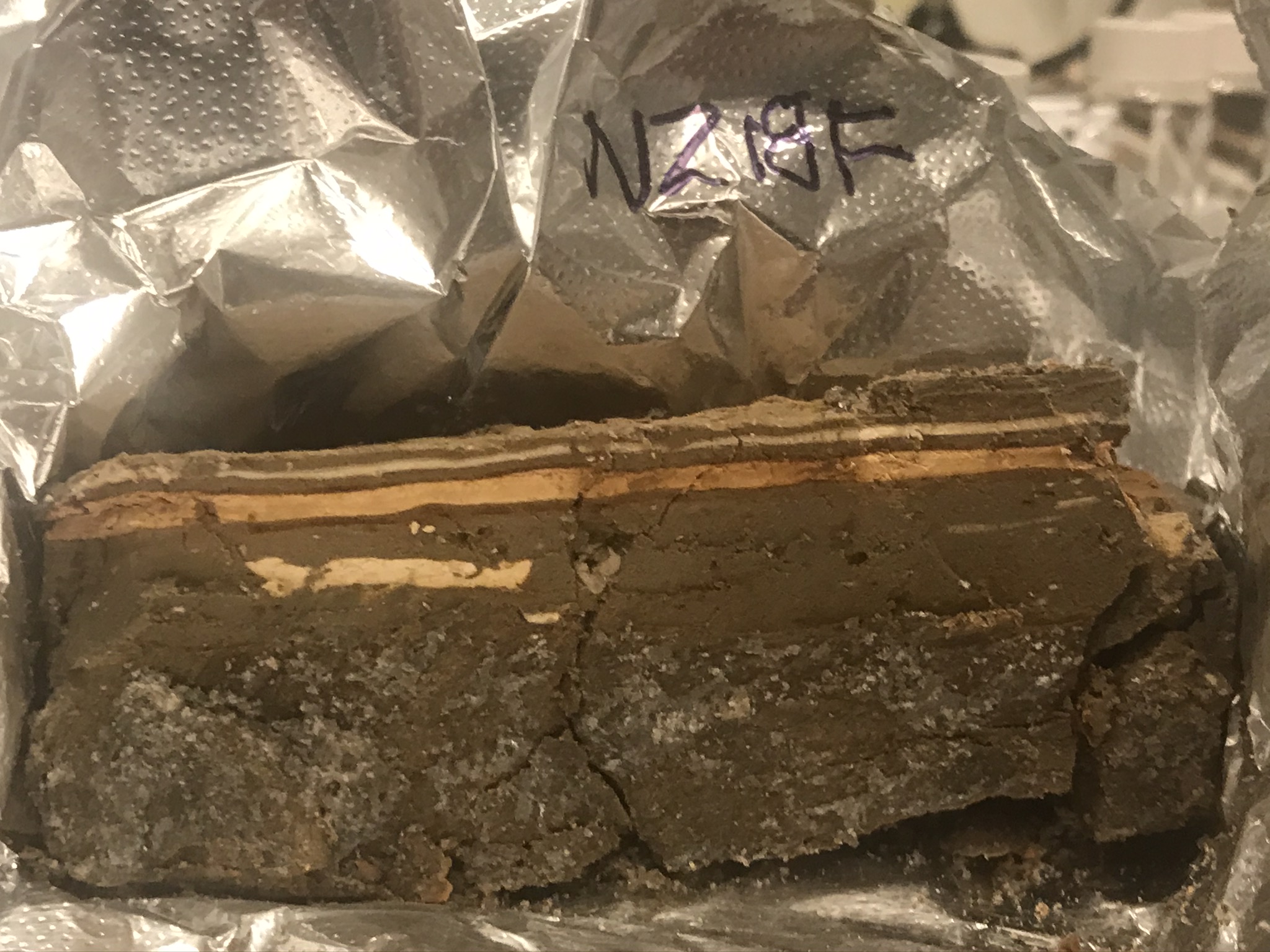
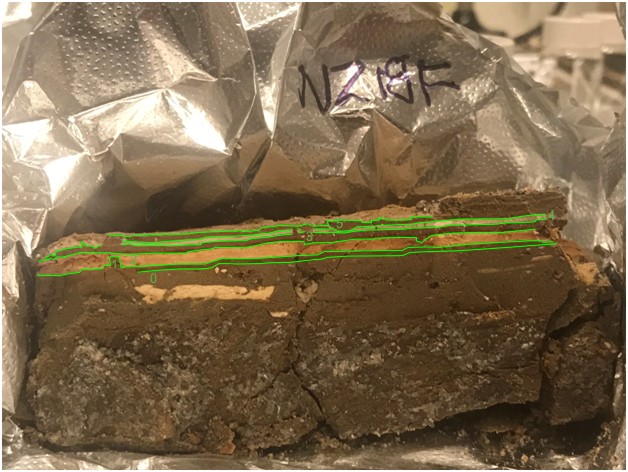
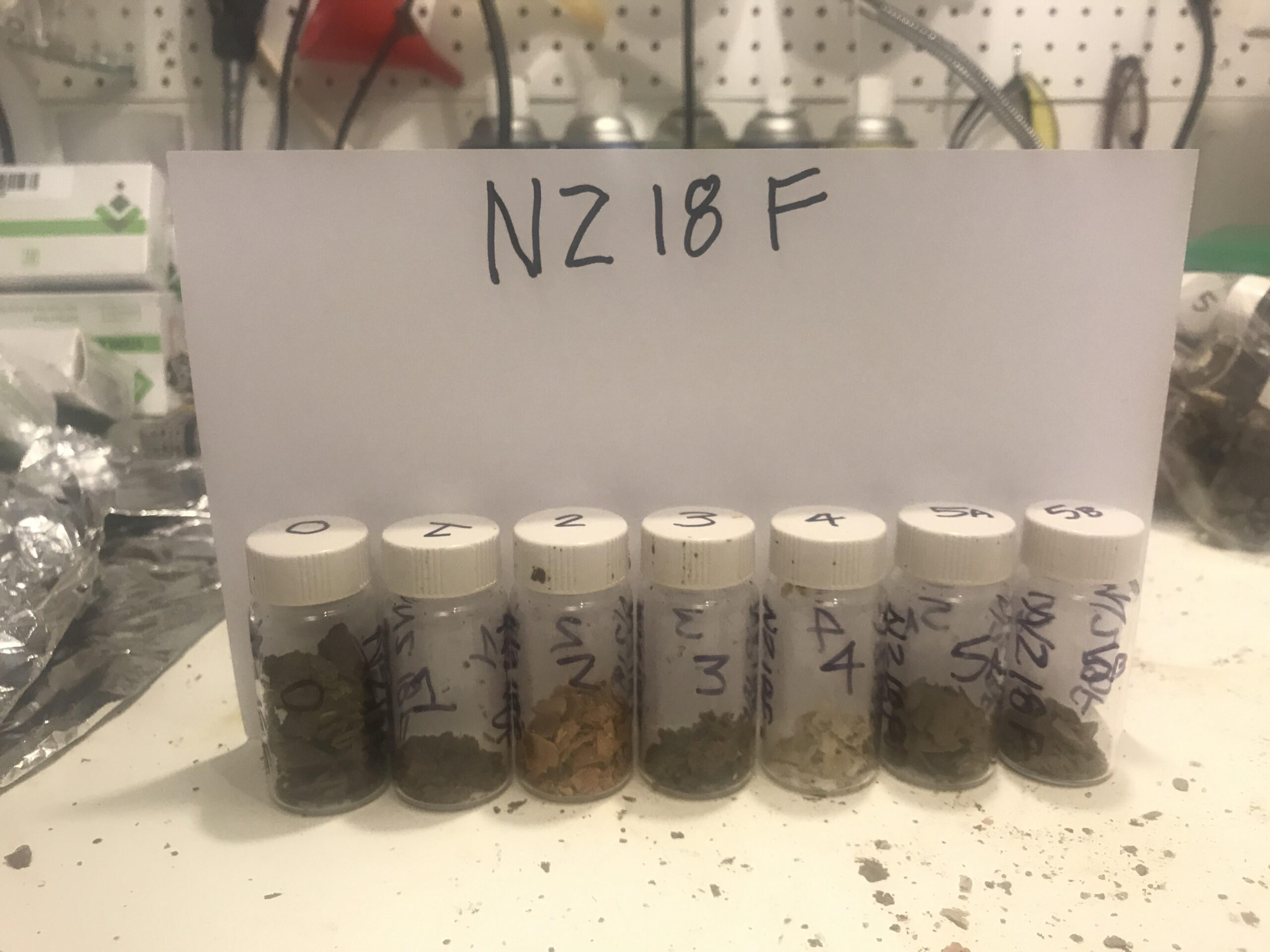
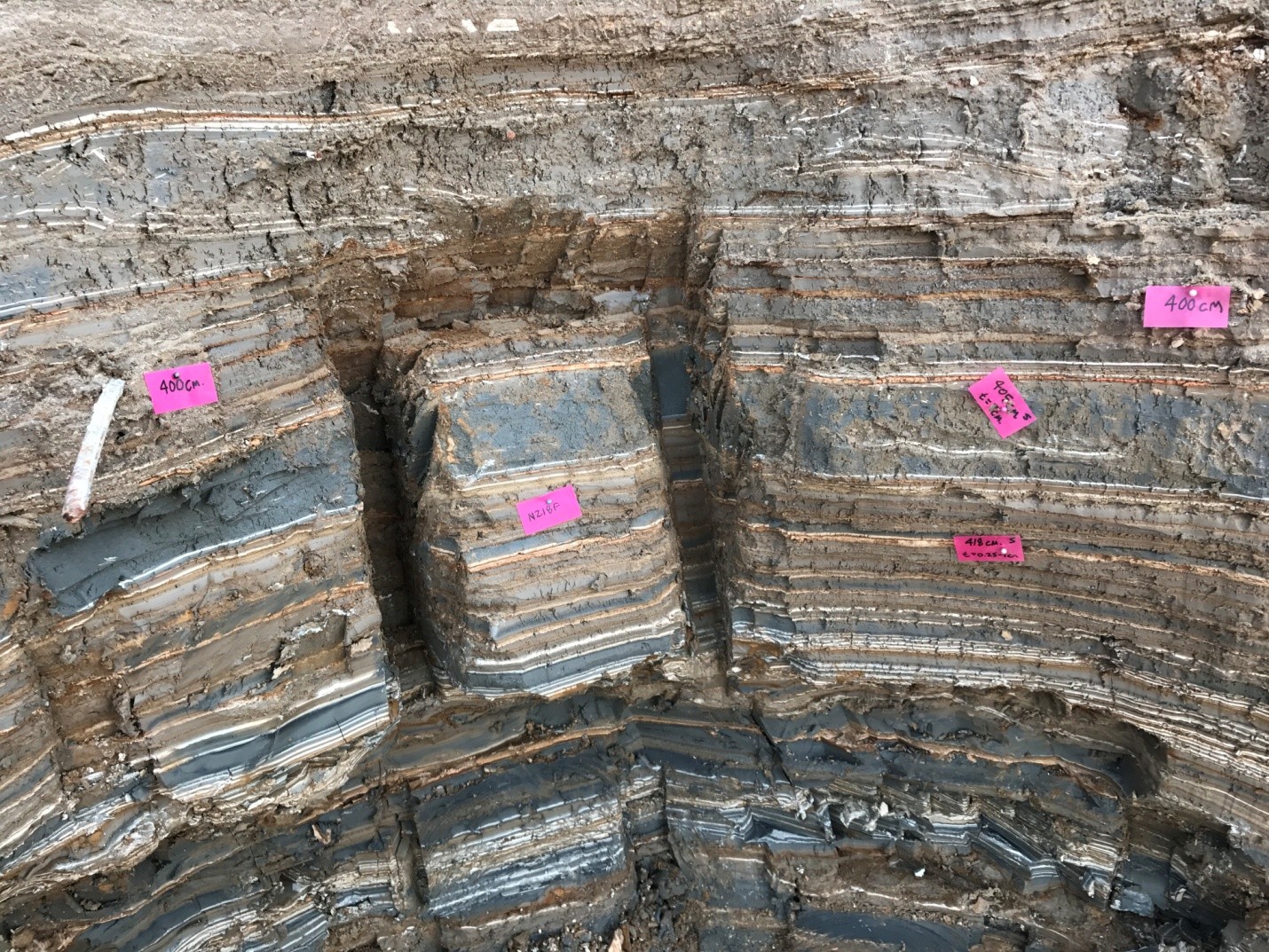
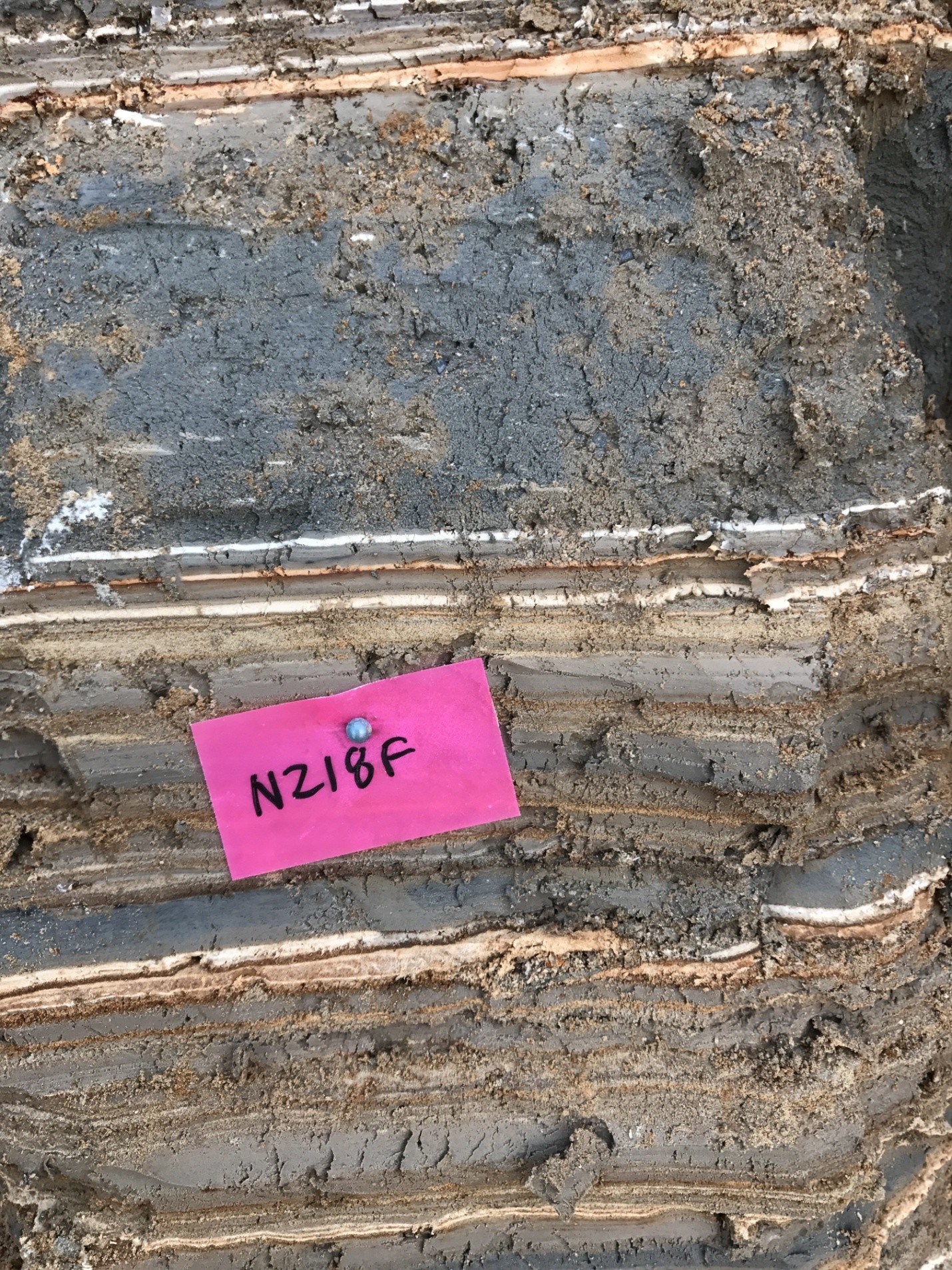
| 405 | 7 | NZ418F |
|
|
|||
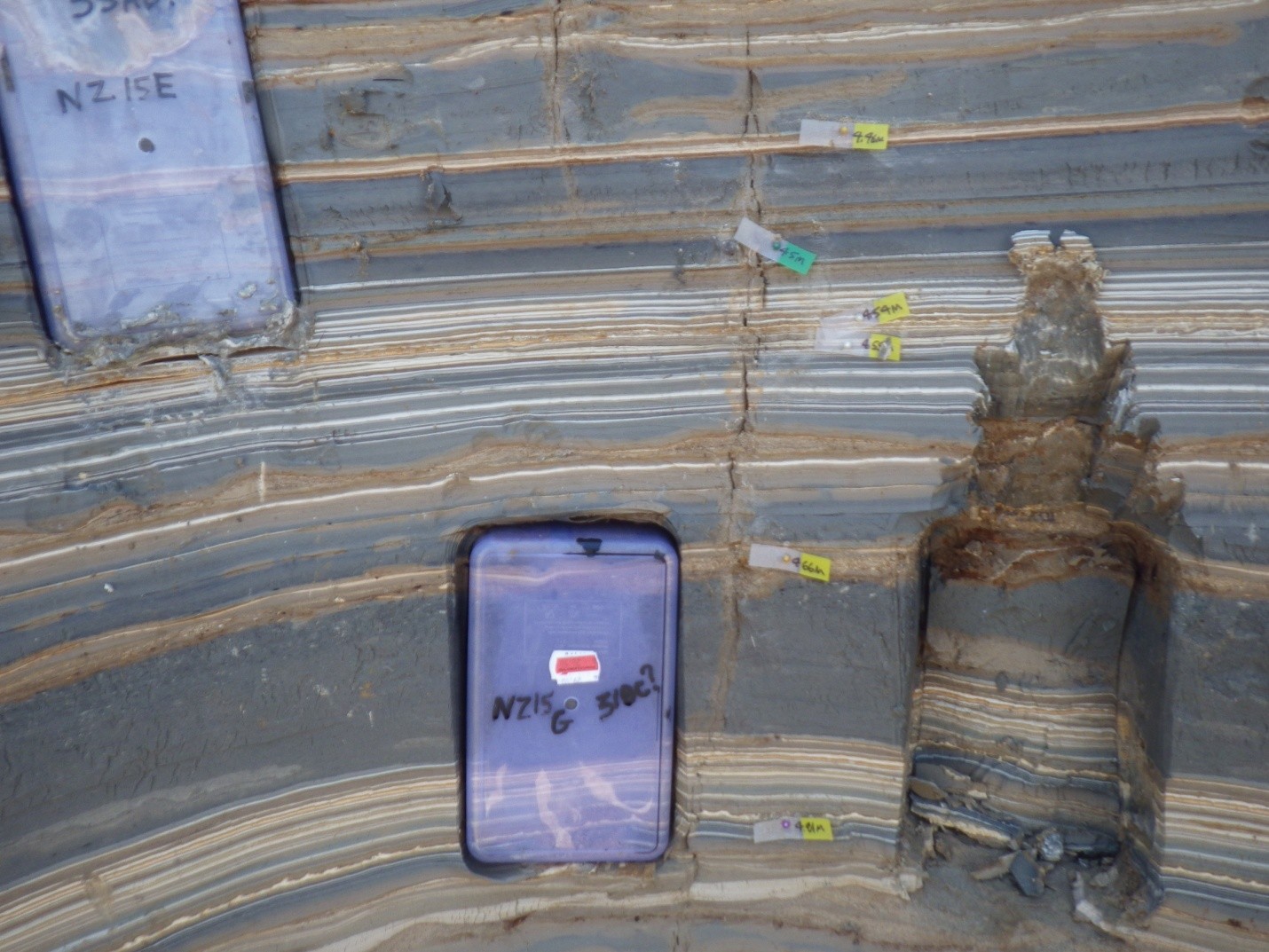
| 466 in 2015 464 in 2018 |
10 in 2015 12-14 in 2018 |
31 BCE ? | NZ415G |
|
|
| Sample | In Situ Photo |
Sample Photo |
Sample Description |
Depth (cm) |
Age (yrs BP) |
Uncertainty (± yrs BP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCNZ18109 | JW: Big Twig, Old, Lab: Wood - in seismite | 113 | 1419 | 24 | ||
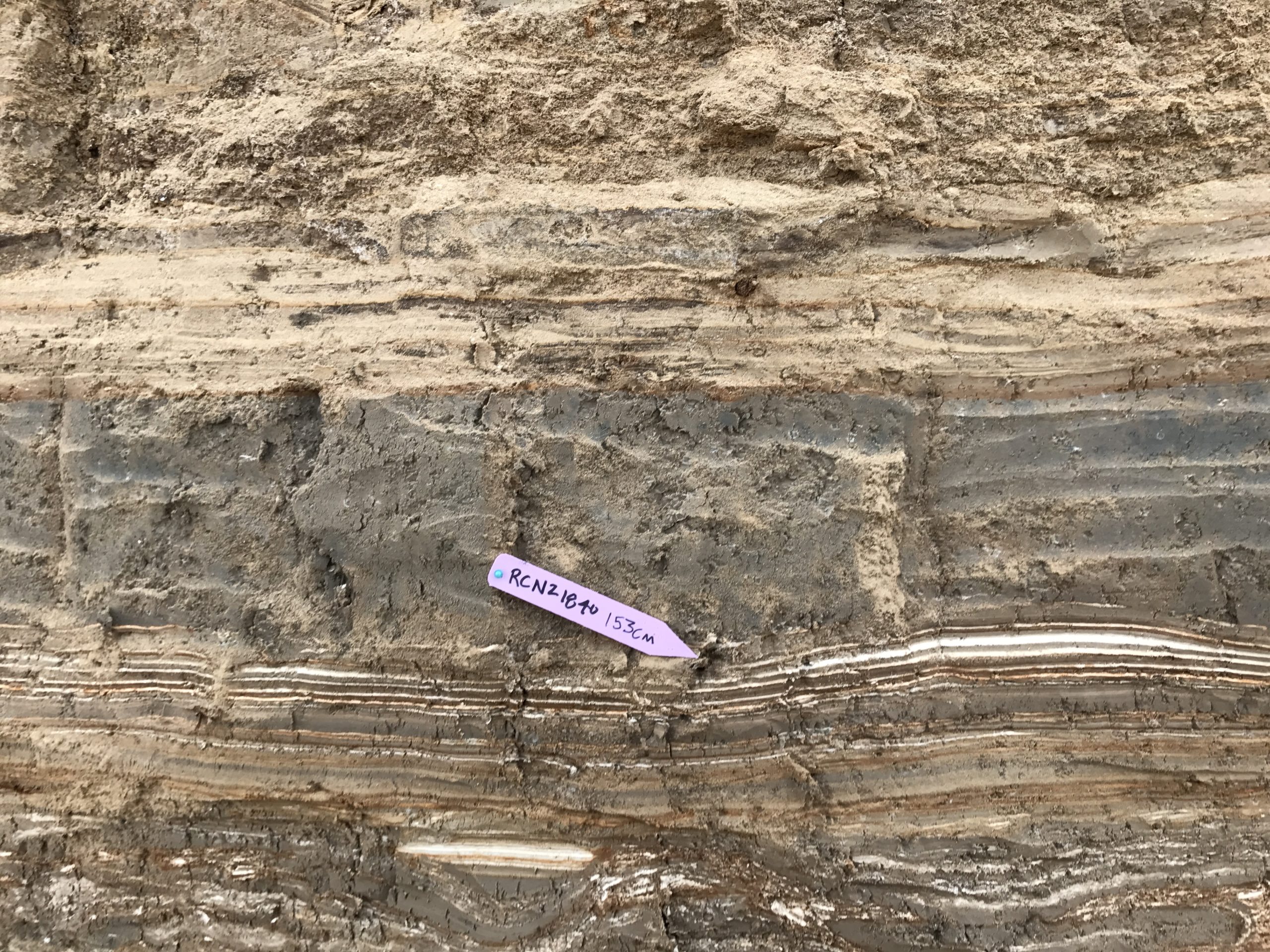
| RCNZ18040 | JW: Big twigs looks old, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 153 | 1361 | 23 | ||
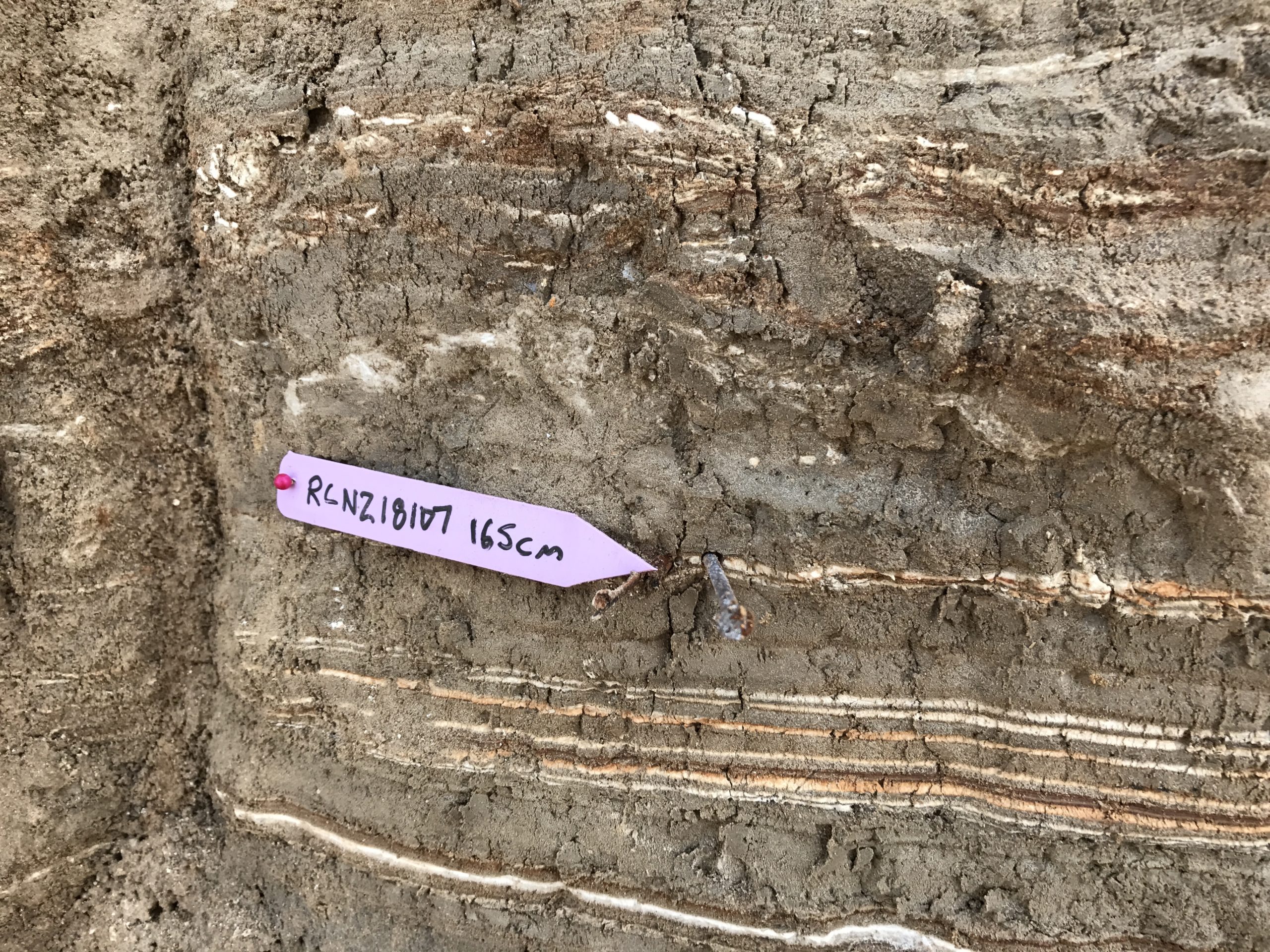
| RCNZ18107 | JW: Big Twig, some burning, Lab: Wood - in seismite | 165 | 1637 | 25 | ||
| RCNZ18200 | JW: 3 big twigs no field photo just above RCNZ18118, Lab: Wood - in seismite | 179 | 1664 | 30 | ||
| RCNZ18106 | JW: Huge looks recent some burning, Lab: Wood - in seismite | 184 | 1666 | 28 | ||
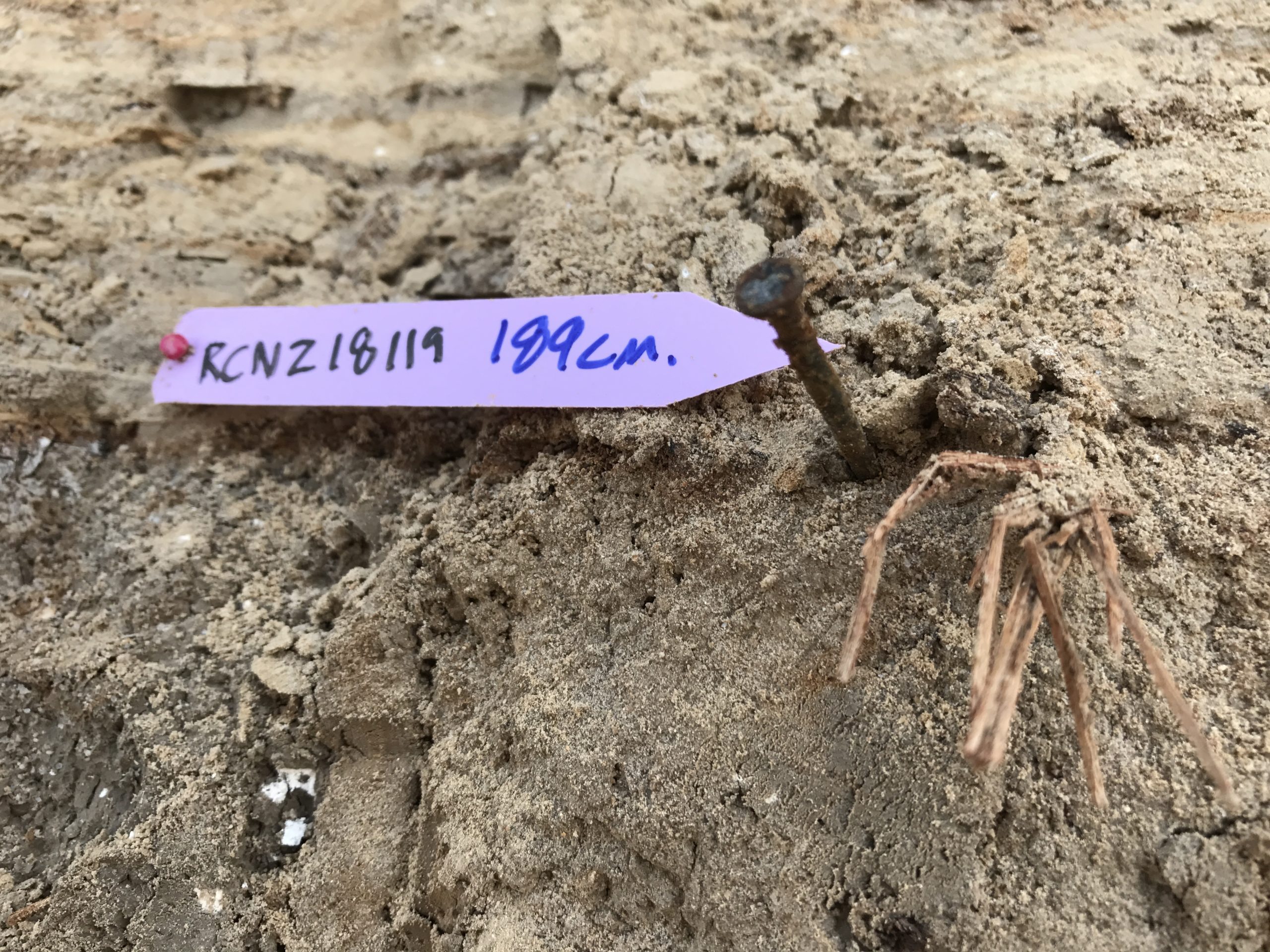
| RCNZ18119 | Sample RCNZ18119 Sample 2 |
JW: Huge some burning, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 189 | 1301 | 26 | |
| RCNZ18035 | JW : Big Twig looks old no field photo, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 225 | 1373 | 26 | ||
| RCNZ18029B | JW : Big Twig looks old, Lab : Wood - not in seismite | 297 | 1831 | 25 | ||
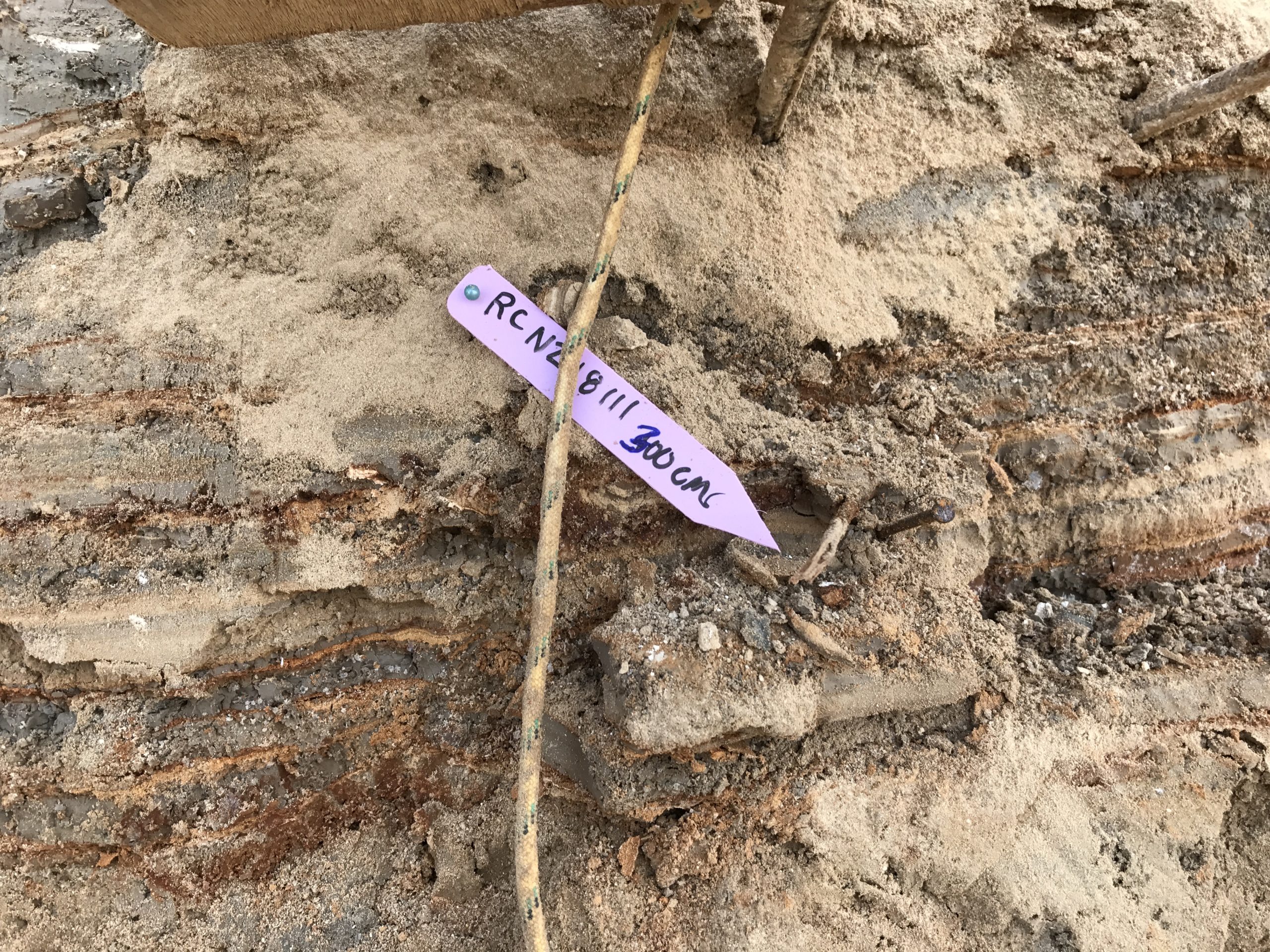
| RCNZ18111 | JW : Huge Twig, Lab: Charcoal - not in seismite | 300 | 1918 | 27 | ||
| RCNZ18034 | JW : Big Twig looks old - no field photo, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 315 | 1845 | 32 | ||
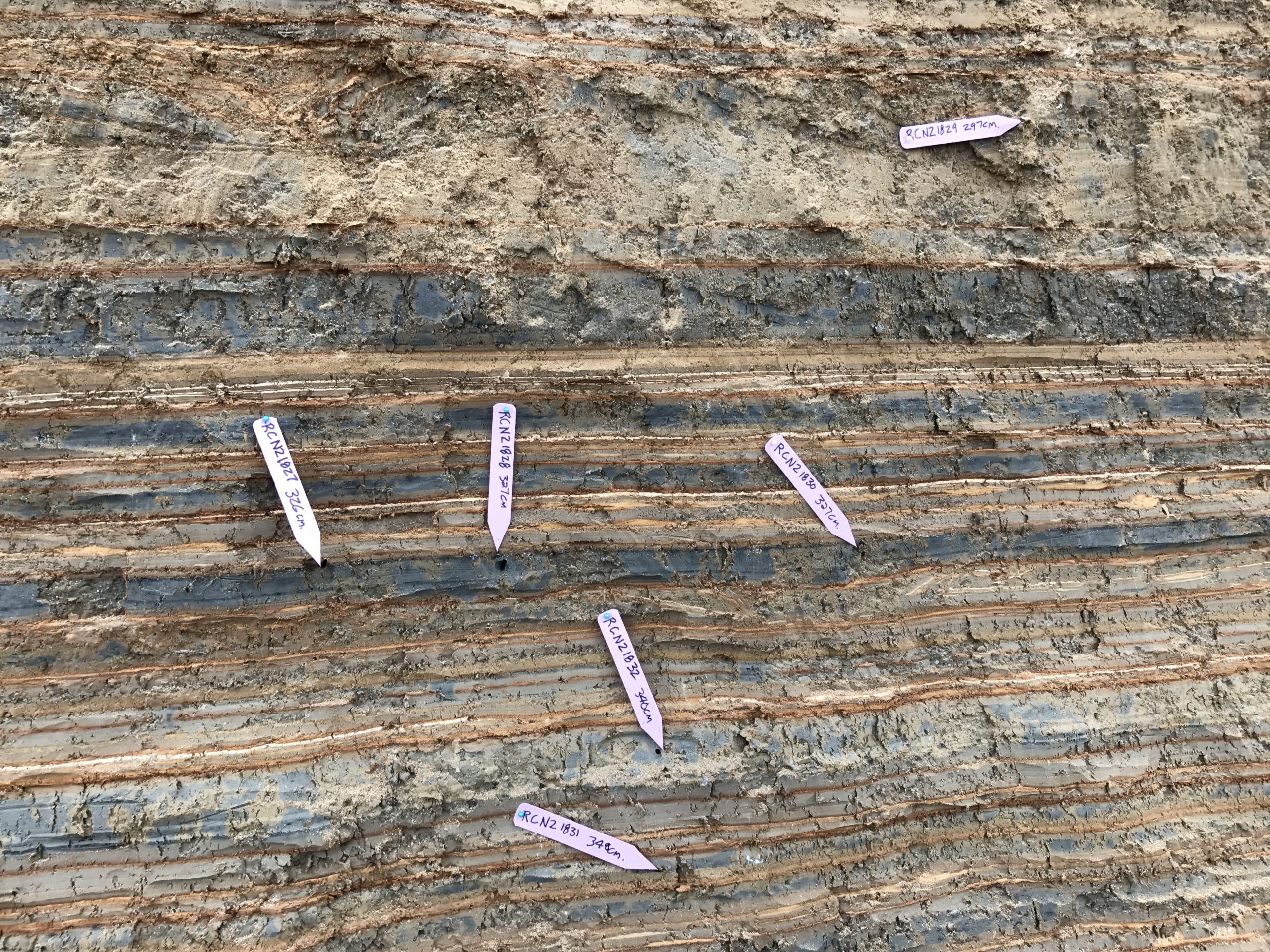
| RCNZ18032 | JW : nice twig, Lab: Charcoal - not in seismite | 340 | 2033 | 27 | ||
| RCNZ18020 | JW : Big poss. recent, Lab: Charcoal - not in seismite | 374 | 2144 | 39 | ||
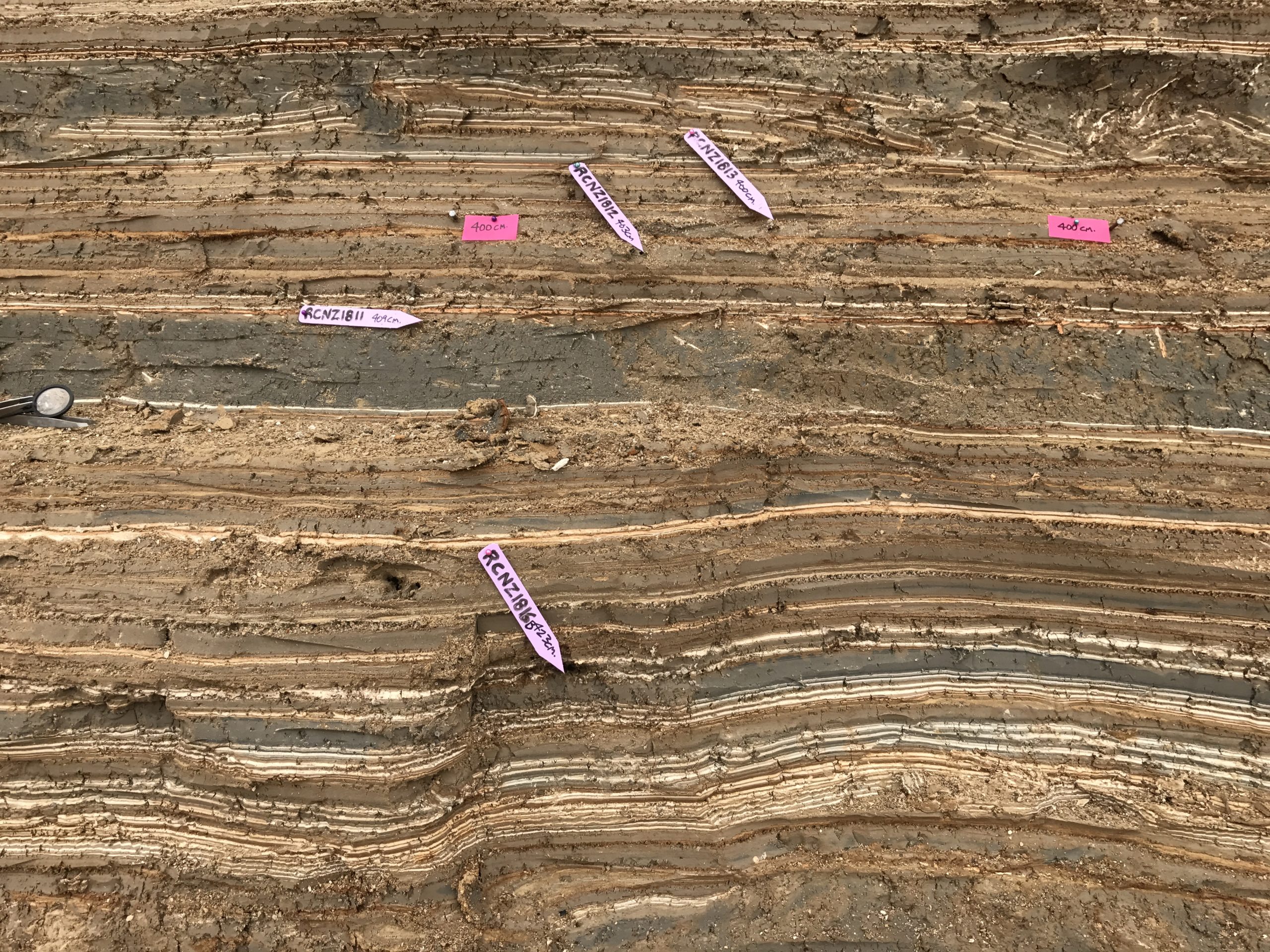
| RCNZ18013 | JW : Twig - some burning, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 400 | 1781 | 33 | ||
| RCNZ18016B | JW : Twigs big Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 423 | 1996 | 25 | ||
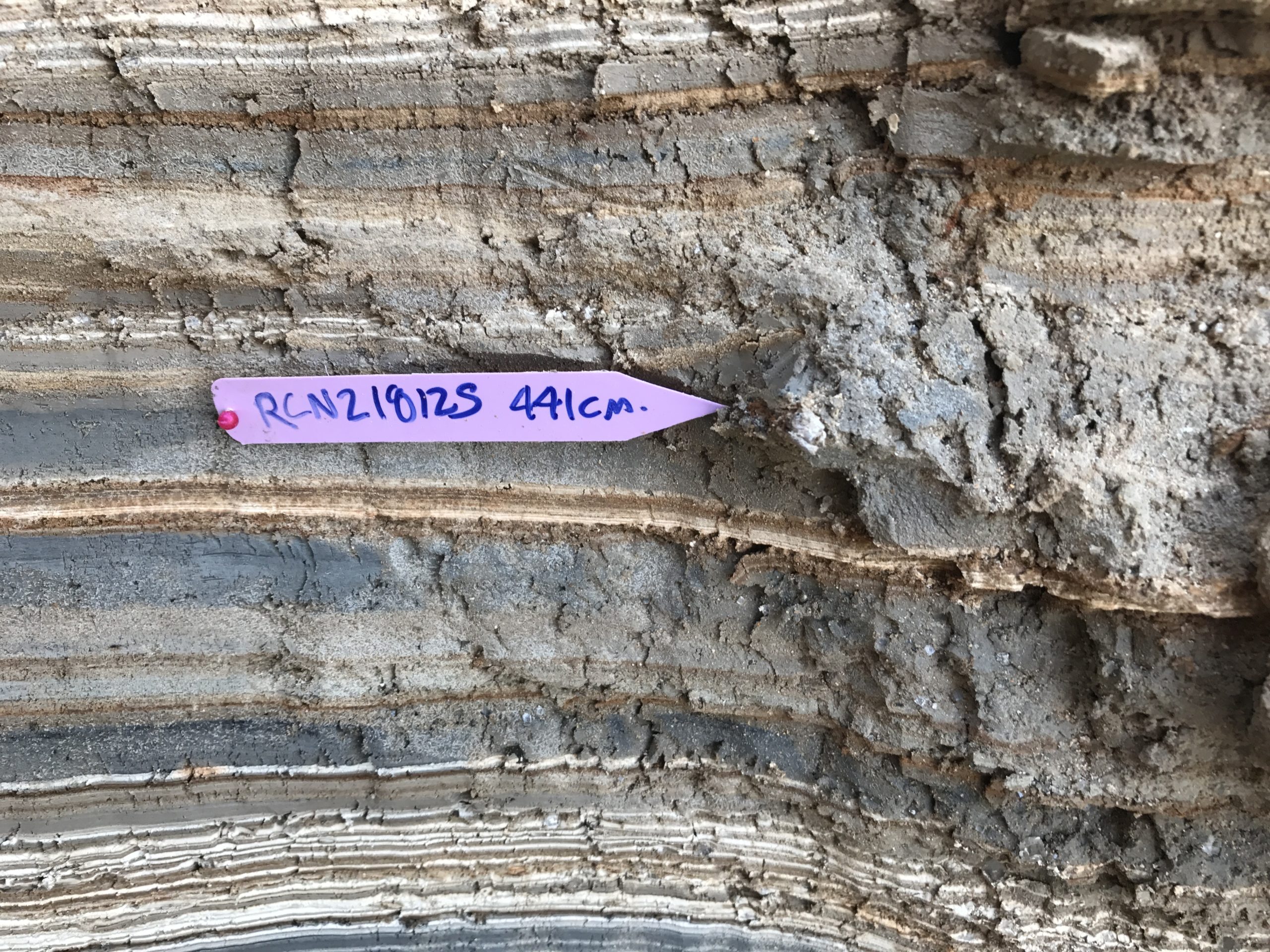
| RCNZ18125 | JW : Big Twig slightly burnt, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 441 | 1998 | 36 | ||
| NZ_15_G | JW : Middle Outcrop 450 mg, Lab: Charcoal - not in seismite | 449 | 2173 | 33 | ||
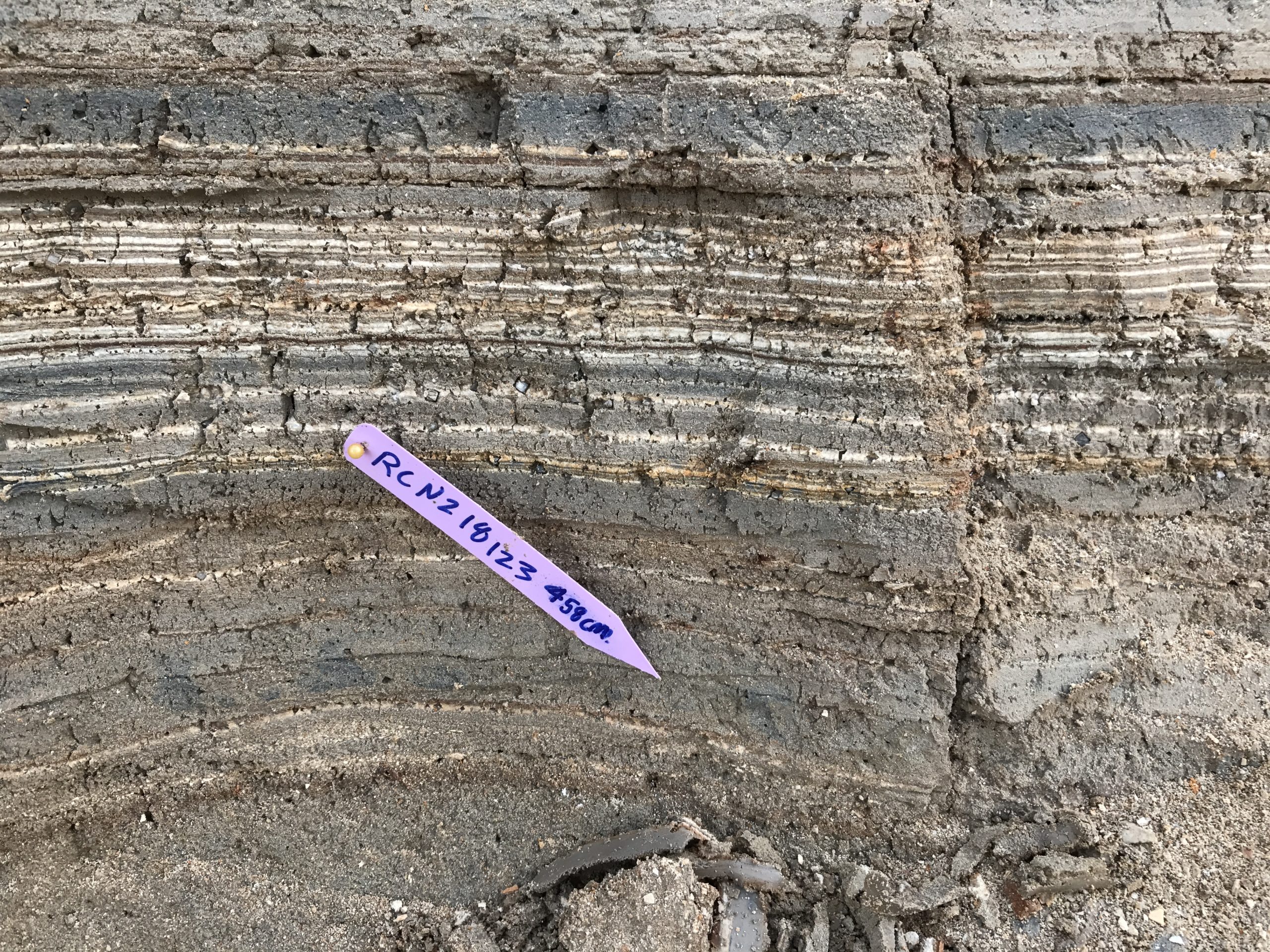
| RCNZ18123 | JW : Big recentish some burning looks old, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 458 | 2020 | 36 | ||
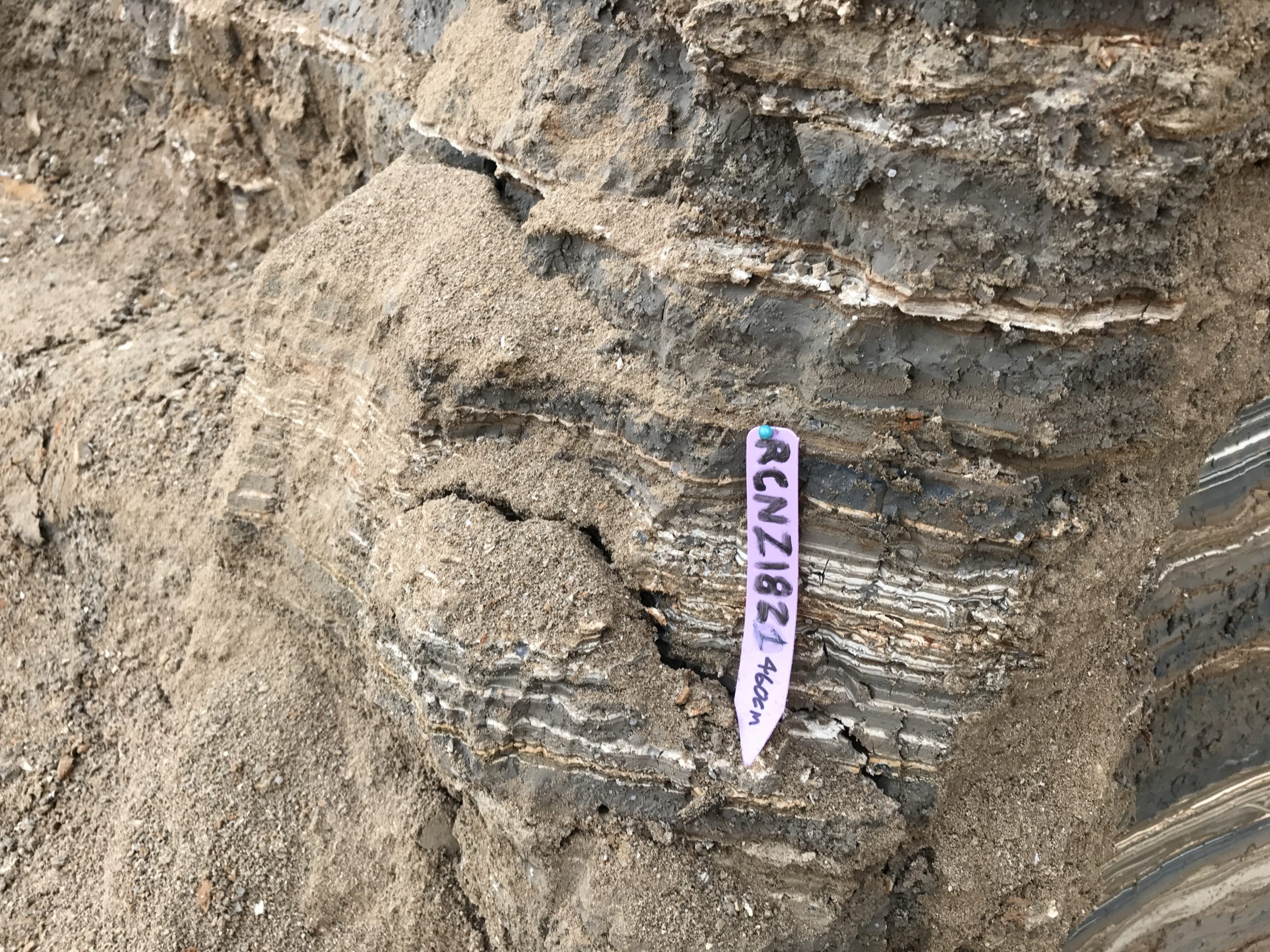
| RCNZ18021 | JW : Big Twig, Lab: Charcoal - not in seismite | 460 | 2118 | 32 | ||
| NZ_15_C | JW : Middle Outcrop 782 mg, Lab: Charcoal - at top of seismite | 466 | 2198 | 34 | ||
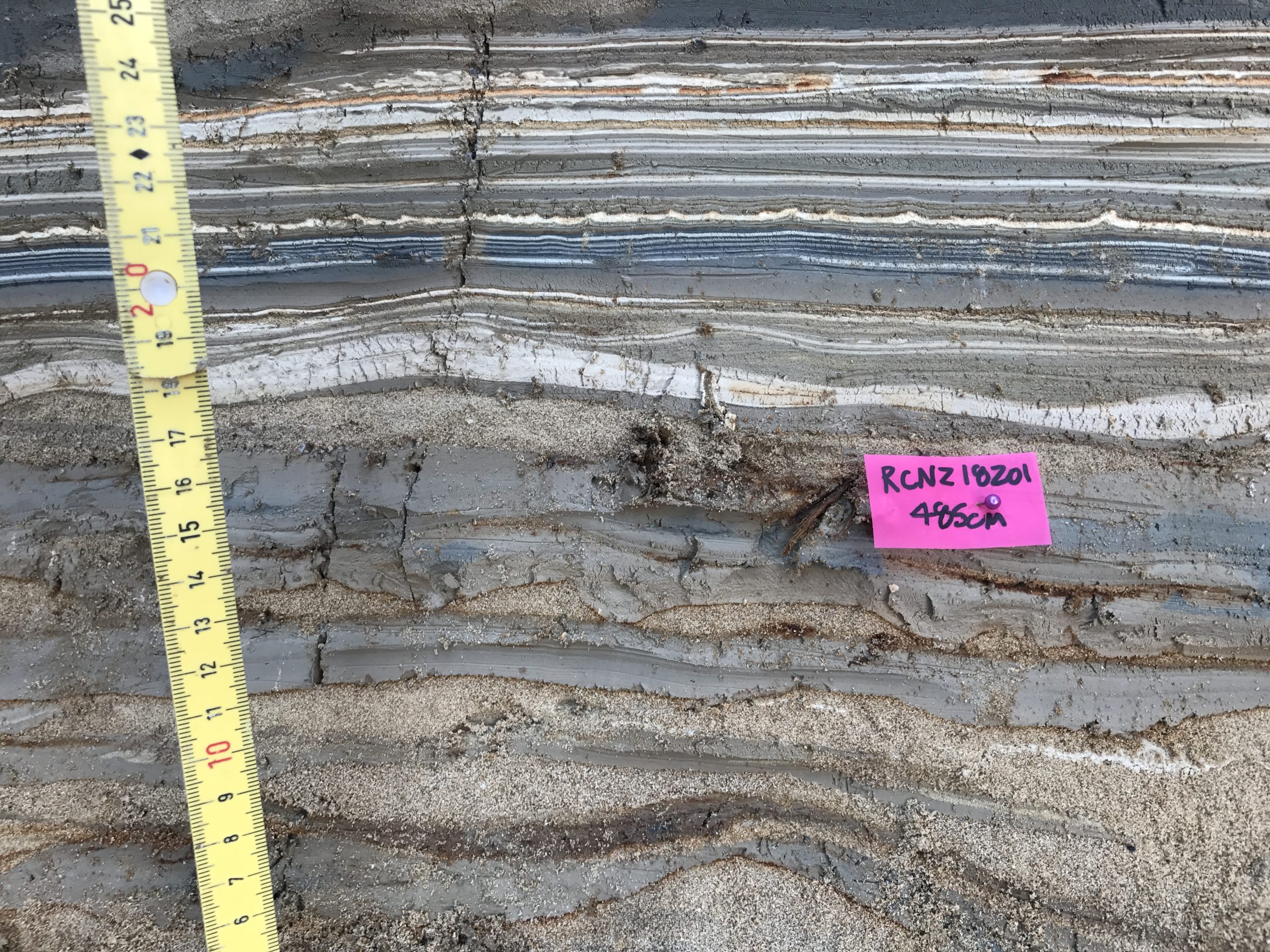
| RCNZ18201 | JW : lots of material recentish, Lab: Wood - not in seismite | 485 | 2152 | 34 |
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2Lithology of the sediment cores and the established age-depth models of the different profiles. The Ze'elim coring profile is paralleled by the Ze'elim gully wall [16] . The Ein Gedi chronology is based on 20 radiocarbon dates and on the varve counted section (black line) in the upper part.
Migowski et. al. 2004
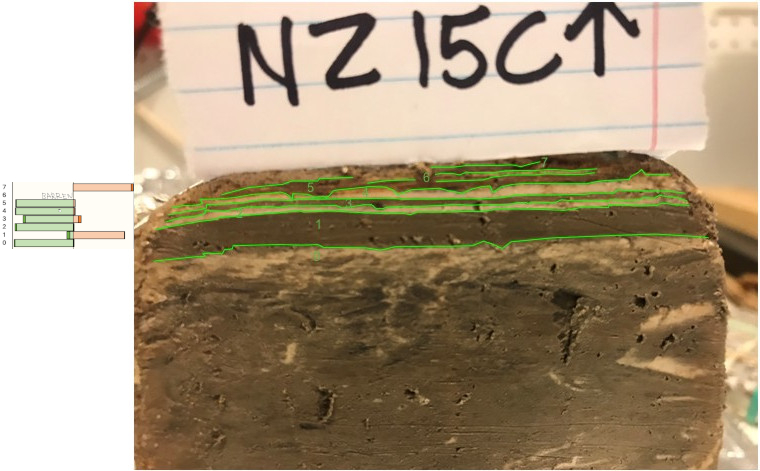
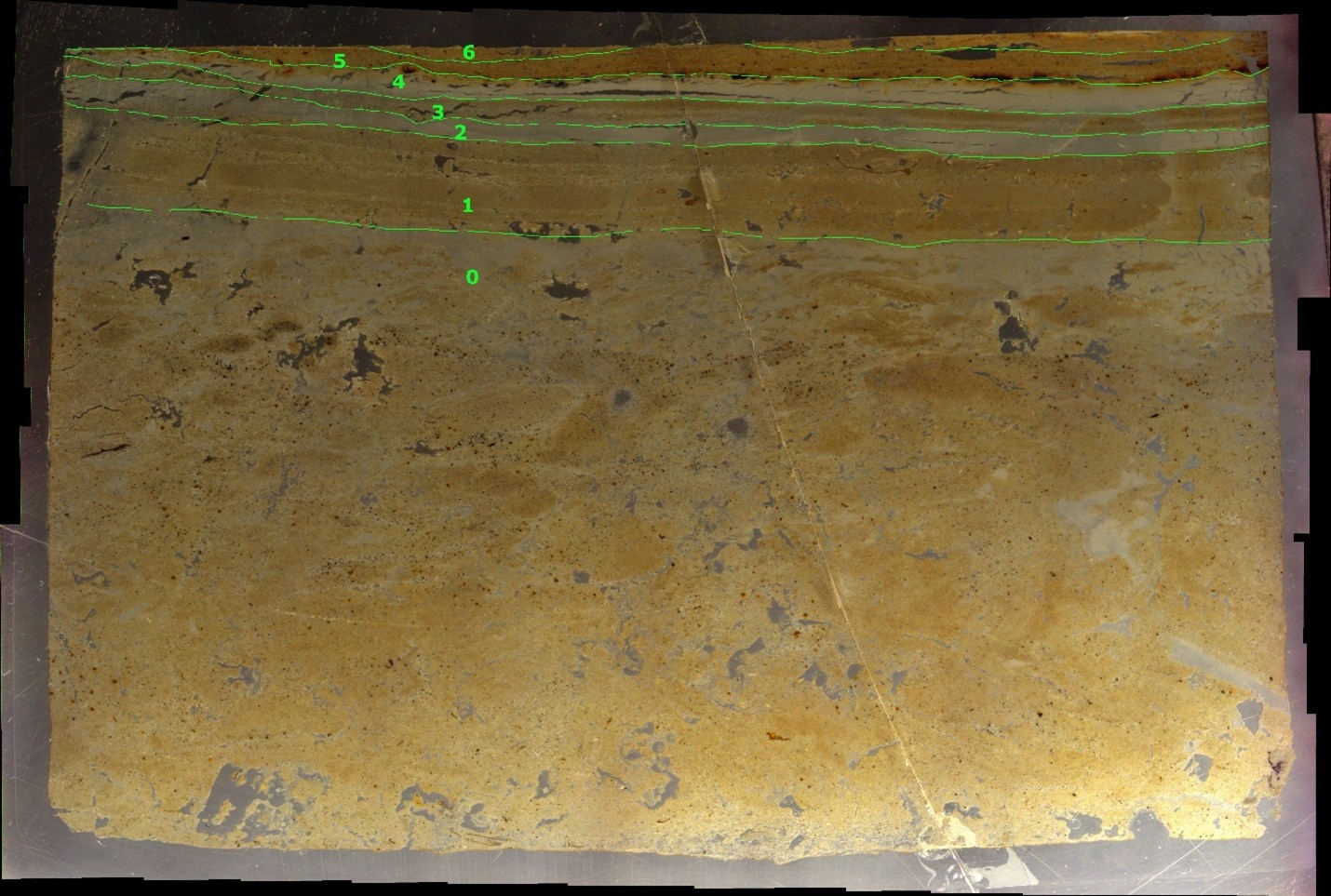
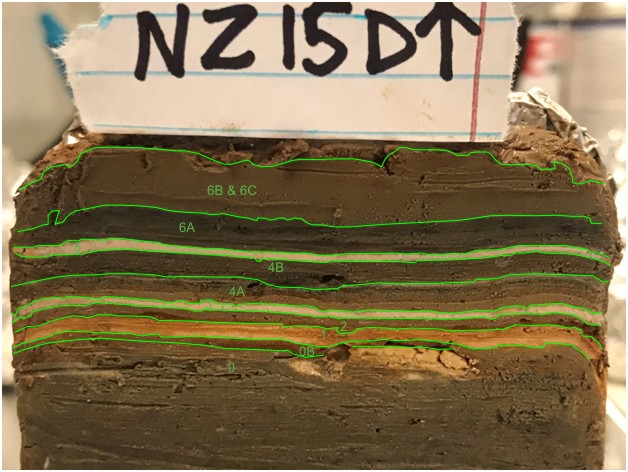
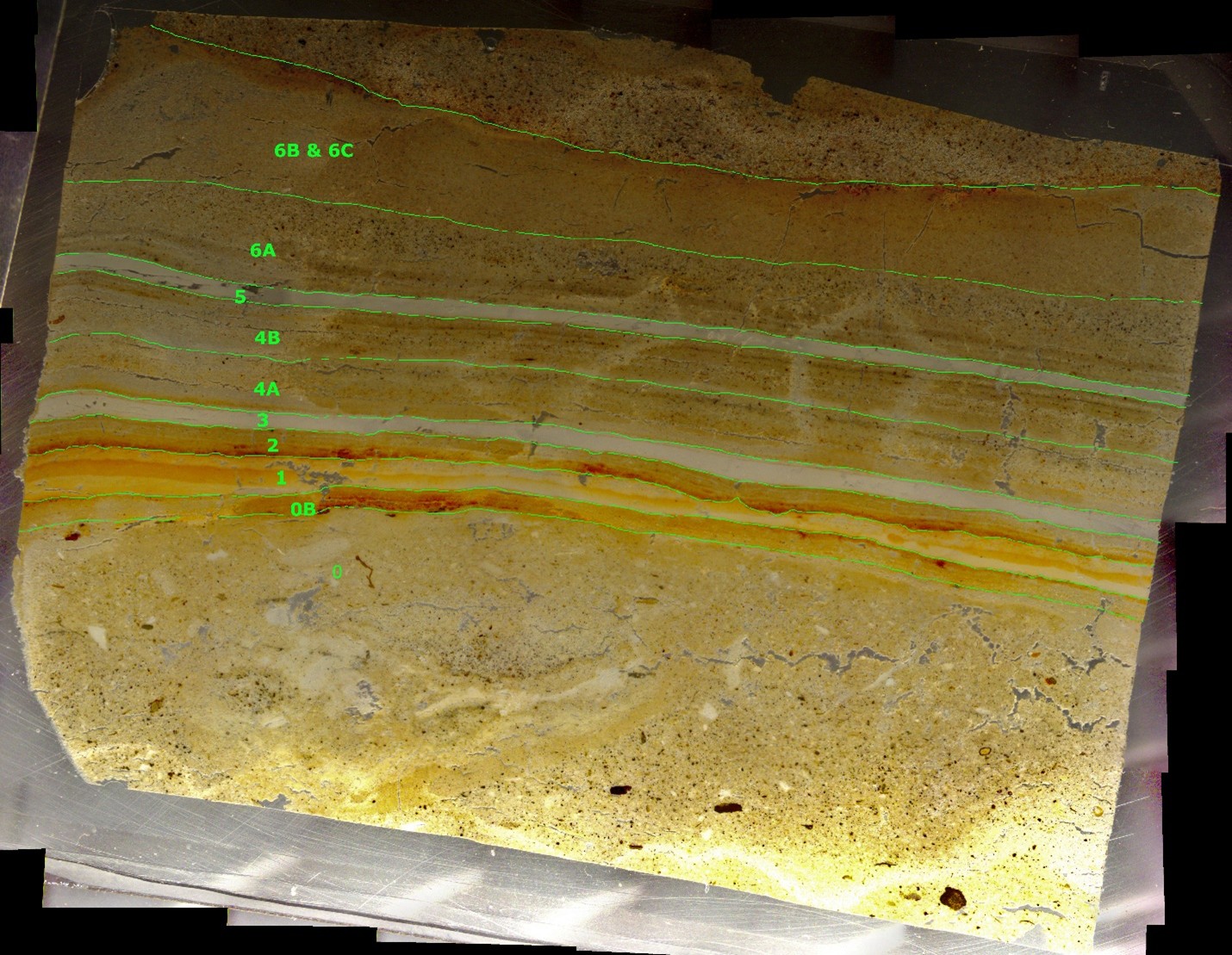
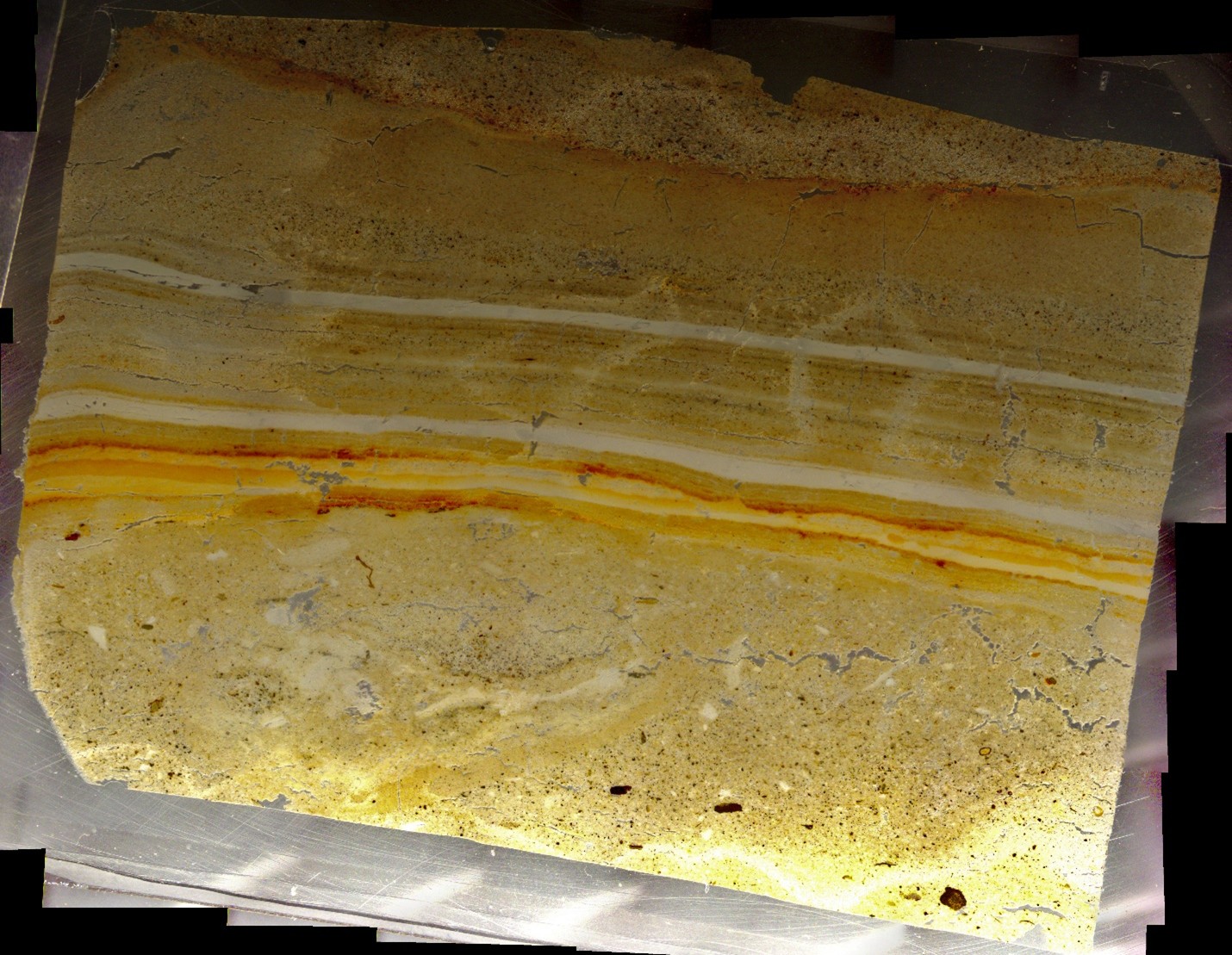
The GFZ/GSI core at Nahal Ze'elim was taken in 1997. Thin Section Slides do not currently have depths logged relative to surface but were created to examine the Jerusalem Quake and the Josephus Quake so
that should provide an approximate depth.
Depths for thin sections is what was written on photo blocks and does not correspond to core depths but likely depth in an individual core section. Depths are measured from bottom to top
(i.e. downhole to uphole) so slide 1 is at the bottom and slide 4 is at the top. Top direction of all slides and images has been confirmed. Slides and images are oriented so the uphole
direction is pointing up. Core Inventory for 1997 GFZ/GSI cores can be found
here
| Image | Description | Image | Description | Image | Description | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

 Thin Section Slide 1
Thin Section Slide 1Flatbed Scan |
Thin Section Slide 1 0-11 |

 Thin Section Slide 2
Thin Section Slide 2Flatbed Scan |
Thin Section Slide 2 9-20 |

 Thin Section Slide 3
Thin Section Slide 3Flatbed Scan |
Thin Section Slide 3 18-29 |

 Thin Section Slide 4
Thin Section Slide 4Flatbed Scan |
Thin Section Slide 4 26.5-37.5 |

 Resin Block for Thin Section Slides 1-4
Resin Block for Thin Section Slides 1-4
|
Resin Block Slides 1-4 |

 Thin Section Slides 1-4 overlapped
Thin Section Slides 1-4 overlapped
|
Thin Section Slides 1-4 Overlapped |
| Description | Flight Date | Pilot | Processing | Downloadable Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZA-4 | 3 Feb. 2023 | Jefferson Williams | ODM - no GCPs | Right Click to download. Then unzip |
| ZA-2 and ZA-3 | 10 Feb. 2023 | Jefferson Williams | ODM - no GCPs | Right Click to download. Then unzip |
| Description | Scan Date | Scanner | Processing | Downloadable Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZA-4 Lateral tracing of Amos Quakes |
12 March 2023 | Jefferson Williams | Photogrammetry | Right Click to download |
| ZA-3 Amos Quakes |
12 March 2023 | Jefferson Williams | Photogrammetry | Right Click to download |
Agnon, A., et al. (2006). "Intraclast breccias in laminated sequences reviewed: Recorders of paleo-earthquakes." Geological Society of America Special Papers 401: 195-214.
Kagan, E., et al. (2011). "Intrabasin paleoearthquake and quiescence correlation of the late Holocene Dead Sea." Journal of Geophysical Research 116(B4): B04311.
Kagan, E., et al. (2011). "Correction to “Intrabasin paleoearthquake and quiescence correlation of the late Holocene Dead Sea”." Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 116(B11): B11305.
Kagan, E. J. (2011). Multi Site Quaternary Paleoseismology Along the Dead Sea Rift: Independent Recording by Lake and Cave Sediments, PhD. Diss. Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
Kagan, E. J., et al. (2015). "Dead Sea Levels during the Bronze and Iron Ages." Radiocarbon 57(2).
Ken-Tor, R., Agnon, A., Enzel, Y., and Stein, M. (2001a). "High Resolution Geological Record of Historic Earthquakes in the Dead Sea Basin." Journal of Geophysical Research 106(B2): 2221-2234.
Ken-Tor, R., Stein, M., Enzel, Y. Agnon, A., Marco, S., and Negendank, J. (2001b). "Precision of Calibrated Radiocarbon Ages of Historic Earthquakes in the Dead Sea Basin." Radiocarbon 43(3): 1371-1382.
Langgut, D., & Finkelstein, I. (2023). Paleo-environment of the Southern Levant during the Bronze and Iron Ages: The Pollen Evidence.
in From Nomadism to Monarchy?: Revisiting the Early Iron Age Southern Levant. O. L. I. Koch, & O. Sergi. Tel Aviv, The Institute of Archaeology, Tel Aviv University: 7-27.
López-Merino, L., et al. (2016). "Using palynology to re-assess the Dead Sea laminated sediments – Indeed varves?" Quaternary Science Reviews 140: 49-66.
Williams, J. B., et al. (2011). "An early first-century earthquake in the Dead Sea." International Geology Review 54(10): 1219-1228.
Williams, J. B. (2004). Estimation of earthquake source parameters from soft sediment deformation layers present in Dead Sea muds. Msc. Thesis,
California State University - Long Beach. M.S. Civil Engineering.
Bookman, R., et al. (2004). "Late Holocene lake levels of the Dead Sea." Geological Society of America Bulletin 116(5-6): 555-571.
Kagan, E. J., et al. (2015). "Dead Sea Levels during the Bronze and Iron Ages." Radiocarbon 57(2).
Langgut, D., et al. (2014). "Dead Sea pollen record and history of human activity in the Judean Highlands
(Israel) from the Intermediate Bronze into the Iron Ages (~2500–500 BCE)." Palynology: 1-23.
Neugebauer, I. (2015). Reconstructing climate from the Dead Sea sediment record using high-resolution micro-facies analyses, Universität Potsdam. PhD.
Neugebauer, I., et al. (2015). "Evidences for centennial dry periods at ~3300 and ~2800 cal. yr BP from micro-facies analyses of the Dead Sea sediments." The Holocene.
Jodell Onstott (personal correspondence, 2023) notes that
My dating is c. 1206. ... I associate the famine in Judges 6, Ruth, and the Hittites/Ramesses as the same event. The language in Egyptian texts is almost identical to Judges.
- Chapter 6
- from sefaria.org
-
Jodell Onstott (personal correspondence, 2023) relates the following:
My treatment of Judges 6 understands the Midianites to have invaded due to famine. They specifically targeted agricultural products (6:3-4). Also telling is that the Midianites were immigrating, which I attribute to famine (v. 5). It also seems that Israel moved its grain stores to caves and other hidden places (v. 2). Israel being delivered into Midian’s hand for 7 years parallels the famine under Joseph1 and could be the duration of the Hittite and Ruth famine as well.
FootnotesJodell Onstott (personal correspondence, 2023) clarified the famine under Joseph as follows:
That famine occurred c. 1750 [BCE]. It is retold in Genesis 41. It specifically affected Egypt and Canaan (the reason Jacob migrated). ..and the reason the Hyksos/Asiatics migrated as well.
- Ruth 1:1 -
In the days when the chieftains ruled, there was a famine in the land ...
- from sefaria.org
Title : Messy and wholly incomplete excerpt from Jodell Onstott's forthcoming book on Chronology
See Chart 11.5 on p. 570 of YHWH Exists vol. 1 for dating Merneptah.
I am not sure on my dating, below. It will fall between 1240-1210. It has been a few years since I’ve worked on this project. I do have some of the sources you recommend incorporated, below.
Jodell
Climate, Geology, and Chronology
The chronology supporting a 16th century Exodus-Conquest date is also supported by climate studies.
Scripture records three major famines within the land of Canaan. The first during Abraham's days
(Gen 12:10, 26:1), which a contextual approach places c. 2190. In one study, a group of scholars
led by Yale University's H. Wiess, have argued that a "markedly dry event" occurred in this
area c. 2300-2200 BCE. Another team led by Neil Roberts focus on the eastern Mediterranean
and lowered the date to 2250-2300. What both studies confirm is that a drying period
occurred in the surrounding Mediterranean territories during the same time that a
16th century Exodus allows. The second significant famine mentioned in Scripture
occurs when Joseph is vizier in Egypt (). This event, according to a contextual
reconstruction, dates to c. 1980 BCE. In another study Dafna Langgut, Israel Finkelstein, and
Thomas Litt found pollen samples during this era indicate that this dry period continued
from around 2000 BCE until about 1800 BCE in Canaan. This again supports the a 16th-century
Exodus chronology. As the Middle Bronze Age passes into the Late Bronze Age, vegetation
such as olive tree production, moisture and humidity continue to increase and reach their
greatest fertility c. 1350 BCE. The authors observe that the "settlement crisis"
during this period was "man-induced rather than a result of environmental change."
This evidence accurately reflects the chronological model of a 16th century Exodus
date where the judge Ehud's campaigns and the Hapiru's assaults on Canaan's villages
are contemporary with the Amarna Tablets. The authors cite the Amarna tablets and note
that no famines or droughts are mentioned in the hundreds of correspondences between
Canaan and Egypt. Thus, the disruption of settlement, according to a 16th-century
Exodus model is due to Israel's ongoing Conquest campaigns, not climate.
In the above mentioned climate study in which Finkelstein participated, the most striking feature of any point in
Holocene history was the dry period that occurred between 1250-1100 BCE. Eric Cline has argued that this vast
famine caused a collapse of the entire civilization. From northern Turkey to the Nile Delta, society fell
prey to the ravages of famine. The Hittites vanish. ?????
During the reign of Merneptah, famine ravaged the Levant. The Hittites invoked their treaty with Egypt and
Merneptah's records record that he shipped grain "to keep alive the land of Hatti." This famine provoked the
Midianites and Amalekites raids on Israel's southern farmlands as recorded in the book of Judges.
The chronology that I have reconstructed based on the contextual approach, places the Midian and
Amalekite raids between 1234-1227 BCE. It is quite likely that famine had begun at least two to
seven years before the tribes began to raid Judah and only after food stores had been exhausted.
Thus, the context within the book of Judges places this famine beginning around 1240 BCE.
This chronology is supported by archaeological studies on the climate in the Levant c. 1250 BCE.
Core soil samples drilled from the Sea of Galilee demonstrate famine of epic proportions from 1250-1100 BCE,
at the end of the Late Bronze Age. In a recent article, Dafna Langgut, Israel Finkelstein, and Thomas Litt
found pollen samples during this era indicated the driest event throughout the Bronze and Iron Ages.
Archaeology indicates that the crisis in the eastern Mediterranean at the end of the Late Bronze Age
took place during the same period—from the mid-13th century to ca. 100 BCE. In the Levant the crisis years
are represented by destruction of a large number of urban centers, shrinkage of other major sites,
hording activities and changes in settlement patterns. Textual evidence from several places in the
Ancient Near East attests to drought and famine starting in the mid-13th and continuing until the
second half of the 12th century.
The Amalekite raids are not the only evidence in Scripture for this famine. In the book of Ruth,
Elimelech emigrated from Judah to Moab due to this same famine.
Cline, E. H. (2021). 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed: Revised and Updated. United States: Princeton University Press. -
can be borrowed with a free account from archive.org
Cline, E. H. (2021). 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed: Revised and Updated. United States: Princeton University Press. -
at JSTOR
Knapp, A.B. & Manning, S.W. (2016). Crisis in Context: The End of the Late Bronze Age in
the Eastern Mediterranean. American Journal of Archaeology, 120(1), 99–149. -
open access