Bet Zeyda

Tying the offsets to event ages. The events that were recognized by Wechsler et al. (2014) are represented by their age probability density functions (pdfs) as generated by Oxcal, and color coded by channel. For each event, an associated offset is attached. Colored boxes at the top represent the age extent of each channel's sediments. Historically known earthquakes are marked by grey lines. There is an age uncertainty as to the age of the oldest units in channel 4 (units 490–499) marked by a dashed rectangle. Inset – the result of the CVt calculation for the earthquake ages.
JW: Shape of events at 1202 and 1759 on this plot understate uncertainty and present unrealistic probability distributions - because these two events came from older work where such a probability density vs. time plot wasn't generated. Event E.H. 1 dates to between 1020 and 1280 CE and very likely reflects the 1202 CE earthquake. Event E.H.2 struck after 1415 CE but it is not known how long after. It could have been a result of a number of different earthquakes such as the 1546, 1759, and 1837 earthquakes. Marco et al (2005) favored the 1759 CE earthquake but considered the possibility of other earthquakes.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
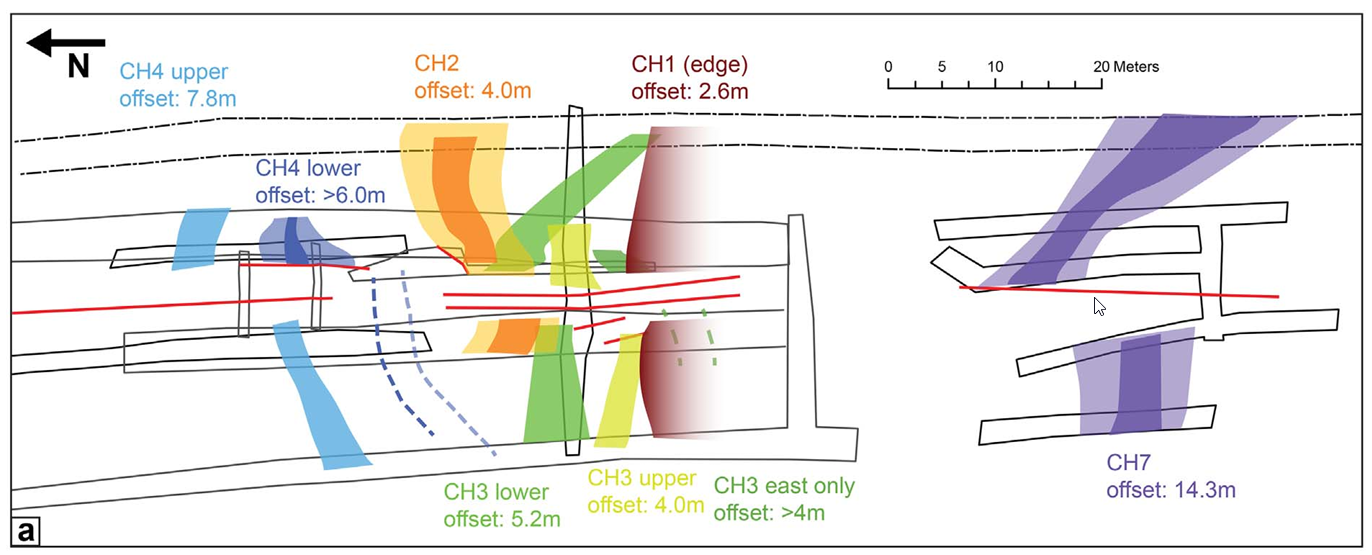
Figure 8a
Generalized map of the channels and their associated offsets
Wechsler at al. (2018)
Results are based on a 3D paleoseismic study conducted over multiple years, utilizing multiple trenches, and performed by multiple researchers at Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha) just north of the Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret). Trenches were dug to examine paleo-channels which intersect and were offset by the active Jordan Gorge Fault. Initial work was done by Marco et al (2005). At Marco et al (2005)'s northern site, they identified two fault ruptures which exhibited a similar temporal pattern to two fault ruptures at the Tel Ateret archaeoseismic site ~12 km. to the north. In their radiocarbon derived age-depth model for Bet Zayda, Event E.H. 1 was tightly dated (1020 - 1280 CE) and likely was caused by the 1202 CE earthquake. Event E.H. 2 was not tightly dated. It struck sometime after 1415 CE. Marco et al (2005) suggested that one of the Baalbek Quakes of 1759 CE was responsible for E.H. 2, but they considered other possibilities such as the 1546 CE and 1837 CE earthquakes. Information from Marco et al (2005)'s work is summarized below:
| Event | Date Range | Quake assignment | Displacement (m) | Estimated Magnitude | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E.H. 1 | 1020-1280 CE | 1202 CE | ~2.2 | 7.1 - 7.3 | Sinistral Slip |
| E.H. 2 | after 1415 CE | 1759 CE | 0.5 | 6.6 - 6.9 | Sinistral Slip |
Wechsler et al (2018) extended and refined previous work of Wechsler at al. (2014). They used Petrel software to create a 3D model of the displaced channels and make estimates of offset for a number of seismic events. This, in turn, allows one to make Magnitude Estimates. The Bet Zayda Master Seismic Events Table has offset and Moment Magnitude estimates on the Summary tab. Wechsler et al (2018) also added a new seismic event (CH2-E1) which appears to capture one of the mid 8th century CE earthquakes.
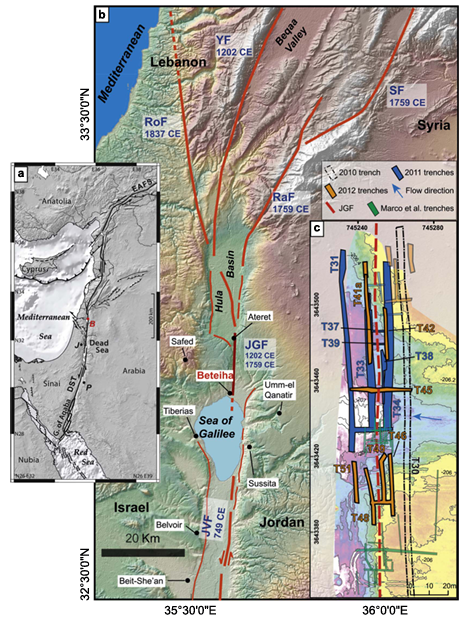
- Plate tectonic settings of the Middle East, with major faults.
- EAFS– East Anatolia Fault
- DST– Dead Sea Transform
- J– Jerusalem
- K– Kerak
- P– Petra
- B– Beteiha trench site
- Location of major and minor faults of the DST in the vicinity of Hula basin and the Sea of Galilee.
- JGF, Jordan Gorge fault
- JVF, Jordan Valley fault
- RaF, Rachaya fault
- RoF, Roum fault
- SF, Serghaya fault
- YF, Yammouneh fault
- Map of the Beteiha paleoseismic site with outlines of all trenches dug during the 3-year campaign, and the approximate location (based on air photos) of the trenches of Marco et al. (2005). The trenches discussed in this paper are highlighted and labeled. Topography model was obtained using TLS (Terrestrial Laser Scanner) prior to 2nd year trenching, courtesy of O. Katz from the Geological Survey of Israel. The contour lines represent elevation b.m.s.l.
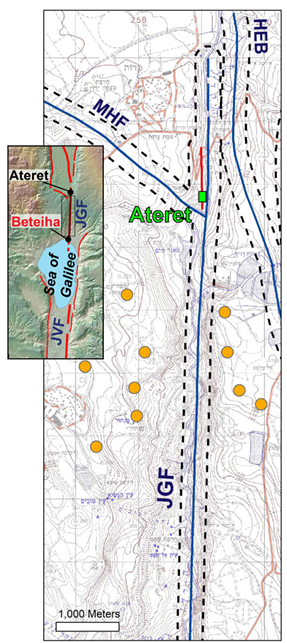
An excerpt from the Israel's active fault map (Sagy et al., 2016) along the JGF. Active faults are marked in red, suspected active in blue. Orange circles mark the near field stations of the GPS campaign measurements locations (Hamiel et al., 2016). The Ateret crusader castle (green rectangle) is situated on top of a branch of the JGF (marked red), parallel to the main fault and north of a branching point with MHF, while the GPS array of Hamiel et al. (2016) crosses the JGF south of the branching point. The Beteiha paleoseismic site is ~4 km south of the map's lower edge. Inset– location map, black rectangle marks the extent of the excerpt from the active faults map. MHF– Mishmar Hayarden fault (normal/ss). HEB– Hula Eastern border fault (normal).
Wechsler at al. (2018)
- Bet Zeyda Trenches Area in Google Earth
- Bet Zeyda Trenches Area on govmap.gov.il
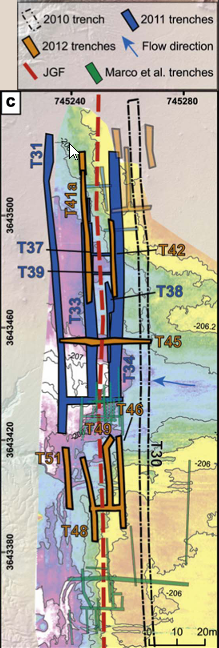
Figure 1c
Map of the Beteiha paleoseismic site with outlines of all trenches dug during the 3-year campaign, and the approximate location (based on air photos) of the trenches of Marco et al. (2005). The trenches discussed in this paper are highlighted and labeled.
Topography model was obtained using TLS (Terrestrial Laser Scanner) prior to 2nd year trenching, courtesy of O. Katz from the Geological Survey of Israel. The contour lines represent elevation b.m.s.l.
Wechsler at al. (2018)

General settings of the Beteiha (aka Bet Zayda) site.
(a) An air photo of the field where the trenches were excavated, with the Jordan River, the main fault, and the local drainage demarcated. The channel flowing west through the trench site (double thin-dashed line) is abandoned and the field is now drained by the marked artificial canal (short thick-dashed line).
(b) A photo of the trench site at the beginning of the first-trenching campaign, looking north toward the Jordan Gorge. A white car stands next to T30. A vegetation lineament associated with the fault is visible at the front.
(c) The trench site with outlines for all trenches dug during our campaign, as well as the location of Marco et al. (2005) trenches. The trenches discussed in this paper are highlighted and labeled. The modern channel margins are marked by a dashed line. The topography model was obtained using a terrestrial laser scanner prior to second-year trenching, courtesy of O. Katz from the Geological Survey of Israel. The contour lines represent variations in elevation.
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Figure 3
Partial trench logs for T45 (north and south walls), focusing on the fault zone. Inset: Location map of trenches and channels mentioned in the paper. The outline of the channels is drawn schematically, based on this study and previous results (Marco et al., 2005; Wechsler et al., 2013). The legend applies to Figures 6–8 as well.
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Figure 6
Trench logs for T37 (north and south walls). Event horizons are marked with dashed lines and faults in gray. The inset map and legend are the same as Figure 3.
Wechsler at al. (2014)
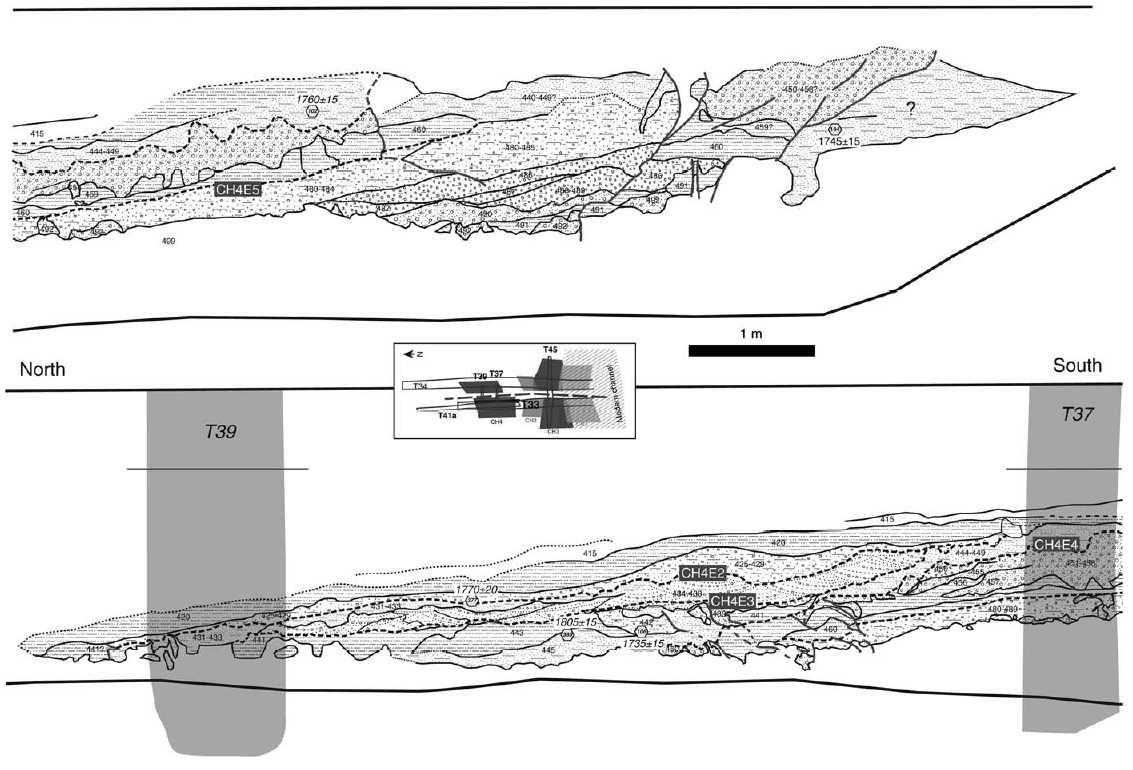
Figure 7
Trench logs for T33 (east wall), where channel 4 is exposed. Event horizons are marked with dashed lines and faults in gray. The intersections with T37 and T39 are marked. Ages in italic denote proxy locations (same unit, different exposure) from another exposure of the same wall (see Fig. S1c available in the electronic supplement). The inset map and legend are the same as Figure 3.
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Figure 8
Trench logs for T39 (north and south walls). Event horizons are marked with dashed lines and faults in gray. The sample at the bottom of T39N is in a proxy location from a lower unit of channel 6, below the channel 4 deposits (see Fig. S1c available in the electronic supplement). The inset map and legend are same as in Figure 3.
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Figure 2
A simplified log of the parts of the west wall of T30 where channels cut into the massive clay. Channels are marked by their corresponding numbers in the text. The legend is the same as in Wechsler et al. (2014). Channel 4 was not exposed in T30. Inset on lower left – an example partial photolog of T37S, where the coarse sediments of channel 4 can be seen in fault contact. Faults are marked in red, event horizons in orange (full log was published in Wechsler et al., 2014).
Wechsler at al. (2018)
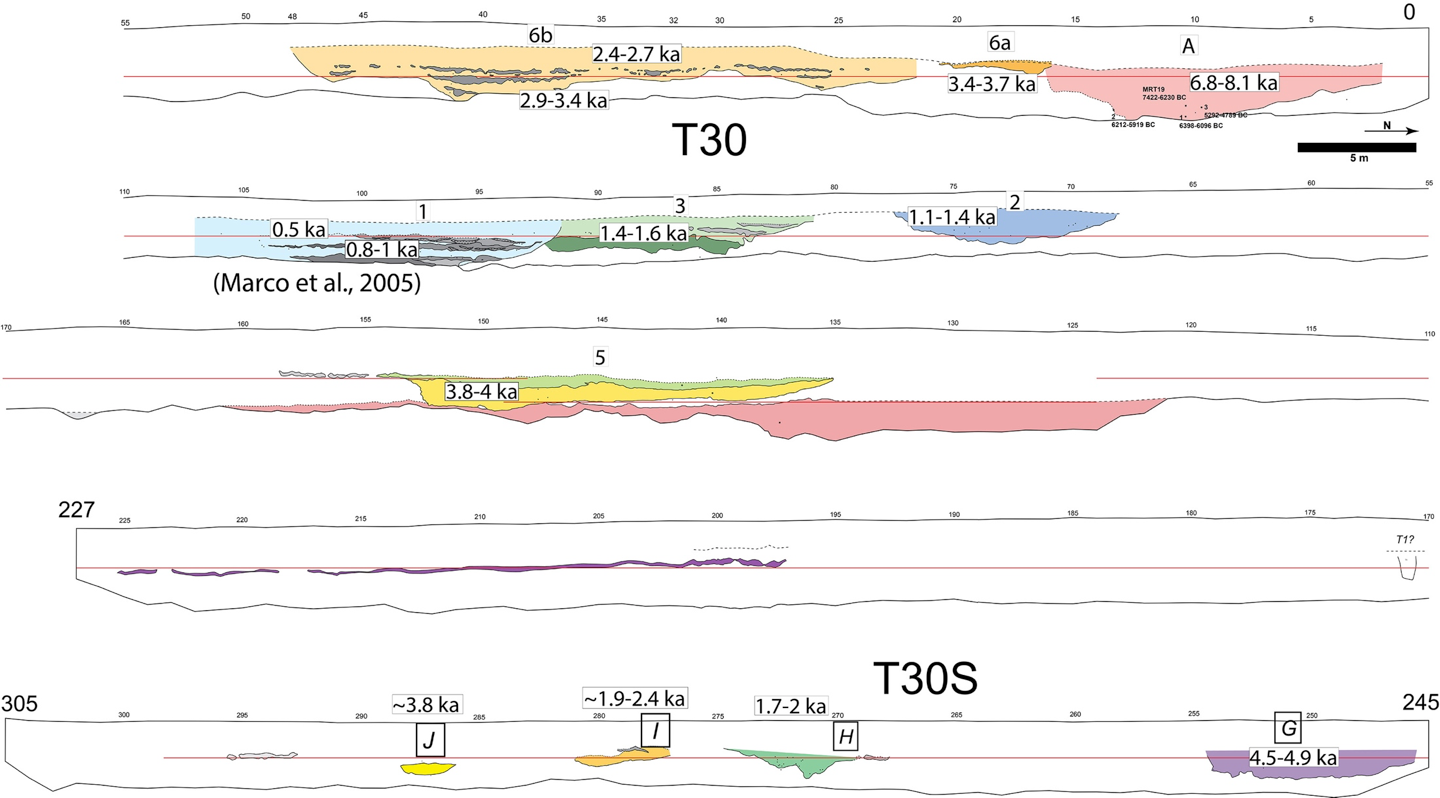
T30 Trench Log
Unpublished Image - courtesy of from Tom Rockwell (email 30 March 2022)
 Figure S1
Figure S1High resolution photomosaic logs of trench walls. 14C sample dates in the log are not calibrated (years BP). For trench locations, see Figure 2c in the main article. Units are numbered and their descriptions appear in Table S1 of the supplementary material:
- north wall of T45
- south wall of T45
- east wall of T41a, which is a deeper re-exposure of T33
- north wall of T37
- south wall of T37
- east wall of T33 where channel 3 is exposed
- north wall of T39
- south wall of T39
- east wall of T34, where channels 2 and 3 are exposed.
Click on image to open a high resolution magnifiable image in a new tab
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Tying the offsets to event ages. The events that were recognized by Wechsler et al. (2014) are represented by their age probability density functions (pdfs) as generated by Oxcal, and color coded by channel. For each event, an associated offset is attached. Colored boxes at the top represent the age extent of each channel's sediments. Historically known earthquakes are marked by grey lines. There is an age uncertainty as to the age of the oldest units in channel 4 (units 490–499) marked by a dashed rectangle. Inset – the result of the CVt calculation for the earthquake ages.
JW: Shape of events at 1202 and 1759 on this plot understate uncertainty and present unrealistic probability distributions - because these two events came from older work where such a probability density vs. time plot wasn't generated. Event E.H. 1 dates to between 1020 and 1280 CE and very likely reflects the 1202 CE earthquake. Event E.H.2 struck after 1415 CE but it is not known how long after. It could have been a result of a number of different earthquakes such as the 1546, 1759, and 1837 earthquakes. Marco et al (2005) favored the 1759 CE earthquake but considered the possibility of other earthquakes.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
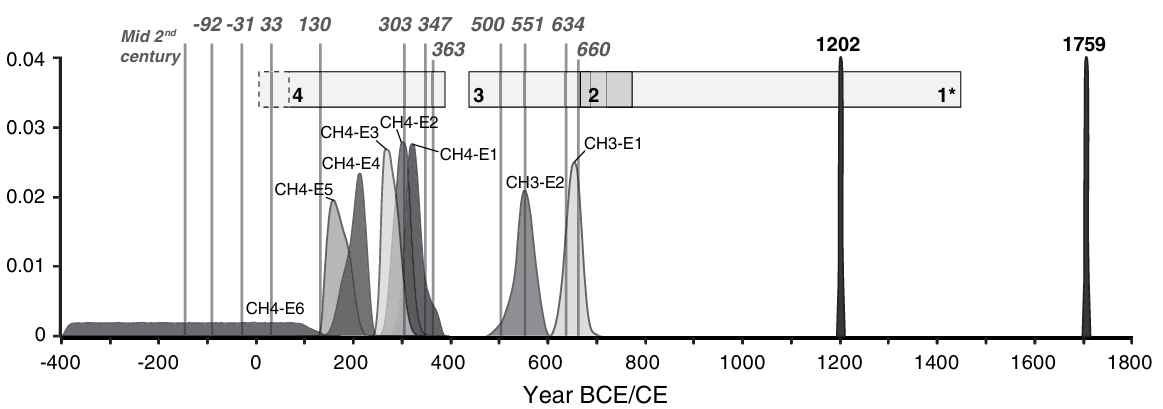
Probability density functions for all paleoseismic events, based on the OxCal modeling. Historically known earthquakes are marked by gray lines. The age extent of each channel is marked by rectangles. There is an age uncertainty as to the age of the oldest units in channel 4 (units 490–499) marked by a dashed rectangle. Channel 1 refers to the channel complex studied by Marco et al. (2005).
JW: Shape of events at 1202 and 1759 on this plot understate uncertainty and present unrealistic probability distributions - because these two events came from older work where such a probability density vs. time plot wasn't generated. Event E.H. 1 dates to between 1020 and 1280 CE and very likely reflects the 1202 CE earthquake. Event E.H.2 struck after 1415 CE but it is not known how long after. It could have been a result of a number of different earthquakes such as the 1546, 1759, and 1837 earthquakes. Marco et al (2005) favored the 1759 CE earthquake but considered the possibility of other earthquakes.
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Figure 4
the revised OxCal model for channels 2 and 3. Changes relative to Wechsler et al (2014) are marked in red
Wechsler at al. (2018)

Figure 4
the revised OxCal model for channels 2 and 3. Changes relative to Wechsler et al (2014) are marked in red
Wechsler at al. (2018)

Figure 5
An OxCal model of the overall stratigraphy of the channel complex using OxCal 4.1 (Bronk-Ramsey, 2009). We use the Marco et al. (2005) ages as an upper bound for our model, and a sample obtained from below channel 4 as a lower bound.
Wechsler at al. (2014)

Figure 5
An OxCal model of the overall stratigraphy of the channel complex using OxCal 4.1 (Bronk-Ramsey, 2009). We use the Marco et al. (2005) ages as an upper bound for our model, and a sample obtained from below channel 4 as a lower bound.
Wechsler at al. (2014)
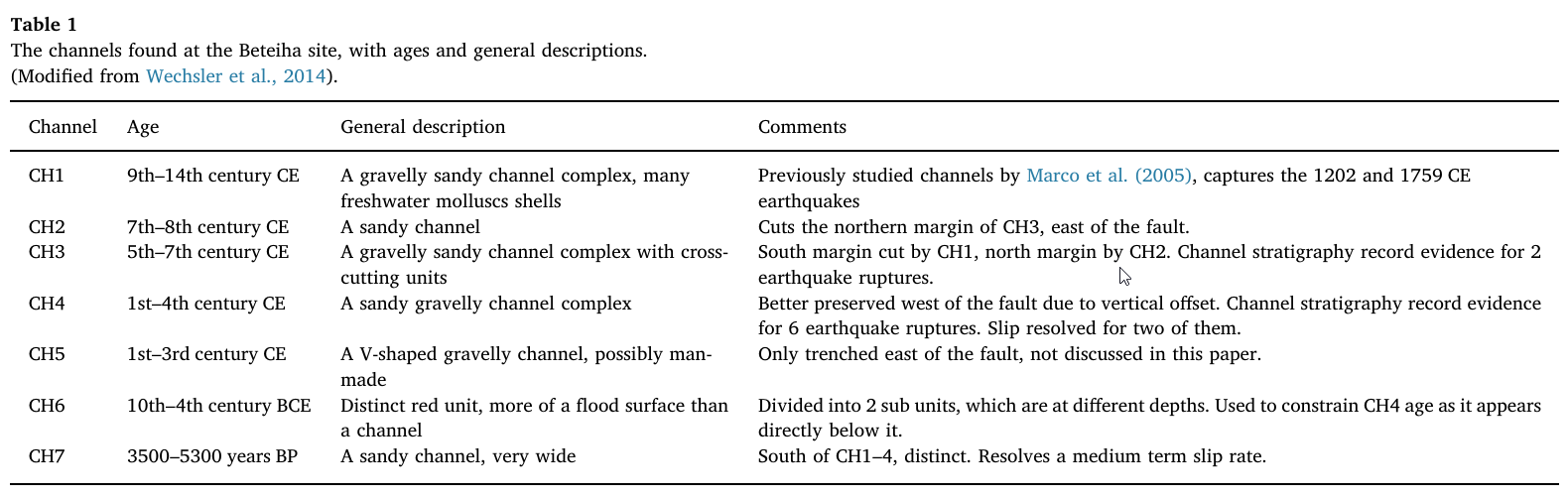
Table 1
The channels found at the Beteiha site, with ages and general descriptions. (Modified from Wechsler et al., 2014).
Wechsler at al. (2018)
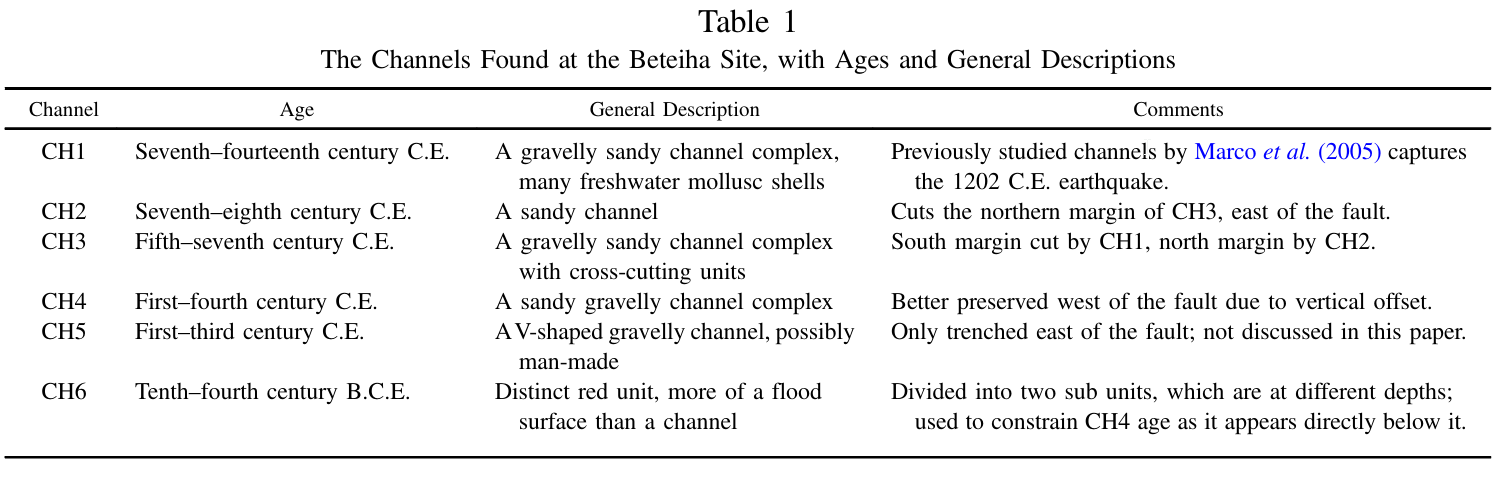
Table 1
The Channels Found at the Beteiha Site, with Ages and General Descriptions
Wechsler at al. (2014)
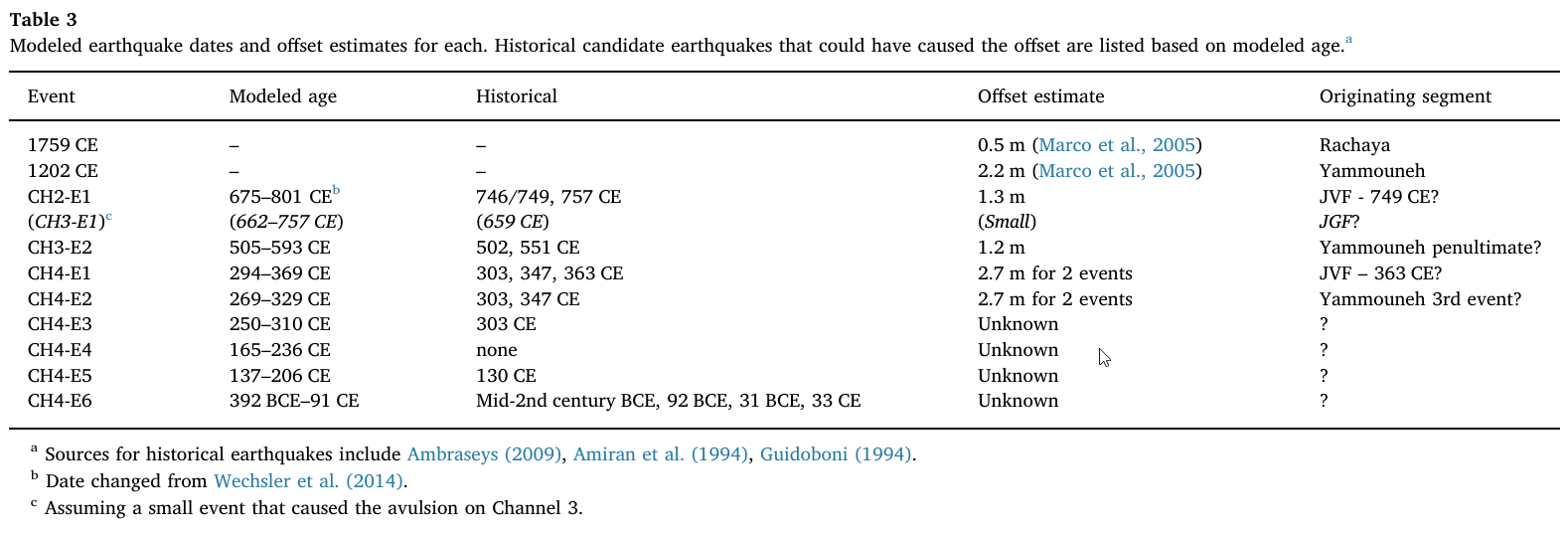
Table 3
Modeled earthquake dates and offset estimates for each. Historical candidate earthquakes that could have caused the offset are listed based on modeled age.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
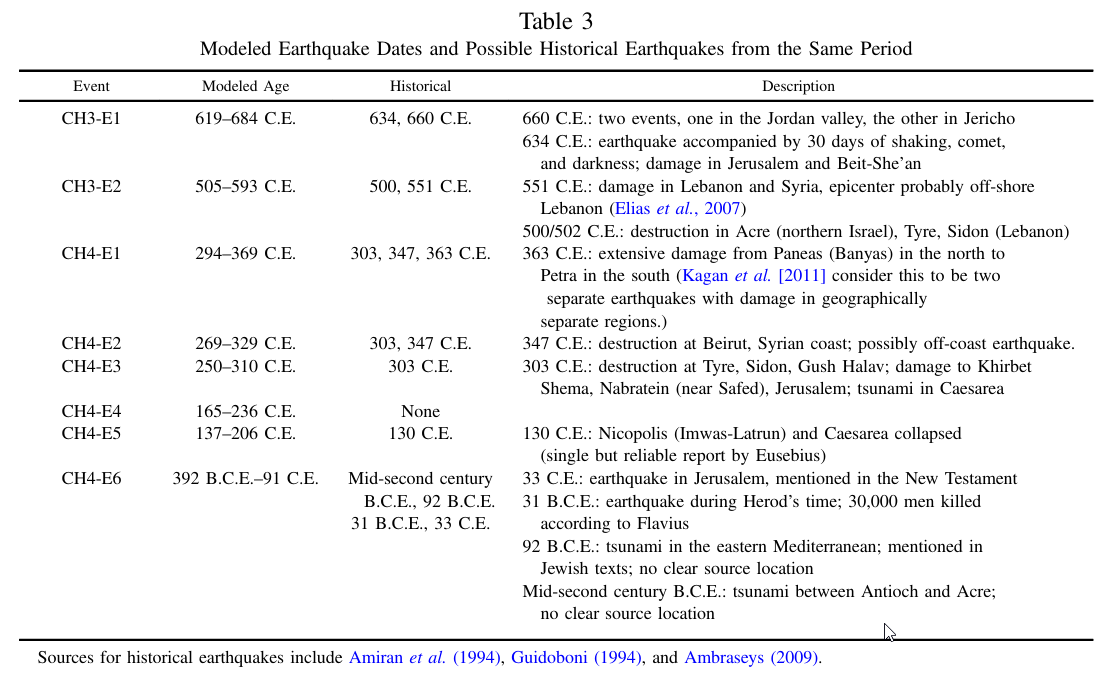
Table 3
Modeled Earthquake Dates and Possible Historical Earthquakes from the Same Period
Wechsler at al. (2014)
| Unit Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 301 | clay with carbonates, brown |
| 305 | sandy clay, yellow |
| 308 | sand |
| 310 | pebbly sand |
| 320 | cross bedded sand and sandy gravel |
| 322 | sandy gravel |
| 323 | sand |
| 324 | cross-bedded sandy gravel with manganese staining |
| 324 | clayey sand |
| 325 | well sorted sand, sometimes with foresets |
| 326 | sand, cross bedding |
| 328 | pebbles and cobbles |
| 328 | basalt gravels, pebbles and cobbles |
| 329 | pebbly sand with fossils |
| 329 | clayey pebbly sand + shells |
| 330 | sandy clay |
| 332 | clayey gravely sand |
| 333 | sandy clay |
| 334 | silty sand |
| 335 | clayey sand |
| 337 | sand |
| 340 | pebbly sandy clay, grey |
| 342 | clayey gravel |
| 345 | silty clay |
| 349 | clayey fine gravel |
| 350 | clayey sand |
| 355 | clayey gravel |
| 360 | clayey coarse gravel and pebbles |
| 365 | gravely sand |
| 370 | clayey gravel |
| 372 | sand |
| 373 | clayey gravel |
| 375 | clayey sandy gravel |
| 380 | clayey sand |
| 382 | clayey sandy gravel |
| 384 | clayey coarse sand |
| 385 | clayey sand |
| 387 | sandy gravely clay |
| 388 | silty clay |
| 390 | sandy gravel |
| 392 | sandy clay |
| 394 | sandy gravel |
| 395 | clayey pebbly gravel |
| 396 | pebbly sand |
| 397 | clayey gravel |
| 398 | clayey sandy gravel |
| 399 | clayey pebbly gravel |
| 400 | dark brown clay below channel deposits |
| 405 | brown clay |
| 415 | calciferous clay with shells |
| 420 | sandy clay |
| 425 | sandy gravelly clay |
| 429 | sandy gravelly clay |
| 431 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 432 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 433 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 434 | gravelly sand |
| 435 | gravelly sand |
| 436 | gravelly sand |
| 437 | gravelly sand |
| 438 | gravelly sand |
| 439 | gravelly sand |
| 440 | clayey gravel |
| 441 | silty clay |
| 442 | clayey gravel |
| 443 | sandy clay |
| 445 | clayey gravel |
| 449 | clayey gravel |
| 450 | clayey gravel |
| 452 | sandy gravel |
| 453 | sandy gravel |
| 454 | sandy gravel |
| 455 | sandy gravel |
| 456 | sandy clay |
| 457 | sandy gravel |
| 458 | sandy gravel |
| 459 | silty clay |
| 460 | sandy clay |
| 480 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 481 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 482 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 483 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 484 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 485 | clayey gravelly sand |
| 486 | clayey gravel |
| 487 | clayey gravel |
| 488 | clayey gravel |
| 489 | clayey gravel |
| 490 | gravelly sand |
| 491 | silty clay |
| 492 | gravelly sand |
| 493 | gravelly sand |
| 494 | silty clay |
| 495 | gravelly clay |
| 496 | gravelly clay |
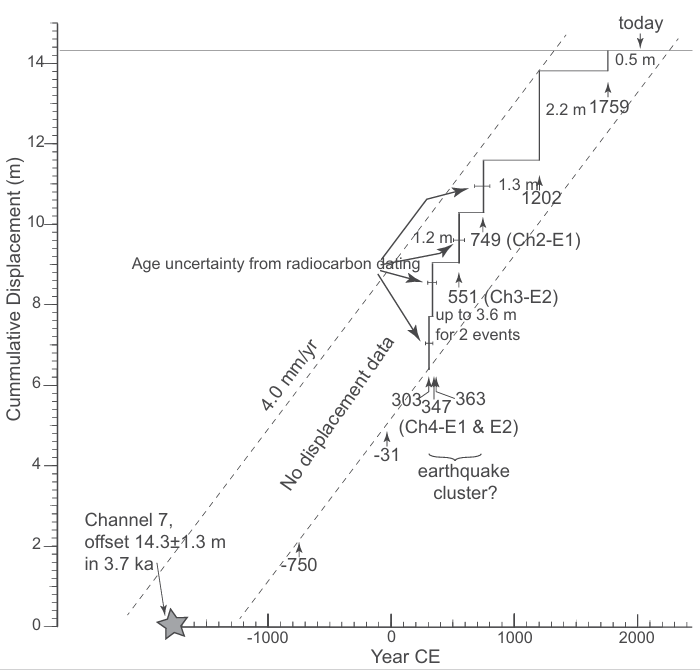
Figure 12
Cumulative displacement vs. time based on historical earthquake dates and offsets from the reconstructed channels.
Wechsler at al. (2018)

Figure 8a
Generalized map of the channels and their associated offsets
Wechsler at al. (2018)
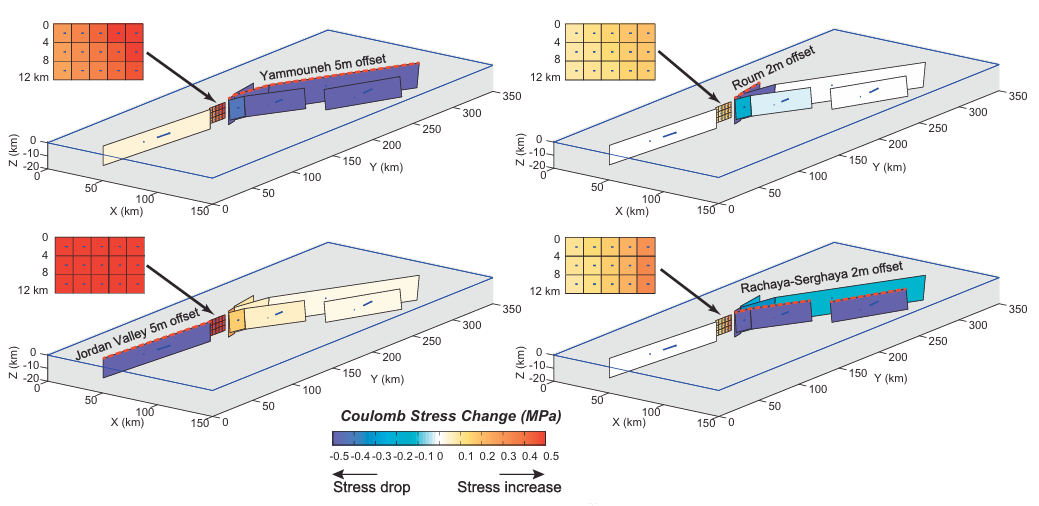
Figure 9
Coulomb Stress modeling (using Coulomb 3.3, Toda et al., 2011) of the area using a simplified fault model of the DST from the Jordan Valley segment to the Lebanese restraining bend (not including the Mt. Lebanon thrust).
In each model, an earthquake was applied on one fault (marked in dashed red line), based on rupture estimates for the last earthquake on that fault (left-lateral strike slip). The resulting Coulomb Stress change on the neighboring faults was calculated.
See Table S1 for model parameters of each run.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
- from Marco et al. (2005)
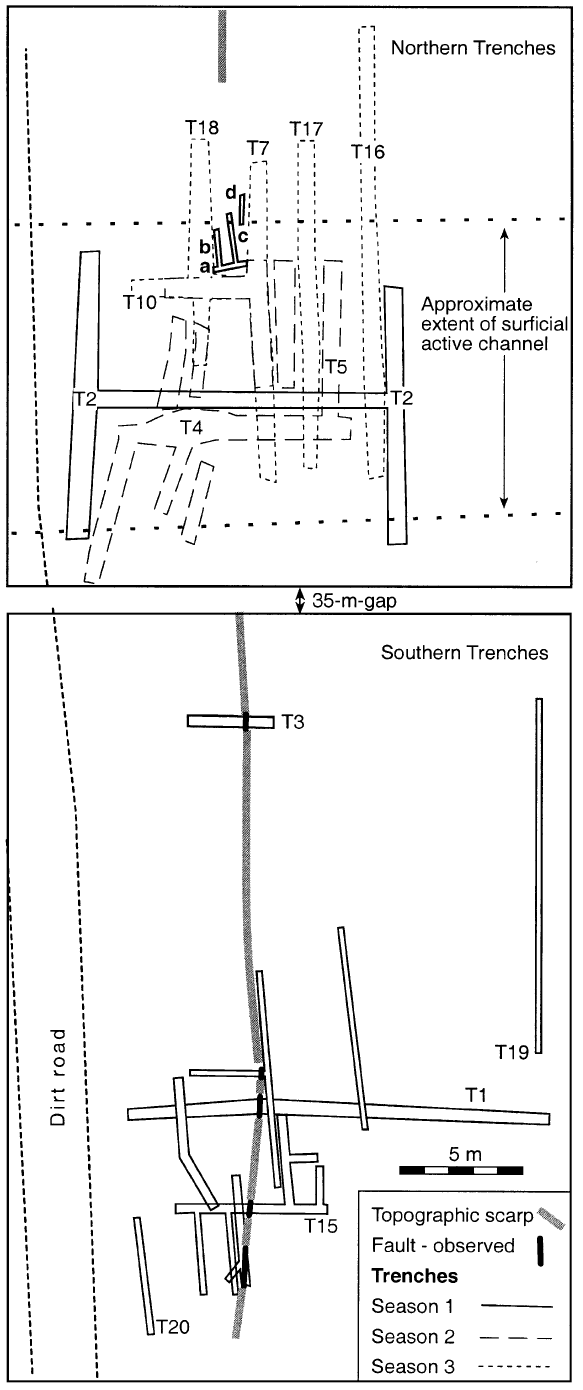
Fig. 4
Map of trench site. The site was developed over three seasons, each marked with a different line.
Marco et al (2005)
- from Marco et al. (2005)

Fig. 6
Fault-parallel trench logs of the northern group show offset stream channels. Alternating alluvium and lake deposits reflect fluctuations of water level of the Kinneret. Clay units 1 and 8 below and above the channels indicate high stands of the Kinneret whereas channel incision indicates low stand.
Marco et al (2005)
- from Marco et al. (2005)

Fig. 7
Trench logs and dated stratigraphy of Trenches T10 (top) and T4 (bottom). Solid lines mark the faults, dashed are very faint,discontinuous disturbances, which we attribute to late adjustments of the overlying strata. Two slip events are observed in T10. Based only onthe 14C dating, the first slip event (E.H. 1) postdates the 12th century and predates the 13th century. The second slip (E.H. 2) postdates the 15thcentury. Based on historical earthquake catalogues and correlation to Ateret we correlated the slip events to the earthquakes of 20 May, 1202 and30 October 1759. The trace of the 1759 slip is not clear in trench T7 because of the poorly-consolidated unit 6c. We therefore mark only E.H. 1.
Marco et al (2005)
- from Marco et al. (2005)

Fig. 8
The stratigraphy near the fault at Trench T15 of the southern group. The oldest age of bulk organic matter leached from of the alluvial sand layer is 5 kaF50 yr. The concordance of the other dates with the stratigraphy indicate their reliability. The top of the trench shows the surface expression of the fault, where the eastern side is about 0.8 m higher than the western side.
Marco et al (2005)
- from Marco et al. (2005)

Top: calibrated date distribution for samples from trenches T2, T4, and T10. Center: probability density functions for radiocarbon dates that constrain the timing of the penultimate event at the Bet-Zayda palaeoseismic site. The dates were trimmed with Bayesian statistics in OxCal,and the probability density function for the event age is calculated from the radiocarbon ages. Note that the historical 1202 earthquake falls within the probability distribution, and is in fact the only historical earthquake in the vicinity that can possibly fit the age distribution. This indicates that the detrital charcoal dated for this study was not resident in the system for an extended period of time (decades versus centuries). Bottom: calibrated date distribution for samples from trench T15. Calibration of 14C ages was done with the Bronk Ramsey’s (2002) OxCal program version 3.8 using the atmospheric data of Stuvier et al.
Marco et al (2005)
- from Marco et al. (2005)
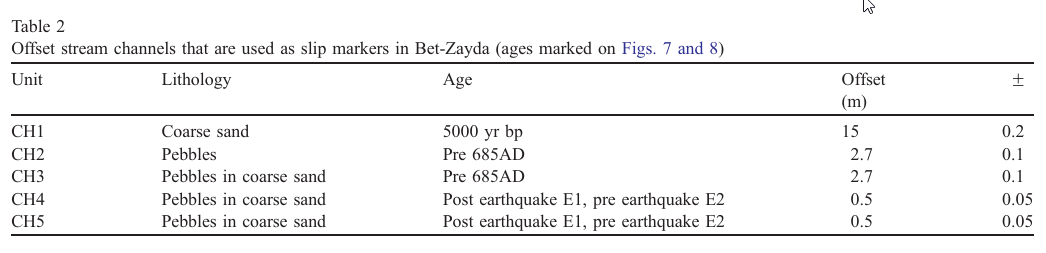
Table 2
Offset stream channels that are used as slip markers in Bet-Zayda (ages marked on Figs. 7 and 8)
Marco et al. (2005)
Wechsler et al. (2014:15) argue that the paleoseismic
investigations of
Marco et al. (2005), which documented ~2.7 m of slip in
two events (1202 CE and sometime after 1415 CE), may represent a seismic
record with a terminus post quem extending as far back as the early
11th century CE, but which Marco et al. (2005) interpreted as 685 CE.
Wechsler et al. (2018:214) further reported that the Channel 1 complex, "a group of channels that were
previously excavated and described as CH2, CH3 and CH4 by Marco et al. (2005)",
contained pieces of detrital charcoal dated from the 9th century to at least as young as the 14th century CE.
Meanwhile,
Wechsler et al. (2014:15) maintain that their investigations
produced a nearly continuous record of on-site seismic activity spanning the 1st to 8th centuries CE, except for
the first half of the 5th century CE. They also suggest the possibility
of “a missing period of deposition between the deposition of channel 1
and channel 2.”
Wechsler et al. (2018) also identified a depositional
disconformity between channels 3 and 4 that may have removed evidence for
two or three seismic events. Their offset analysis revealed ~2.7 m of
unaccounted lateral displacement between the two channels.
Finally,
Wechsler et al. (2014:15) also note that their record did not
include deposits that would have captured the
Tiberias Landslide Quake (850-854 CE).
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) identified six earthquakes in
paleo-channel 4 (CH4).
Wechsler et al. (2018:216) add that channel 4 crossed
the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is
interpreted to have produced localized uplift east of the main fault,
while subsidence to the west caused sediment thickening. Event CH4-E6 was
recorded in the basal deposits of channel 4, exposed in
Trench T37. Evidence for rupturing included the upward
termination of individual faults, folding, and angular
unconformities created by these folding events. The
presence of growth strata and possibly a colluvial wedge,
together with fissures capped by undisturbed layers,
support the interpretation of an earthquake at
this horizon.
Although
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) were unable to estimate
offset associated with this event,
Wechsler et al. (2014:13) suggested that
Event CH4-E6 was a stronger event than CH4-E5 and CH4-E4.
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) date this event from 392 BCE to 91 CE.
Wechsler et al. (2014:14) discussed dating difficulties noting that
the basal deposits of channel 4 in trench T37 lack
reliable age control which limits precise dating of
event CH4-E6. Although the Bayesian OxCal model for channels 3
and 4 provides probability distributions for events
CH4-E6 through CH4-E1, CH4-E6 remains poorly constrained
because no direct dates exist from the faulted basal
layer. They report that the only available sample predates the entire
channel 4 complex, yielding a broad probability range
of ~400 B.C.E. – ~100 C.E. Since the basal deposits are
clearly tied to channel 4 and unlikely to be much older
than its other basal layers, they suggest that the event is more plausibly
placed between the first century B.C.E. and the first
century C.E.
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) identified six earthquakes in
paleo-channel 4 (CH4).
Wechsler et al. (2018:216) add that channel 4 crossed
the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is
interpreted to have produced localized uplift east of the main fault,
while subsidence to the west caused sediment thickening.
Wechsler et al. (2014:13) report that
Event CH4-E5 was “interpreted from many small faults that
break to the top of unit 480 and are capped by units
450–469.” On the south wall of Trench T37, they observed
stratigraphic growth where strata thickened along the axis
of a small syncline in the area of maximum change in
bedding dip, noting that “these strata thin onto the fold
scarp of the pressure ridge” crossed by Channel CH4. They added that “the amount
of deformation [in CH4-E5] appears relatively minor when compared with
that in event CH4-E6,” and therefore “interpret this [CH4-E5] as a
smaller event.”
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) date this event to 137-206 CE
but were unable to estimate offset associated with this event. Dating is based
on a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages.
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) identified six earthquakes in
paleo-channel 4 (CH4).
Wechsler et al. (2018:216) add that channel 4 crossed
the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is
interpreted to have produced localized uplift east of the main fault,
while subsidence to the west caused sediment thickening.
Wechsler et al. (2014:13) identified
evidence for Event CH4-E4 in Trenches T37, T33, and at the
base of the south wall of Trench T39. On both walls of
Trench T37, several small faults ruptured “up through
units 450–469,” and were capped by “unbroken strata of
units 440–449.” Within this faulted area, a large fissure
was exposed on the south wall, while the “unbroken strata
of units 440–449” were observed to “thin and pinch out
onto the fold scarp, indicating growth of the
fold/pressure ridge after deposition of unit 450.” In
Trench T33, minor faults displaced “strata up through unit
450 and appear capped by unit 440–449.” Wechsler et al. (2014:13) concluded that
“evidence is strong for the occurrence of an event between
deposition of units 449 and 450, although the amount of
deformation appears less than that associated with event
CH4-E6.”
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) date this event to 165-236 CE
but were unable to estimate offset associated with this event. Dating is based
on a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages. Wechsler et al. (2014:14) note that
"the strata between events CH4-E3 and CH4-E4 are only dated by a single [radiocarbon] sample".
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) identified six earthquakes in
paleo-channel 4 (CH4).
Wechsler et al. (2018:216) add that channel 4 crossed
the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is
interpreted to have produced localized uplift east of the main fault,
while subsidence to the west caused sediment thickening.
Wechsler et al. (2014:13) found evidence for
Event CH4-E3 primarily in Trench T39 although evidence was also found in Trench T33.
Event CH4-E3 is associated with a number of fault strands, some of which
re-ruptured in later events. Wechsler et al. (2014:13) also interpreted thickening of some units into a
"a shallow synclinal form" as a by-product of Event CH4-E3.
Wechsler et al. (2014:13) also observed strata thinning and terminating against the fold scarp of the
pressure ridge, which was taken as further evidence of a seismic event.
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) date this event to 250-310 CE
but were unable to estimate offset associated with this event. Dating is based
on a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages.
Wechsler et al. (2014:14) note that
"the strata between events CH4-E3 and CH4-E4 are only dated by a single [radiocarbon] sample".
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) identified six earthquakes in
paleo-channel 4 (CH4).
Wechsler et al. (2018:216) add that channel 4 crossed
the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is
interpreted to have produced localized uplift east of the main fault,
while subsidence to the west caused sediment thickening.
Wechsler et al. (2014:14) report that evidence for CH4-E2 was
"weaker than that of some events", manifested by "several small faults terminating
at the top of unit 430, and capped by unit 429" and some synclinal fold growth.
They interpreted the event horizon as between unnits 429 and 430 and characterized it as
an event "that exhibits relatively minor overall deformation".
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) estimated
that Events CH4-E2 and CH4-E1 combined to produce 2.7 m of offset.
Wechsler et al. (2018:219) suggest that it is
"likely both are moderate in size, each with about 1.3 m of horizontal slip."
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) identified six earthquakes in
paleo-channel 4 (CH4).
Wechsler et al. (2018:216) add that channel 4 crossed
the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is
interpreted to have produced localized uplift east of the main fault,
while subsidence to the west caused sediment thickening.
Wechsler et al. (2014:14) found evidence for Event CH4-E1 in Trench T39
where it "breaks up through unit 425 and into unit 420 on several faults on both walls of T39".
Because the strata of unti 420 is relatively thick, they were unable to locate an event
horizon. However, since there is "a thickening of unit 420 in the synclinal trough," They
suggest that "the deformation is synchronous with the deposition of unit 420", making unit 420
the "approximate event horizon."
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) date this event to 294-369 CE.
Dating is based on a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages. Only one radiocarbon sample
was found and dated in unit 420 and it was towards the top of unit 420. They suggest that Event CH4-E1
"occurred early in the deposition of unit 420" which would place the lone radiocarbon sample above the
faulting. However, they noted that if this sample was taken in a faulted part of unit 420,
"the date of event CH4-E1 may be as much as a century younger." They added that CH4-E1 cannot be younger
than the basal deposit of Channel CH3.
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) estimated
that Events CH4-E2 and CH4-E1 combined to produce 2.7 m of offset.
Wechsler et al. (2018:219) suggest that it is
"likely both are moderate in size, each with about 1.3 m of horizontal slip."
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
In their analysis of channel offsets,
Wechsler et al. (2018:217, 219) identified ~2.7 m of
unaccounted difference in offset channels 3 and 4. They
proposed that “there may be a younger event between CH4-E1 and CH3-E2”
that left no preserved seismic evidence in the trenches, due to a
"disconformity in the deposition sequence". They
noted that the missing offset could be "divided between two or three surface ruptures."
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) report that Event CH3-E2 was
identified and dated on both walls of fault-perpendicular
Trench T45, where strata were folded, fault-displaced, and
tilted westward by as much as 30°. Above these deformed
layers, an unconformity truncates the earlier deposition,
and undeformed unit 375 overlies this surface. Because
“both the deformed strata and secondary fault strands are
capped by unit 375,”
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) inferred “this
contact [the unconformity] to be the event horizon.”
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) further examined this
event, using a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages to date it to
505–593 CE.
Wechsler et al. (2014:214) reported that the age of
CH3-E2 is “well constrained by 14C ages that date the event to
the sixth century CE.”
Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) also estimated that the
event produced ~1.2 m of left-lateral displacement.
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Wechsler et al. (2014:9) report that Event CH3-E1 was identified and
dated on both walls of fault-perpendicular Trench T45 as “an upward
truncation of fault strands.” Within the
fault zone along a “secondary fissure,” they documented “a large fissure
that contains rotated blocks of coherent stratigraphy floating inside
more massive fissure-fill material (between 14 and 15 m).” Additional
observations of this event led them to conclude there was strong evidence
for a “surface-rupturing event.” They further speculated that the event
“produced uplift of the central block within the fault zone.”
Wechsler et al. (2018:214) revised the date of CH3-E1
originally reported in
Wechsler et al. (2014), suggesting that “the event age
is younger than previously inferred.” They observed that this revised age
overlapped with CH2-E1, suggesting that CH2-E1 and CH3-E1 could represent the
same event. In Table 3,
Wechsler et al. (2018) date CH3-E1 to 662–757 CE using
a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages, and characterize the associated
offset as small. It should be noted that they measured 1.3 m of left lateral offset for
event CH2-E1.
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Event CH2-E1 was identified by
Wechsler et al. (2018) who inferred its existence
"from the difference in offsets between Channels 1 and 2, without cross-fault
evidence of an event horizon".
Wechsler et al. (2018) also discussed the possibility that
CH3-E1 and CH2-E1 are the same event. Wechsler et al. (2018:Table 3) date this event to 675-801 CE
based on a Bayesian model of radiocarbon ages. They estimated
that Event CH2-E1 produced 1.3 m of left lateral offset.
Wechsler et al. (2018:214) note that a lack of exposure
of Channel 2 across the fault meant that the measured offset
"may represent slip from two events of smaller magnitude, similar to that which occurred with the 1759 earthquake."
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Initial paleoseismic investigations at Bet Zeyda were conducted by Marco et al. (2005). At Marco et al. (2005)’s northern site, two fault
ruptures were identified, showing a similar temporal pattern to two
fault ruptures at the Tel Ateret archaeoseismic site approximately 12 km
to the north. In their radiocarbon-derived age–depth model for Bet
Zeyda, Event E.H.1 was tightly dated (1020–1280 CE) and was most likely
caused by the 1202 CE earthquake. This event exhibited ~2.2 m of
sinistral slip displacement, corresponding to an estimated magnitude
between 7.1 and 7.3.
Slip displacement was calculated by subtracting the ~0.5 m of left-lateral offset
observed in the younger channels CH4 and CH5 (dated to after 1415 CE) from the
cumulative ~2.7 m left-lateral offset observed in the older channels CH2 and CH3.
The displacement in these older channels was attributed to the combined effects
of two events — E.H. 1 and E.H. 2. Event E.H. 1 post-dates depostion of channels CH2 and CH3
and pre-dates deposition of channels CH4 and CH5. Event E.H. 2 post-dates depostion
of channel CH5.
At the deltaic site of Bet Zeyda (aka Beteiha), just north of the
Sea of Galilee (aka Lake Kinneret), three-dimensional
paleoseismic investigations were conducted by multiple
researchers over a number of years using numerous trenches.
The studies examined a series of ~E–W-oriented
paleo-channels intersected and sinistrally displaced by
the ~N–S-trending active Jordan Gorge Fault, producing a
detailed chronology of fault activity over roughly the
past 2,000 years, based on radiocarbon dating of
detrital charcoal.
Once outliers are excluded, this
material appears to have a residence time of decades
rather than centuries (e.g. see Marco et al., 2005:200). Results indicate that seismic events were more
frequent and produced greater fault slip during the first
millennium CE than in the second, suggesting the region
may be approaching another period of heightened seismic
activity.
Initial paleoseismic investigations at Bet Zeyda were conducted by Marco et al. (2005). At Marco et al. (2005)’s northern site, two fault
ruptures were identified, showing a similar temporal pattern to two
fault ruptures at the Tel Ateret archaeoseismic site approximately 12 km
to the north. In their radiocarbon-derived age–depth model for Bet
Zeyda, Event E.H.1 was tightly dated (1020–1280 CE) and was most likely
caused by the 1202 CE earthquake..
Event E.H. 2 was not so tightly dated. It struck sometime after 1415 CE.
Marco et al (2005) suggested that one of the Baalbek Quakes of 1759 CE was
responsible for E.H. 2, but they considered other possibilities such as the
1546 CE and 1837 CE earthquakes. Event E.H. 2 was observed to produce ~0.5 m of
left lateral offset of paleo-channels CH4 and CH5, which led to a Magnitude estimate of 6.6-6.9.
Three-dimensional excavations of buried stream channels that have been displaced by the Jordan Fault, the primary strand of the Dead Sea fault zone in northern Israel, demonstrate that late Holocene slip has been primarily strike–slip at a minimum rate of 3 mm/yr. The palaeoseismic study was carried out in the Bet-Zayda Valley, the delta of the Jordan River at the north shore of the Sea of Galilee. The site was chosen where a north-striking scarp with up to 1-m vertical expression crosses the flat valley. One group of trench excavations was located where a small stream crosses the scarp. The active stream, which is incised into the scarp, is not offset by the fault. However we found two palaeo channels about 2 m below the surface offset sinistrally 2.7±0.2 m by the fault and two younger nested channels offset 0.5±0.05 m. Based on radiocarbon dates we attribute the last 0.5 m rupture to the earthquake of October 30, 1759. The older offset of 2.2 m most probably occurred in the earthquakes of May 20, 1202. These two events correlate with the findings at Ateret, about 12 km north of Bet-Zayda, where the 1202 earthquake produced 1.6 m of lateral displacement in E–W-striking defence walls of a Crusader castle, and an Ottoman mosque was offset 0.5 m in the earthquake of 1759. In the second group of trenches some 60 m farther south we found another offset channel. Its northern margin is displaced 15 m sinistrally whereas the southern margin shows only 9 m of sinistral offset. The dip slip component is 1.2 m, west side down. The different amounts of margin offset can be explained by erosion of the southern margin during the first 6 m of displacement. Additional slip of 9 m accrued after the stream had been abandoned and buried by a 2-m- thick lacustrine clay layers. Radiocarbon dates on organic residue provide the age control which indicates that the 15 m of slip has accrued over the past 5 kyr, yielding a short-term slip rate of 3 mm/yr for the late Holocene. It is possible that our study covers only part of the fault zone, hence we regard this mean slip rate to be a minimum for the DST. Based on other palaeoseismic studies the best estimate for Quaternary slip rate is 4 ± 1 mm/yr.
Basic data required for the characterization of seismic activity include the magnitudes and recurrence times of the large earthquakes, the time of the last event on each segment, and the amount of slip in each of the latest earthquakes. In addition to understanding the earthquake phenomenon, this characterization is essential for the assessment of seismic hazard.
We began to recover geological data on seismic activity of the Jordan Gorge Fault, a segment of the Dead Sea Transform (DST). The DST accommodates sinistral motion between the Arabia and the Sinai tectonic plates, transferring the opening at the Red Sea to the Taurus–Zagros collision zone (Fig. 1).
The paradigm of left-lateral shear along the DST since the Middle Miocene explains the systematic offset of numerous pre-Miocene geologic features by a total of 105 km [1, 2]. It is also consistent with palaeoseismic and archaeoseismic observations [3–6], and with earthquake focal plane solutions [7–9].
Our study was conducted at the Jordan Gorge fault segment, which connects two pull-apart basins in northern Israel, the Sea of Galilee (Kinneret in Hebrew) and the Hula valley (Fig. 1).
A previous archaeoseismic study determined that E–W trending walls of the Vadum Iacob (Ateret) Crusader fortress, which was built across the Jordan Gorge fault, are offset left-laterally 2.15+0.05 m. An Ottoman mosque, which was built on top of the fortress, is displaced by 0.5+0.05 m [10]. About 1.6 m of the offset was attributed to the large earthquake of 20 May 1202 while the mosque was displaced in the earthquake of 30 October 1759 [3]. These well-dated displacements occurred over a time interval too short to yield meaningful slip rate. The pre-1202 slip event in the study area is also uncertain. Furthermore, geologic mapping and aerial photograph analysis of the Ateret site indicate the presence of another lineament, possibly a fault strand, which does not cross the Ateret structure. Thus the slip determinations on the castle and mosque structures are minimums for slip in both of these earthquakes at this site, as well as for estimating longer-term slip rates.
The southern end of the Jordan Gorge segment is the basin of the Kinneret, a fault-bounded complex graben [11,12]. The activity in the area is characterized by both strike–slip and normal faulting. Geophysical data from the Kinneret, including seismic imaging [12], gravity [11], and magnetic field [13] do not show a fault along the projected line of the JGF south of the Bet-Zayda. This can be explained by the Jordan delta sediments masking the geophysical signature of the fault, or by the fault terminating just south of the northern lakeshore.
In contrast to a single major fault north of the Kinneret, geological mapping and seismic reflections show that there are two active faults south of it [12,14].
In order to expand our knowledge of the northern part of the DST we searched for a suitable site that can yield a longer earthquake record and impose better constraints on the slip in the historical earthquakes and on the mean slip rate. We hereby report the results of a palaeoseismic trench study in the Jordan fan delta at the Bet-Zayda Valley (also called Beteiha) some 12 km south of Ateret (Fig. 1), near Tel Bet-Zayda, where the miracle of the fish and loaves happened according to Christian tradition. We identified several indicators for a fault and potential slip markers: a lineament co-linear with the Jordan Gorge fault is visible on Landsat 5 images and on air photos (Fig. 2). The lineament is formed by a north-striking scarp, with up to 1 m of vertical expression, which crosses the flat valley. A major fault is observed in deep seismic reflection at the same location [15]. Because the location of the fault at the surface cannot be determined precisely on the deep seismic reflection profile, and in order to examine the width of the fault zone and the number of fault strands near the surface we performed a high-resolution seismic reflection survey across the valley. Offsets of shallow reflectors are clearly seen on this seismic image (Fig. 3). A stream channel that crosses the scarp from east to west is not affected by faulting (Fig. 2) but it was a clue for deeper and older streams suitable for measurements of slip. The palaeo-channels at this site were the target of our trench study.
The trench site (Figs. 4 and 5) was developed during 3 seasons because the area is cultivated and the trenches had to be filled back at the end of every season. In order to be able to return to exactly the same trench walls we laid nylon sheets of different color for each season before filling the dirt back. We then were able to return in the following year with utmost accuracy.
The first trench, T1, was aimed at confirming the location of the fault. It was dug across the highest part of the scarp, and indeed exposed a clear fault truncating a layer of coarse fluvial sand. This sand layer was observed only on the upthrown (eastern) side. Realizing the fluvial nature of the sand layer, we later opened a series of trenches, called "Southern Trenches", in order to trace the margins of the sand and delineate the alluvial channel.
Trench 2 was the first in the "Northern Trenches" group. It was located in the middle of the stream channel that crosses the scarp some 60 m north of T1, across the projected line of the scarp. Since the channel is incised into the scarp we expected to find here channel deposits overlying the fault and postdating the last faulting event. We also anticipated lower and older channels that may have been offset by the penultimate and perhaps even earlier events. The fault was indeed found at the bottom of T2, offsetting vertically by about 20 cm a layer of channel deposits containing mostly coarse pebbles. Alternating fluvial and lacustrine layers overlay the fault. We subsequently dug two fault-parallel (N-striking) trenches at both ends of T2 in order to search for the channel margins. The margins on the east were found some 2.7 ± 0.3 m north of the margins on the west. Subsequently we excavated additional fault-parallel trenches approaching the fault from both sides until the uncertainty was minimized.
Trench 3 was dug approximately half way between T1 and T2 in order to obtain additional points on the fault trace. In T3 we encountered massive dark-brown clayey soil with carbonate concretions cut by a 1-m-wide fault zone. The fault zone is characterized by abundant shear planes, and vertically smeared carbonate concretions. The sand layer that we saw in T1 was missing in T3, indicating that its margins are between T1 and T3. Therefore we traced the margins of the sand in a series of fault-parallel trenches on both sides of the fault.
We ended up excavating a total of 25 trenches across and parallel to the fault over a period of 3 years. The northern trenches revealed a set of displaced nested- channels below the unfaulted present stream. In the southern trenches we exposed a single displaced channel. The fault zone, which is less than 1 m wide, is very clear (Fig. 5). It is the data collected from these excavations (Figs. 5–9 and Tables 1 and 2) that we use to reconstruct the earthquake history of the northern Bet-Zayda Valley.
The Bet-Zayda site is located on the delta of the Jordan River, where it discharges into the Sea of Galilee (Kinneret) at 208–207 m below mean sea level. Consequently, the stratigraphy reflects this depositional environment. The Bet-Zayda Valley is flooded only during extreme high stands. For example, water levels during the 20th century were 214 m and 208 m, but in "normal" years they fluctuated between 211 in the autumn and 209 in the spring [16].
The exposed sediments represent basically three different types of deposition:
- massive clays, which we interpret as lacustrine in nature
- fossiliferous, foreset-bedded gravelly sand that is limited to channels and is interpreted as estuarine and deltaic distributary channel alluvium
- pebbles and coarse sand of channelled fluvial alluvium, which locally may interfinger with distributary channel alluvium.
Unit 1 is a deposit of dark stiff clay that underlies the entire area of study. Locally, the colour of this clayey deposit was greenish-bluish grey when trenches were first opened, but rapidly oxidized to a grey hue after a few days. The clay was found to be generally massive, without any recognizable stratigraphy, possibly due to bioturbation. Based on its fine texture, we infer a lacustrine origin for the clay unit, indicating high stand of Lake Kinneret. Unit 1a consists of sandy clay, which appears irregularly, possibly attesting to lens- like distribution. A series of stream channels that represent deposition and lateral migration over some period of time is denoted as CH1–CH5. CH1 appears only in the southern trenches. The oldest and deepest channel in the northern trenches, unit CH2, contains a conglomerate of up to fist-size pebbles, devoid of fossils. We interpret this to be a fluvial channel incised into the previously deposited lake clays of unit 1. CH2 is overlain by fine to coarse sand. In some exposures, the sand is stratified, with foreset beds defining much of the stratigraphy. Thus the channels of units CH2 through CH5 must have been deposited during a period of relative low lake-level when base-level lowering would have forced incision of distributary channels, somewhat similar to the present state.
Unit CH3 flowed across the fault a few meters north of CH2, almost at the same level. The relative age of the two channels is based on on-lapping relationships in trenches T16, T17, and T7, where the southern margins of CH3 lay on top of CH2 (Fig. 6). Incised into the channel CH3 deposit and into the basal clay is channel CH4. CH4 deposits are locally stratified, with foreset-bedded sandy gravel interbedded or channelled with more massive gravelly alluvium. An associated fine-grained cap of clayey alluvium apparently represents deposition in a quiet water environment after channel abandonment. These gravels are also generally devoid of fossils so we interpret these channels as primarily fluvial in nature. CH4 is thin on the east in trenches T16, T17, and T7 but widens and becomes thicker and about half a meter deeper in T18, forming a small fan upon crossing the fault to the west. We interpret this change as an indication for a small scarp of about 0.5 m.
Unit 6 is variable, and we divide it into three different facies denoted 6a–c, which show irregular shapes, perhaps reflecting shifting streams and erosion. Unit 6a, which appears in trench T7 is made of fine gravel and some pebbles, with scattered, mostly broken and fragmented fossils. Unit 6b is fossiliferous sandy gravel, but no pebbles. The fossiliferous nature of this alluvium suggests that it was deposited in a low energy distributary channel environment. Unit 6c is sandy clay with scarce fossils, which disappears toward west and is absent in trench T18. Units 6b and 6c lay on top of CH4 but farther west unit 6b interfingers with it. On the eastern wall of T18 CH4 is overlain by channel CH5, which was truncated before units 6b and 6c were deposited. The irregular appearance of units 6a–c probably reflects meanders of the palaeochannel, therefore we do not use them to measure slip.
Unit CH5 is a gravel-filled, southwest-trending channel. Its southern margin, which is exposed in the large trenches and in small ones (20-cm-wide) excavated very close to the fault (denoted a–d on Figs 4 and 10), is displaced by 0.5 m, the same as CH4. The northern margins of this channel are not exposed in the trenches. Channel CH5 can be interpreted as conformable with the underlying unit 6, but it locally truncates the bedding of unit CH4 as seen in trench T18 East. A distinct difference between CH5 and the older channels CH3 and CH4 are the presence of numerous mollusc shells stratified within the younger deposit. This observation suggests a return to deltaic distributary channel deposition, or even estuarine, probably suggesting a slight rise in lake level.
The sandy clay of unit 6c grades upward into clayey, fossiliferous alluvium, which we designate as unit 7. Without the fossils, unit 7 would look very similar to the clayey alluvium of unit 6c. Consequently, we interpret them to have been deposited in a similar depositional environment. Thus, it appears that the increase in lake level indicated by the shale deposits of unit 6c and the fossils in unit CH5 has persisted through the deposition of unit 7.
Unit 8 is a generally massive, dark, organic-rich clayey deposit, capped at the surface by a soil layer. This unit, which forms the surface of most of the study area, is commonly up to 1.5 m thick, composed of massive, dark brown clay, devoid of stratification. No fossils were found, but a few shards of ceramics were encountered, unfortunately too small to identify. The soil’s uppermost ~50 cm is ploughed. Roots are abundant.
The stratigraphy in the southern group of trenches is much simpler than the northern group (Fig. 8). The same basal massive dark clay of unit 1 is found there too. A variegated layer of alluvial coarse sand with no fossils in it was found in the form of a stream channel. The alluvial sand is overlain by a massive dark-brown clayey soil whose thickness is 1.5 m on the eastern side of the fault and about 3 m west of it. We correlate it with unit 8 of the northern trenches. The transition between unit 1 below the sand and unit 8 above it is gradual whereas the contacts with the sand are mostly sharp. Abundant calcite concretions characterize the area east of the fault as well as some places below the sand layers. The trench map view reveals that the northern margin of the stream is offset by 15 m by the fault and the southern margin is offset by 9 m.
We collected all the detrital charcoal that was encountered in the trenches. The samples were dated in the Kimmel Center of the Weizmann Institute using conventional alpha counting. Small samples were measured by Atomic Mass Spectroscopy. The possibility to date the shells was considered but since the systematics of 14C in this environment is unknown, in particular the reservoir time, we decided to examine this option in a separate study. Age data are summarised in Fig. 9 and Table 1.
Trench T10 (Fig. 7), which cut the fault zone within the northern trenches, yielded a few indicative ages corresponding to two groups of faults. The earlier group offsets the stratigraphic units from which 14C ages range from 720–770 AD to 980–1020 AD. These faults terminate upward at unit 6b, in which 14C ages are from 1285–1380 AD to 1330–1415 AD. The second group of faults offsets unit 6b and the lower part of Unit 7. Hence, the first faulting is constrained between 1020 AD and 1280 AD. Two 14C dates in trench T4 also show that the first faulting is constrained between 1020–1150 AD and 1195–1275 AD (Fig. 7). Based on the historical earthquake record and the observations at Ateret [3] the first slip event can be correlated to the historical earthquake of May 20, 1202. The time of the second event has only a lower bound—it postdates 1415 AD.
In Fig. 9 we present probability density functions for the radiocarbon dates that constrain the timing of the penultimate event at Bet-Zayda. The historical 1202 earthquake falls within the probability distribution, and is in fact the only historical earthquake in the vicinity that can possibly fit the age distribution. This indicates that the detrital charcoal dated for this study was not resident in the system for an extended period of time (decades versus centuries).
In the southern trenches we did not find any charcoal. We therefore dated the disseminated organic matter and carbonate concretions extracted from the sediment by dissolving all the carbonate material in the samples. The earliest age of the distinct sand unit was determined to 5 ka ± 50 yr and the youngest age in it is about 700 AD ± 50 yr (Fig. 8; Table 1). All 14C ages from trench T15 but one are in agreement with the stratigraphy. This agreement indicates that the organic matter in the clay unit has been stable since deposition and no major re-distribution occurred. One sample of humic acid, T15b, is younger than the organic residue samples T15c and T15a from the same level.
The linear channels CH2–CH5 (Fig. 6), which cut across the fault, provide the piercing points for measuring slip. The southern margins of both CH2 and CH3 are offset 2.7 ± 0.2 m measured less than 0.5 m from the fault (Fig. 10). The northern margin of CH3 shows a sigmoid shape, which we interpret as the result of erosion of the opposing corner by the west-flowing stream soon after slip occurred. Measured about 2 m away from the fault the offset is exactly the same as the southern margins, 2.7 ± 0.3 m. The margins of the younger channel CH4 are offset 0.5 ± 0.1 m. The southern margin of the youngest buried channel, CH5, shows 0.5 m offset. We did not reach the northern margin of this channel. We interpret the offset channels as showing two slip events. The first, 2.2 ± 0.3 m, postdates CH2 and CH3 and predates CH4 and CH5. Additional 0.5 ± 0.1 m postdates CH5. The active stream at the surface is not faulted (Fig. 2).
The first E-striking trench T1 was excavated where the scarp is at its maximum height in order to expose the fault plane. The section on the eastern side of the trench includes four units: massive dark brown clay with carbonate concretions at the bottom, a layer of sandy soil, made of clay and coarse sand of less than 0.5-cm-grains, another layer of dark brown clay, very similar to the one at the bottom, and an uppermost half meter of clayey soil that has been ploughed and is heavily bioturbated. A vertical fault plane was identified at the middle of the trench, characterized by densely spaced shear planes (Fig. 8). The sandy soil layer is truncated by the fault and the section on its western (downthrown) side includes only massive dark-brown clayey soil with carbonate concretions. The fault is recognizable almost up to the surface. The soil in the 2–3 m adjacent to the fault is significantly darker due to high content of organic matter. The dark soil possibly formed in sag ponds, which were rapidly buried at the base of the fault scarp. The only clue for significant horizontal slip in Trenches T1 and T15 is the steepness of the fault plane. The array of southern trenches, which were aimed at tracing the sand’s margins enables the resolution of the horizontal and vertical components of the slip to 15 m and 1.2 m respectively. In Trench T15 the sand layer appears only in the western downthrown side. By connecting the sand margins in the trenches on a map (Fig. 10) we realized that the northern margin is offset sinistrally 15 m and the southern margin is offset 9 m. We attribute the smaller offset to erosion of the corner that opposed the flow after slip events. The 14C ages of the sand layer, the oldest of which is 3030–3080 BC provide a mean slip rate of 3 mm/yr for this fault strand. The absence of detailed stratigraphy does not allow resolution of single ruptures.
The faulting in the northern trenches postdates the carbon dates of 1200 AD (Fig. 7). We consider earthquakes that were reported to have caused damage in northern Israel and Jordan, southern Lebanon, and SW Syria as candidates for being associated with slip at the Bet-Zayda. Catalogues of historical earthquakes [17, 18] list the earthquakes of 1837, 1546, 1759, and 1202. The 20 May 1202 event displaced the walls of the Crusader fortress of Ateret by 1.6 m [3]. Its estimated zone of damage to buildings (meisoseismal zone) extends from ~90 km south to ~160 km north of the Bet-Zayda. It was felt in the entire eastern Mediterranean region and throughout the Levant. The magnitude was estimated at 7.6, with maximum displacement of about 2.5 m [19]. The 1546 earthquake was considered strong [18], but we accept Ambraseys and Karcz’s analysis [20] that shows grossly exaggerated reporting and concludes that it was a medium-size earthquake, which caused minor damage in the Judea. Two close events occurred on 30 October and 25 November 1759. Sieberg [21] located the maximum damage zone of the October earthquake between the Sea of Galilee and the Hula Valley, and that of the November event some 150 km farther north in northeast Lebanon. Ambraseys and Barazangi [22] quote a letter dated 1760 in which the French ambassador to Beiruth reports surface ruptures along 100 km of the Yammuneh segment of the Dead Sea Transform and attributes them to the November 1759 earthquake (JW: Studies conducted by Daeron et. al. (2005) proposed that the 1759 earthquakes were caused by a rupture on the Rachaiya Fault in October followed by a rupture on the Serghaya fault in November and the Yammouneh segment broke in 1202 CE. See also 1759 CE Safed and Baalbek Quakes). They estimate the magnitude of the 25 November 1759 earthquake at ~7.4. The October 1759 M ~6.6 foreshock, determined on the basis of isoseismals that centre at the Jordan Gorge [21,22], could be related to faulting along the Jordan Gorge, at Ateret as well as at Bet-Zayda. The most recent destructive earthquake to strike the study area was the 1 January 1837 Safed earthquake. The severe damage in Safed and Tiberias, IX–X Mercalli intensity, probably biased Vered and Striem to draw isoseismals that centre at the Jordan Gorge [23]. However, using previously unavailable additional data to re-evaluate the meisoseismal zone led to the conclusion that it was an M 7, probably a multiple event, which ruptured the Hula–Roum fault [24]. We accept the latter analysis and assume that the 1837 earthquake did not rupture the fault at Bet-Zayda. Hence the most probable ruptures observed in the northern trenches at Bet-Zayda are associated with the 20 May 1202 and 30 October 1759 earthquakes.
An important observation can be made regarding the reliability of historical accounts. We note that the centre of damage in the crude isoseismal maps [21], which are based on data available in the early 20th century, is confirmed by our studies along the Jordan Gorge. It seems that earthquakes that are well documented by contemporaries can be characterized fairly reliably in terms of the maximum damage zone, from which the magnitude and rupture segment can be roughly estimated. The trenches prove that N-striking topographic step crossing the otherwise flat Bet-Zayda valley is definitely a fault-related scarp. The presence of the scarp in spite of ploughing, occasional inundation of the Valley by the Sea of Galilee, and the sediments brought by the Jordan River and smaller streams from the Golan Heights require its recent renewal. The locations and amount of slip, which we observe in the trenches, are in agreement with previous estimates of the earthquake magnitudes based on the extent of damage [19,22]. However the available data are not sufficient yet to constrain the length of the ruptures. Based on empirical relations (e.g., [25,26]) the ~M7.6 1202 earthquake may have ruptured about 100 km long fault, and the October 1759 earthquake may have ruptured about 15–20 km. Therefore we expect to find different palaeoseismic record on the southern side of the Sea of Galilee at least for a few earthquake cycles, somewhat similar to the behaviour of the North Anatolian Fault in the 20th century [27].
In the southern trenches we recognize an older single slip marker in the form of alluvial sand layer, confined laterally with margins showing a sand-to-clay transition typically over less than 0.5 m. The northern margin is offset left-laterally 15 m and the southern margin is offset only 9 m. This difference can be explained if the stream incised into the scarp and truncated the corners that formed as the southern margin moved northward on the eastern side during slip events. This process of smoothing the southern margin went on for some time during which the fault slipped 6 m. After the channel was abandoned and became inactive, it was buried by lacustrine clay and subsequent 9 m of slip took place. The total slip is therefore 15 m on the north and only 9 m on the south. We are unable to separate the total of 15 m into individual slip events. The mean slip rate is 3 mm/yr for the last 5 kyr or 12.3 m in 3800 years prior to the 1202 event, i.e., 3.2 mm/yr. We do not see any other fault strand at the surface in the Bet-Zayda Valley but this possibility cannot be excluded because the seismic reflection shows several strands in the fault zone (Fig. 3). Hence the 3 mm/yr slip rate is a minimum for the DST. Other slip rate estimates vary between less than 1 mm/yr and 20 mm/yr (Table 3). Estimates based on palaeoseismic data from the Arava Valley south of the Dead Sea are just slightly higher than 3 mm/yr and can be considered in agreement with our result. However palaeoseismic data in the northern part of the DST suggest a slip rate of 7 mm/yr in the late Holocene [5]. One possible reason for these apparent discrepancies might be the different time windows and different fault segments examined in the various studies. Temporal and spatial clustering of earthquakes may lead to estimations of slip rates that do not represent the long-term behaviour of faults [28].
Our best estimate for the Holocene is 4 ± 1 mm/yr. The long-term slip on the DST, assuming the total 105 km of slip postdates the emplacement of 20 Ma dikes in Sinai and Arabia, is about 5 mm/yr [29]. Our Holocene slip rate value may be lower either due to insufficient sampling (missed parallel segments) or some aseismic slip, or due to slowing of the plate movements. Garfunkel et al. [30] estimated that the seismic slip during historical earthquakes accounts for about one-third of the long-term geologic slip. The new data reduce the discrepancy but do not eliminate it. The current low level of microseismic activity along the DST probably indicates that it behaves in a stick–slip manner, although a-seismic motion (creep or silent earthquakes) cannot be precluded. To resolve this problem we need to know the detailed geometry of the fault zone and the slip on all parallel fault strands, impose tighter constraint on the time of DST initiation, and acquire geodetic measurements on both sides of the fault.
Three-dimensional trenching proved to be a successful method in the Bet-Zayda Valley. Our study demonstrates how a palaeoseismic investigation is complemented by archaeological and historical data to characterize the seismic activity along the northern DST. We conclude that the JGF has been the main active strand of the DST during Late Holocene. Other normal faults have been also active in the Plio-Pleistocene, keeping up with, and even exceeding sediment accumulation in the basin. The Late Holocene motion on the JGF has been primarily strike-slip (15 m); vertical component is only 1.2 m. A similar proportion is estimated between the total 100 km slip on the DST and the thickness of the fill in the Dead Sea Basin [31]. Our observations confirm the plate tectonics paradigm of sinistral slip between the Arabia and Sinai.
14C dating of bulk organic matter constrain the minimum age of the layer that is offset by 15 m to 5 kyr, yielding a minimum average Late Holocene slip rate of 3 mm/yr. This rate is of the same order of the model based on GPS geodesy [32] and results of palaeoseismic studies south of the Dead Sea [4,6] but the rate during the last two millennia further north is more than double [5].
Our observations establish the last two earthquakes at the Jordan Gorge fault segment occurred on May 20 1202 and October 30 1759. They were associated with significantly different amount of rupture, 2.2 ± 0.2 m in the 1202 earthquake and 0.5 ± 0.1 m in the 1759 earthquake. Along-strike variation of slip is apparent for the 1202 event, which offset only 1.6 m at the Ateret site, 12 km north of the Bet-Zayda Valley. The 1759 slip is the same at both sites. This result is incompatible with the "characteristic earthquake" model [33].
The independent analyses of the damage inflicted by the 1202 and 1759 earthquakes [19,21,22] yielded a correct estimate of the location and magnitude of the ruptures. We believe that historical earthquakes that were relatively well documented can be characterized quite reliably in terms of their locations and magnitudes by careful analysis of historical reports.
- from Chat GPT 5, 15 August 2025
- from Marco et al. (2005)
Key paleoseismic observations
– Southern margins of CH2 and CH3 are offset 2.7 ± 0.1–0.3 m within ~0.5–2 m of the fault; matching northern margins confirm the same separation (erosional smoothing noted locally).
– Younger channels CH4 and CH5 each show 0.5 ± 0.05–0.1 m left-lateral offset, demonstrating that the 2.7 m total on CH2/CH3 records two events rather than persistent creep.
– In Trench T10, the earlier fault set terminates upward below Unit 6b, and ages bracketing E1 fall between AD 1020–1280 (with parallel constraints in T4), uniquely compatible with 1202 CE in the regional catalogs.
Interpretation
Subtracting the younger 0.5 m slip (E2) from the 2.7 m cumulative offset yields ~2.2 ± 0.3 m left-lateral displacement for E1 (1202 CE). The rupture cut CH2/CH3 but predates CH4/CH5 deposition; faulting style is dominantly strike-slip within a <1 m-wide zone traced in multiple trenches.
- from Chat GPT 5, 15 August 2025
- from Marco et al. (2005)
Key paleoseismic observations
– Measured offsets on CH4 and CH5 are ~0.5 ± 0.05–0.1 m, constrained with fault-parallel micro-trenches located within tens of centimeters of the main strand.
– In Trench T10, the younger faulting clearly offsets Unit 6b and the base of Unit 7, setting a lower bound of > AD 1415 for the event; the historical correlation and co-site consistency indicate 1759 CE.
– Thickness changes and west-side thickening of CH4 near T18 imply a small ~0.5 m scarp at the time of deposition, consistent with a moderate strike-slip rupture localized to the JGF segment.
Interpretation
E2 (1759 CE) accounts for the ~0.5 m of late slip recorded on CH4–CH5 and, when combined with E1’s 2.2 m, explains the 2.7 m cumulative separation preserved by the older CH2/CH3 markers at Bet-Zayda.
We present new results from a paleoseismic trenching campaign at a site across the Jordan Gorge Fault (JGF), the primary strand of the Dead Sea Transform in northern Israel. In addition to the previously recognized earthquakes of 1202 and 1759 C.E., we observe evidence for eight surface-rupturing earthquakes prior to the second millennium C.E. The past millennium appears deficient in strain release with the occurrence of only two large ruptures, when compared with the preceding 1200 years. Assuming Gutenberg–Richter magnitude–frequency distribution, there is a discrepancy between measured rate of small-magnitude earthquakes (M LT 4) from instrumental records and large earthquake rates from paleoseismic records. The interevent time of surface-rupturing earthquakes varies by a factor of two to four during the past 2 ka at our site, and the fault’s behavior is not time predictable. The JGF may be capable of rupturing in conjunction with both of its southern and northern neighboring segments, and there is tentative evidence that earthquakes nucleating in the Jordan Valley (e.g., the 749 C.E. earthquake) could either rupture through the stepover between the faults or trigger a smaller event on the JGF. We offer a model of earthquake production for this segment in which the long-term slip rate remains constant while differing earthquake sizes can occur, depending on the segment from which they originated and the time since the last large event. The rate of earthquake occurrence in this model does not produce a time-predictable pattern over a period of 2 ka as a result of the interplay between fault segments to the south and north of the JGF.
The DST is a major plate boundary in the Middle East, accommodating the relative sinistral motion between the African and Arabian plates (Quennell, 1956), both moving northward with respect to Eurasia with differing velocities (Reilinger and McClusky, 2011). The DST transfers slip northward from the oblique opening of the Red Sea to the East Anatolian fault zone. The cumulative offset of the DST is ∼105 km, representing the total motion between the Arabian plate and Sinai subplate since the middle Miocene (e.g., Freund et al., 1968; Garfunkel, 1981). The rate of ongoing sinistral motion measured across the fault from Global Positioning System (GPS) kinematics is estimated to be between 3 and 7 mm/year in northern Israel (Reilinger et al., 2006; Le Beon et al., 2008, and references therein).
In the northernmost part of Israel, in the Hula basin area, the DST deviates into a restraining bend and branches from a single, relatively straight fault into several subparallel strands. The main strike-slip fault runs from the Jordan Valley, entering the Sea of Galilee from the south where it continues north underwater next to its eastern shores; its precise location inside the lake basin has been difficult to determine (Ben-Gai, 2010). At the northern shore of the Sea of Galilee, the fault emerges in the Bet-Zayda (Beteiha) floodplain approximately 2–3 km to the west of its northward projection, implying the existence of a pull-apart basin within the lake (Marco et al., 2005; Meiler et al., 2011). From there, a single main segment continues north, producing a fault-controlled river gorge (the Jordan Gorge fault [JGF]). Upon entering the Hula basin, the fault splits into eastern and western segments (Heimann, 1990; Rybakov et al., 2003; Heimann et al., 2009), which extend to the Rachaya–Serghaya and the Yammouneh faults, respectively. An additional branch, the Roum fault, extends from the northwest of the Hula basin, striking north-northwest for about 35 km. The Sea of Galilee basin is considered to be a barrier for large earthquakes, whereas the Hula basin is not, based on paleoseismic and gravity data (Marco et al., 2005; Schattner and Weinberger, 2009).
Our work is focused on the Jordan Gorge segment between the Sea of Galilee and the Hula basin, where the fault location is known and only one main strand is thought to accommodate most of the ongoing sinistral movement, although a small amount may be accommodated by block rotation of the elevated saddle between the Sea of Galilee and the Hula basin (Heimann and Ron, 1993). In previous works, the rupture history of the JGF was explored at two sites that are spaced about 15 km apart. At the Vadum Iacob site (also referred to as Ateret; Ellenblum et al., 1998), it was established that a Crusader castle had been sinistrally offset by 2.1 m, out of which 1.6 m of displacement is attributed to the well-documented historical earthquake of 1202 C.E. (Ellenblum et al., 1998), to which Ambraseys and Melville (1988) assign a magnitude of 7.6. A more recent event offsets an Ottoman mosque constructed above the ruins of the castle by an additional 0.5 m (Ellenblum et al., 1998). The 0.5 m offset is attributed to the October 1759 earthquake, in which the damage was centered on the Jordan Gorge segment (Ambraseys and Barazangi, 1989). Recent excavations have revealed a Hellenistic wall (dated to the second century B.C.E.) that is offset by ∼6 m, and an Iron Age wall on the west side of the fault that is offset by at least 8 m, with its east side counterpart likely north of the excavated zone and therefore still unearthed (Ellenblum et al., 2013).
Marco et al. (2005) excavated paleoseismic trenches at a second location across the Jordan Gorge segment at the Beteiha site and exposed a number of buried channels that were offset by the fault. They resolved the timing and displacement of the last two events and, similar to Vadum Iacob, estimated the displacement in the 1202 earthquake as ∼2.2 m, with an additional 0.5 m of sinistral displacement attributed to the 1759 earthquake, a total of 2.7 m. A fourth channel that dates between 3 and 5 ka is displaced up to 15 m, yielding a minimum 3 mm/year slip rate for the late Holocene (Marco et al., 2005).
Other paleoseismic works on adjacent segments of the DST include Ferry et al. (2011) who recorded 12 faulting events within the past 14 ka on the Jordan Valley segment to the south and calculated an approximate slip rate of 3.3 mm/yr based on an inferred displacement of 3.3 m per event. Yet, they point out that their record contains sedimentary hiatuses and is therefore incomplete, except for the last five earthquakes. Moreover, the recurrence interval between earthquakes for those last five events is highly variable, between 284 and 1508 years. North of the Hula basin, Daëron et al. (2005, 2007) trenched across the Yammouneh fault in the Bekka Valley and found evidence for 10–13 surface-rupturing earthquakes within the last 12 ka, yielding an average recurrence interval of ∼1100 years, though the large uncertainty in event ages, especially the older ones (2σ larger than 600 years), does not support the assumption of periodicity.
Gomez et al. (2003) studied the Serghaya fault, which last ruptured in the November 1759 earthquake, and determined that the penultimate event was approximately 2 millennia earlier. They have found evidence of six events over the last 7 ka, but the poorly constrained timing of past events did not permit a reliable estimate of the recurrence interval. Nemer and Meghraoui (2006) trenched across the Roum fault and found evidence for five events during the past 2 ka, but the dates were not sufficiently well constrained to permit a good estimate of the recurrence interval. Elias et al. (2007) studied the Mt. Lebanon thrust fault, surfacing primarily offshore, and determined that it was the source for the 551 C.E. earthquake and tsunami. They documented evidence that the fault generates large earthquakes every 1500–1750 years, based on uplifted Holocene marine terraces, and may possibly rupture together with the Roum fault.
None of the above studies demonstrate clear evidence for periodic earthquake production along the DST, and some aforementioned records may even be interpreted as exhibiting strong temporal clustering. To test the behavior of the JGF section of the northern DST, we conducted new extensive paleoseismic investigations in the Bet-Zayda Valley, including both 2D and 3D trenches to resolve both timing and displacement, with timing being the focus of this paper. The new work presented here greatly expands our knowledge of the earthquake history of this part of the fault for the past two millennia and allows a better assessment of both the behavior of this fault, as well as the likelihood of future earthquake activity in the region.
The shallow subsurface stratigraphy is composed of several buried gravel- and sand-filled channels encased into massive lacustrine clays deposited during lake highstands. The ages and general descriptions of the buried channels are summarized in Tables 1 and Ⓔ S1 (available in the electronic supplement to this article). We numbered the channels according to their relative age, starting with the channel 1 complex, which is composed of three distinct subchannels. These were previously excavated and described by Marco et al. (2005). Channels 2, 3, and 4, each also composed of multiple subchannels, record fluvial flow across the fault during most of the first millennium. The channels that Marco et al. (2005) excavated were dated from the ninth century to at least as young as the fourteenth century C.E., when the channel complex was buried by lake deposits. The modern channel may have been active after the lake level dropped and up until about the 1970s, when artificial drains were excavated to improve the drainage for agriculture. Thus, collectively, these channels and lake deposits contain the complete displacement and earthquake history for the past 2000 years.
Channels 3 and 4 each spanned several centuries of time, and trenches excavated to expose these channels across the fault exhibited clear evidence of multiple earthquakes having occurred while they were active. In contrast, all of the dates from channel 2 fall within a short, 100-year time period centered around 720 C.E., indicating that this channel represents a fairly short period of flow. We did not trench channel 2 across the fault; however, from cross-cutting relations in T34 and T38, we inferred that channel 2 is younger than channel 3. Consequently, we focus now on the event evidence recorded in the stratigraphy of channels 3 and 4, as described next.
Channel 3 is a west-flowing sandy gravelly channel complex that was crossed in several fault parallel trenches (T30, T33, T34, and T38) and in one fault- crossing trench (T45). The channel units were numbered between 300 and 399 (older units higher numbers) for reference. T45, the fault-crossing trench, also represents a longitudinal profile of channel 3 and was used to study earthquake history. The logs of T45 are presented in Figures 3 and Ⓔ S1a–b, and the unit nomenclature is described in Table S1 available in the electronic supplement.
Channel 3 was divided into lower and upper units based on the channel morphology, with the upper units (units 306–329) cutting into and eroding the lower units (units 330–399) east of the fault (T45 log, Figs. 3 and Ⓔ S1a–b available in the electronic supplement). These upper units strata were not observed in fault contact on the west side of the fault. The youngest units (301–305) are capping the faults on the west side and appear unrelated to the upper channel 3 units.
The strata in channel 3 vary in composition from large, rounded pebbles and cobbles at the base of individual subchannels in the lower part of the section, to foreset- bedded gravelly sand and silty clay in the upper part. Furthermore, the upper part (units 310–329) of channel 3 exhibits an anomalous trend on the east side of the fault zone, with indications of an along-fault flow direction (northsouth). The upper part also has many gastropod shells within it, indicating a rise in lake level and probable influence from motion on the eastern fault strand, as discussed later. The foreset bedding (units 320–328) is also consistent with deposition in standing water, which supports the inference of an increase in lake level.
We collected nearly 100 samples of detrital charcoal from the strata of channel 3, of which 36 were dated by 14C mass spectroscopy methods at the Center for Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (CAMS) facility at University of California, Irvine. Twenty-eight of these dates are from trench T45 or from strata exposed in fault- parallel trenches near T45 that could be confidently traced into the strata of T45 (indicated as proxy dates on the trench logs) and are used in this paper. Many of the samples yielded dates that are much older than other samples from the same stratum, including one as old as 12,000 years. Consequently, not all were used in the chronologic model to constrain the ages of faulting events exposed in T45.
Taking the youngest dates from each unit as closest to the actual age of their respective strata, and discarding dates that are out of stratigraphic sequence, we are left with 10 dates that we used in our chronologic model (Fig. 4). From these, the ages of the lower strata from channel 3 range from the mid-fifth century C.E. to the mid-seventh century C.E. whereas a single date from the upper portion of channel 3 yielded a mid-seventh to mid-eighth century date.
As an additional age constraint, we used 5 of the 11 radiocarbon dates from channel 2 that span the entire section of the channel as an upper-bound constraint on the ages of strata in channel 3, based on cross-cutting relations from fault parallel trenches (ⒺFig. S1i available in the electronic supplement). All five dates yielded ages in the late-seventh to mid-eighth century C.E., consistent with the date from the upper part of channel 3 and suggesting there is not much time between the abandonment of channel 3 and formation of channel 2, although the stratigraphic evidence indicates a rise in lake level. A lake level rise may have forced the avulsion from channel 3 to channel 2, an event that may have occurred in only a few decades, or less, as suggested by the 14C dates.
We also used Marco et al. (2005) samples to constrain the youngest event in channel 3. Dates are modeled using OxCal (BronkRamsey, 2009) and IntCal09 calibration-curve (Reimer et al., 2009), as summarized in Figure 5 and Table 2.
Trench T45 exposes evidence for two surface ruptures captured in the stratigraphy of channel 3 (Fig. 3), which we number CH3-E1 and CH3-E2. Event names represent the channel in which they are identified (the first number) and their stratigraphic order from younger (E1) to older (E2). There is also evidence for displacements younger than E1 that involved the overlying strata, and these are most likely the previously documented 1202 and 1759 C.E. earthquakes and any other events that postdate channel 3.
The fault zone itself, as exposed in T45, is divided into two main strands, 1–2 m apart, plus several subsidiary faults. The eastern strand truncates the manganese-stained, cross- bedded upper channel 3 sandy gravel strata (units 320–329). Within and west of the fault zone, units attributed to the lower section of channel 3 are preserved across all fault strands and contain the evidence for the surface ruptures. Hence, the two surface ruptures we identify fall in the time frame of the lower channel 3 section, or between about the mid-fifth to mid-seventh centuries C.E. There are no equivalent upper channel 3 units exposed in T45 west of the eastern fault branch, except the capping units 301–305, which only appear west of the eastern fault branch, and therefore their stratigraphic relation with the younger units west of the fault is unclear. This could be a result of horizontal offset, of local changes in the channel flow near the fault zone, or both.
Event CH3-E1 is expressed on both trench walls as an upward truncation of fault strands that are capped by unit 305. In T45N, within the fault zone along a secondary fault strand, there is a large fissure that contains rotated blocks of coherent stratigraphy floating inside more massive fissure- fill material (between 14 and 15 m). Another fault strand that bounds the fault zone on the west also appears to rupture to the same stratigraphic position (at 17 m), and both faults and the fissure fill are capped by unit 305, whereas all other fault strands rupture to higher levels and presumably moved in later earthquakes. On the south wall of the trench, a single fault strand was found that ruptured up through the channel stratigraphy and was capped by unit 305 (at 16.5 m). Taken together, we consider this strong evidence for a surface-rupturing event that occurred high in the section of the lower channel 3 alluvial fill. We speculate that this event, which produced uplift of the central block within the fault zone, may have caused local damming of channel 3, thereby disrupting the stratigraphy of upper channel 3 deposits.
Event CH3-E2 is also well expressed on both trench walls, with lower channel 3 alluvium of units 380–384 folded or tilted by as much as 30° to the west and in fault contact, followed by truncation of these deformed strata and deposition of undeformed lower channel 3 alluvium. Both the deformed strata and secondary fault strands are capped by unit 375, so we infer this contact to be the event horizon.
The ages of the surface-rupturing events interpreted in the sediments of channel 3 are presented as probability density functions in OxCal (Bronk-Ramsey, 2009) in the chronologic model in Figure 5. Based on this OxCal model, event CH3- E1 falls in the range of 619–684 C.E., with a peak probability at about 653 C.E., whereas CH3-E2 is dated to between 505 and 593 C.E., with a peak probability at about 551 C.E. Because the probability distributions are nearly symmetric, we present them as 653 ± 36 C.E. and 551 ± 42 C.E., with uncertainties reported at 2σ.
The sandy channel complex of channel 4 was exposed in trenches T33, T37, and T39 (Figs. 6–8), with the latter two trenches crossing the fault. Captured within the strata of channel 4, we found evidence for up to six paleoearthquakes, which are numbered CH4-E1 through CH4-E6. The stratigraphic units in channel 4 are numbered 400–499, from youngest to oldest, and represent nearly continuous deposition of sand, gravel, and mud across the fault for several hundred years.
Channel 4 crossed the fault in an area where a long, linear, and narrow pressure ridge is interpreted to have caused a very localized uplift within the fault zone itself. This is obvious in the expression of faulting, as exposed in trenches T37 and T39, where the strata of channel 4 are warped up into the fault. It is partly due to this localized style or expression of the fault that we were able to confidently distinguish individual faulting events.
Trench T33 was excavated west of the fault to identify channel locations, but we use the stratigraphy exposed in the vicinity of trench T37 and T39 to wrap all stratigraphic units in all three exposures, so correlation of strata are certain. From this exercise, two other important elements are apparent. First, the stratigraphy in trench T37 is mostly older than the strata exposed in T39, because T33 shows that strata offlap to the north west of the fault zone. Thus, as seen by the depositional relations between the units in T33 (Figs. 7 and ⒺS1f available in the electronic supplement), strata are progressively older to the south on the west side of the fault, which is consistent with a model in which the faults motion during the period of channel flow created a progression of overlapping subchannels west of the fault, from the oldest in the south to the youngest in the north, consistent with the faults left-lateral motion.
Second, there is a locally significant down-to-the-west component of vertical motion, although a lesser down-to-the-east component is observed on the east side of the pressure ridge. Thus, from the exposures in T33, T37, and T37, the stratigraphy is most consistent with the overall model of left-lateral displacement across a narrow pressure ridge with central uplift and an overall west-side-down long-term component of vertical motion. It is within this context that we discuss the evidence for multiple surface ruptures in the channel 4 complex.
The overall chronology of the channel 4 complex is provided by the radiocarbon dating of 24 samples from these three trenches. As with all detrital charcoal, some samples yielded ages that are too old relative to other sample ages, reflecting either the burning of older wood or their residence within the system for an extended period of time. Nevertheless, 10 of the samples yielded ages in stratigraphic order, assuming the youngest dates from each strata are closest to the actual depositional age of a stratum, and we use these dates to construct a chronologic model to constrain the event ages.
From these dates, channel 4 ranges in age from at least as early as the first century C.E. up through the fourth century C.E., although the lowermost sandy gravel of channel 4 remains undated and may extend back into the latest part of the third millennium, as its age is only constrained by one sample (sample 364, see Table 2) taken from an older channel below channel 4 (Ⓔ Fig. S1c available in the electronic supplement).
Evidence for the oldest of the interpreted events, CH4-E6, is captured in the basal channel 4 deposits exposed in trench T37 (Figs. 6, Ⓔ S1d–e available in the electronic supplement). Ruptures are indicated by both upward termination of individual faults and folding, with angular unconformities identified that resulted from the folding events. Deposition of growth strata and possibly a colluvial wedge, along with fissures capped by undisturbed strata, support the interpretation of an event at this horizon. In the north wall of T37, units 490, 492, and 493 comprise a sandy gravel deposit that is strongly disrupted by many small faults and probable liquefaction. Units 491 and 494 are silty-clay layers and are strongly deformed at the bottom of the trench. This section is folded up onto the pressure ridge and generally maintains a similar thickness, indicating deformation took place after the deposition of unit 490. Units 480 through 489 thin onto the scarp/pressure ridge, indicating deposition after the deformation associated with event CH4-E6, and unit 489 caps many small faults that disrupt strata up through unit 490. Furthermore, units 480–489 thicken across the older folded strata, indicating postevent growth. Similar relationships are observed on the south wall of the T37, with units 480–489 capping many small faults and thinning onto the pressure ridge. These relationships argue that event CH4-E6 produced significant deformation at this site and was likely a relatively large earthquake.
Event CH4-E5 is interpreted from many small faults that break to the top of unit 480 and are capped by units 450–469. On the south wall of T37, stratigraphic growth is seen where units 450–460 thicken in the axis of a small syncline in the area of the greatest change in bedding dip, and these strata thin onto the fold scarp of the pressure ridge, thereby also supporting growth of the primary structure. However, the amount of deformation appears relatively minor when compared with that in event CH4-E6, so we interpret this as a smaller event.
Evidence for event CH4-E4 is observed in both trenches T37 and T33, and there is also evidence at the bottom of the south wall of T39. In T37, several small faults rupture up through units 450–469 and are capped by unbroken strata of units 440–449, and this relationship is consistent on both walls. Included within these many faults is a significant fissure exposed on the south wall that is either capped or filled by unit 449. Further, units 440–449 thin and pinch out onto the fold scarp indicating growth of the fold/pressure ridge after deposition of unit 450. In trench T33, minor faults displace strata up through unit 450 and appear capped by unit 440–449, which appeared as a single stratum in this exposure (Figs. 7, Ⓔ S1f available in the electronic supplement). Altogether, the evidence is strong for the occurrence of an event between deposition of units 449 and 450, although the amount of deformation appears less than that associated with event CH4-E6.
Evidence for the youngest three interpreted events in the channel 4 complex is observed primarily in trench T39 (Figs. 8, Ⓔ S1g–h available in the electronic supplement), although evidence for event CH4-E3 is also seen in T33. In fact, it is in T33 where stratigraphic separation can be demonstrated between events CH4-E4 and CH4-E3, with CH4-E4 breaking up through unit 450 and capped by the sandy-clay strata of units 440–449, and CH4-E3 breaking through 440–449 and into the bottom-most unit (439) of the gravelly sand package of units 430–439. The gravelly sand fills down into the fault, indicating the event occurred during deposition of this channel deposit and was later capped by similar gravelly sand units.
The same deposit (units 440–449) is identified in trench T37, where it is above the event horizon for CH4-E4, and it is exposed in trench T39, where CH4-E3 is interpreted at precisely the same level. On both walls of T39, many fault strands break into the 439–449 units package, with the sand and gravel filling into each fault. Many of the faults re- ruptured in subsequent events, but many did not. Many of the faults are capped by strata of units 430–438, which are similar to unit 439. These units also thicken in a shallow synclinal form that we interpret as produced by event CH4- E3. Finally, strata of units 430–438 thin onto and terminate against the fold scarp of the pressure ridge. One interesting aspect of the T39 exposure is that units 440–449 also appear to thicken into the same synclinal trough as the overlying strata of units 430–439. As these are the basal channel deposits exposed in this trench, this observation suggests that units 440–449 filled a synclinal depression adjacent to the linear pressure ridge, consistent with an event immediately prior to their deposition. This is stratigraphically consistent with event CH4-E4. Evidence for event CH4-E2 is weaker than that of some events, with several small faults terminating at the top of unit 430, and capped by unit 429. On the north wall of T39, units 425–429 thicken in the synclinal trough, arguing for fold growth after unit 430. Also on the north wall, there are several small faults filled with sediments of units 430– 438 (undetermined due to mixing?) that are capped by unbroken strata of unit 429. Collectively, we argue for an event horizon between units 429 and 430 that exhibits relatively minor overall deformation.
Finally, event CH4-E1 breaks up through unit 425 and into unit 420 on several faults on both walls of T39. There is no clear event horizon because the strata are relatively massive, but there is a thickening of unit 420 in the synclinal trough, arguing that the deformation is synchronous with the deposition of unit 420, which we consider as the approximate event horizon. It should be noted that each of the identified events is based on local evidence within the strata of channel 4, whereas there has clearly been substantial additional deformation of the section as a result of more recent ruptures. This is seen by the substantial warping and displacement of units 425 and all overlying strata, where preserved. In the capping lake clay, shears may be evident above recognizable faults that penetrate the base of the clay but are then obscured and completely transparent in the massive clay itself.
The ages of individual rupture events in the channel 4 complex are best constrained by 10 radiocarbon dates from samples taken from within the channel 4 deposits, age constraints from the younger channel 3 complex, and from a single charcoal sample from underneath the channel 4 complex. The lack of good age control on the basal channel 4 deposits in trench T37 limits our ability to precisely date event CH4-E6, although additional historical information allows some additional constraints. Using the OxCal model developed for all of channels 3 and 4 and adding the additional date from underneath channel 4, we calculate the probability distributions for each event from CH4-E6 through CH4-E1 (Fig. 5). Event CH4-E6 is the least well constrained because we have no dates from the basal faulted deposit, and therefore the age is only constrained by a sample that is likely considerably older, as it predates the channel 4 complex altogether. The probability distribution exhibits a boxcar distribution that places the age of the event between 400 B.C.E. and 100 C.E. However, as the basal deposits are clearly associated with channel 4 and are probably not substantially older than other basal deposits of channel 4, we assume the base of channel 4 is on the young side of this distribution, likely making this event fall within the range of the first century B.C.E. to first century C.E.
Events CH4-E2 through CH4-E5 all have direct radiocarbon control, although the strata between events CH4-E3 and CH4-E4 are only dated by a single sample. Nevertheless, the calculated ages for the events are as follows: event CH4-E5 dates between 137 and 206 C.E. with a peak probability at 169 ± 38 C.E.; event CH4-E4 dates between 165 and 236 C.E., with a peak probability at 204 ± 34 C.E.; event CH4-E3 dates between 250 and 310 C.E., with a peak distribution at 277 ± 30 C.E.; and event CH4-E2 dates between 269 and 329 C.E., with a peak probability at 299 ± 30 C.E.
Event CH4-E1 occurred during the deposition of unit 420, and this unit has only a single date that provides some age constraint. The sample was taken from near the upper boundary of this unit, so we assume the sample age postdates the timing of event CH4-E1 because unit 420 appears to thicken in the synclinal axis, which suggests the event occurred early in the deposition of unit 420. With this assumption in place, we calculate the age of event CH4-E1 to be in the range of 294–369 C.E., with a peak probability at 326 ± 36 C.E. If the date actually is in the faulted part of unit 420, then the date of event CH4-E1 may be as much as a century younger. However, it cannot be as young as the basal deposit of channel 3 unless both channels were active at the same time, which we consider unlikely.
We present evidence for eight events that pre-date the 1202 and 1759 C.E. earthquakes identified by Marco et al. (2005). The youngest of them, event CH3-E1, dates to the mid-seventh century C.E. Marco et al. mention 685 C.E. as an upper bound date of the offset units that recorded 2.7 m offset (Marco’s CH2, CH3). However, they do have younger dates from the same unit, so, assuming the older dates are residuals, this upper bound is pushed to the beginning of the eleventh century C.E.
There is no lower age constraint because they did not date samples from below those units. Based on the detrital carbon ages from the channel units discussed above, we consider the period between the first and eighth centuries C.E. to be well covered, with the exception of the first half of the fifth century C.E. (Fig. 9). The nearly continuous sedimentary record for that period recorded eight earthquakes, and it is reasonable to assume this is a complete record of surface-rupturing earthquakes on the JGF for that period. There may be a missing record for the period between the deposition of channel 2 and channel 1.
The historical catalogs mention a destructive earthquake and landslide in Tiberias, on the west coast of the lake, in 850–854 C.E. We do not have channel deposits with ages that cover the period and therefore cannot determine whether this earthquake ruptured at the Beteiha site.

Probability density functions for all paleoseismic events, based on the OxCal modeling. Historically known earthquakes are marked by gray lines. The age extent of each channel is marked by rectangles. There is an age uncertainty as to the age of the oldest units in channel 4 (units 490–499) marked by a dashed rectangle. Channel 1 refers to the channel complex studied by Marco et al. (2005).
JW: Shape of events at 1202 and 1759 on this plot understate uncertainty and present unrealistic probability distributions - because these two events came from older work where such a probability density vs. time plot wasn't generated. Event E.H. 1 dates to between 1020 and 1280 CE and very likely reflects the 1202 CE earthquake. Event E.H.2 struck after 1415 CE but it is not known how long after. It could have been a result of a number of different earthquakes such as the 1546, 1759, and 1837 earthquakes. Marco et al (2005) favored the 1759 CE earthquake but considered the possibility of other earthquakes.
Wechsler at al. (2014)
Table 3 and Figure 9 summarize the event ages obtained from the OxCal model and compare them with known historical earthquakes from that period. The uncertainty regarding the age of the oldest event in channel 4 makes finding the equivalent historical earthquake difficult; however, if indeed the lower part of channel 4 is closer in age to the rest of the channel units, then it is reasonable to assume the event occurred around the turn of the millennium and could correlate with the 31 B.C.E. earthquake of Herod’s time. Earlier candidate events include 92 B.C.E. and an earthquake in mid-second century B.C.E., but the location of those events is not clear (Table 3).

Table 3
Modeled Earthquake Dates and Possible Historical Earthquakes from the Same Period
Wechsler at al. (2014)
In the historical records there is no mention of any earthquake anywhere along the DST between 130–303 C.E., and the same is true for the Dead Sea cores (Kagan et al., 2011). Channel 4 units span this period of time, and in them we detected evidence for 3–4 events with model ages that over-lap this time period (events CH4-E5 through E2), and one of those events fall completely within the supposed seismic quiescence period (CH4-E4). It is well known that the historical earthquake record is incomplete in general, and specifically for that time period (Late Roman) during which the Roman empire was in decline, and the main historical texts describing this period are compilations written by historians who lived during later periods. It is therefore likely that a moderate earthquake could occur and not be recorded in either historical sources or by the Dead Sea seismites, yet cause sediment disruption and surface rupture along the JGF. An earthquake of magnitude ∼6–6:5 would rupture the surface at Bet-Zayda Valley and be detectable in trenches (e.g., Liu-Zeng et al., 2007) but not by Dead Sea seismites that are more than 100 km away (figure 9 of Kagan et al., 2011).
In the historical earthquakes catalog for the time period equivalent to the paleoseismic record, there are a few earthquakes with evidence of damage that are not centered along the JGF or in northern Israel. For example, the 551 C.E. earthquake is thought to have ruptured offshore Lebanon, on the Mount Lebanon Thrust (Elias et al., 2007). Yet we must consider the possibility that the rupture extended to the south, along the Roum fault (Darawcheh et al., 2000) and onto the JGF (Wechsler et al., 2009) or that what is described as one earthquake in the historical record was actually a series of events, one triggering the other, that were amalgamated in the historical record. Some of the ruptures recorded in the paleoseismic record could be either the rupture tip of an earthquake that originated on another fault segment (north or south of the site) or a triggered event on the JGF that would not merit its own historical mention. An example for an earthquake that originated to the north is the 1202 C.E. event, which was centered on the Yammouneh fault but also ruptured all the way south through the JGF and maybe even farther south.
Other known historical earthquakes that were not centered on the JGF, but which may have either ruptured to the Sea of Galilee or triggered slip or an aftershock include earthquakes in 33, 130, 303, 347, 363, 500, 634, and 660 C.E. (Fig. 9, Table 3). Considering that all detrital charcoal ages are maximum ages for the host deposit because the date reflects the growth and death of the original wood rather than its burning or deposition, some of the events we identify and date in the channel stratigraphy may have a slight bias toward an older age, in which case most may actually be represented in the historical record. In any case, a slight shift in event ages does not affect our overall conclusion that there was a cluster of earthquakes that produced surface rupture along the JGF during the first millennia C.E., followed by a relative dearth of events in the second millennia C.E.
In the past 2000 years, we observe evidence for a total of 10 surface-rupturing earthquakes, of which seven or eight events occurred in the first millennium, compared to just two in the second millennium C.E. This demonstrates that the fault is not behaving in a periodic fashion on a scale of 2000 years and several earthquake cycles. Based on model ages and taking into account the uncertainties in modeled event ages, the overall earthquake occurrence interval for the last 2 millennia is 199 ± 111 years. When computed separately for each millennium, it is 553 ± 32 years for the second millennium and 80 ± 106 for the first millennium (excluding CH4-E6, the oldest event, for which the lower age constraint is poor). These recurrence values do not account for differing earthquake magnitudes and demonstrate how the recurrence interval can be a misleading quantity when trying to estimate the regional earthquake risk.
The past 1000-year period appears deficient in strain release, starting from the Lebanese restraining bend (Däeron et al., 2007), through the Jordan Valley (Ferry et al., 2007) and southward to the Gulf of Aqaba (Klinger et al., 2000). Thus, in terms of moment release, most of the plate boundary has remained locked and has been accumulating elastic strain, as supported by recent GPS data (Sadeh et al., 2012). In contrast, the preceding 1200 years or so experienced a spate of earthquake activity, with large events along the Jordan Valley segment alone in 31 B.C.E., 363, 749, and 1033 C.E. (Guidoboni, 1994; Marco et al., 2003; Guidoboni and Comastri, 2005). Thus, the recurrence interval appears to vary by a factor of two to four during the historical period in the Jordan Valley, as well as at our site.
Studies of the recent seismic activity and frequency–magnitude relations in northern Israel suggest an estimated return period of 340 years for M >6 and 4500 for M >7 earthquakes using the Gutenberg–Richter (GR) relation, with a corresponding slip rate of 1.9 mm/yr (Shapira and Hofstetter, 2002). Hough and Avni (2009) combined available instrumental and historical earthquake data for the region and surmised that the GR distribution is valid for the DST. We compare the earthquake occurrence rate for the Sea of Galilee and Hula area from modern seismic records (Shapira et al., 2007) to the recurrence rate of large earthquakes based on paleoseismic records (Fig. 10), assuming a magnitude equal to or larger than 6.5 ± 0.5 for the surface-rupturing events. The result does not follow the GR distribution; rather it is similar to the characteristic earthquake distribution, with a discrepancy in the rate of small-magnitude earthquakes, as also observed on other faults (Hecker et al., 2013).
This discrepancy can be explained if we consider that the instrumental record is missing both moderate-to-large events and their aftershocks, which can decrease the a-value of the GR distribution by a factor of 2 (Page et al., 2008). A possible explanation for the earthquake behavior observed at the Beteiha site is that it is affected by its southern neighboring segments, as there is the possibility that earthquakes nucleating in the Jordan Valley can rupture through the Galilee stepover to the south of Bet-Zayda (Fig. 2). Ruptures originating from the north are also likely, as demonstrated by the 1202 earthquake (Marco et al., 2005). Another possibility is that large earthquakes on the Jordan Valley, Yammounneh, Roum, or Sergaya segments may trigger smaller aftershock events on the Jordan Gorge segment, in which case the historical record may tend to amalgamate any evidence for multiple, closely timed events into one large event.
The temporal variations in earthquake production may conform to a slip-predictable fault behavior, but more slip per event data are needed to determine the validity of the slip-predictable model for the JGF. A scenario of unzipping of the whole DST system, similar to the behavior of the North Anatolian fault (Stein et al., 1997), can account for periods of lesser activity. The nonperiodic behavior of the DST over the millennial timescale makes it more difficult to meaningfully predict the probability for a large earthquake soon. It may be that the 1995 M 7.3 Aqaba earthquake is the first in a sequence of future earthquakes that will soon be followed by several large earthquakes from south to north. It is also possible that a new cluster of moderate earthquakes was initiated with the October 1759 earthquake on the JGF, in which case we might expect several such events prior to a repeat of a 1202-type very large rupture. Regardless, in terms of moment release, most of the fault has remained locked and is accumulating elastic strain. Therefore, it is imperative to prepare for a large earthquake on the DST, which will occur sooner or later.
- Events for which Chat GPT made egregious errors are excluded
- from Chat GPT 5, 15 August 2025
- from Wechsler et al. (2014)
Paleoseismic trenches at the Bet-Zayda (Beteiha) site along the Jordan Gorge Fault (Dead Sea Transform), northern Israel. Lower channel-3 alluvium (units 380–384) observed on both trench walls.
Stratigraphy & Fault Observations
Units 380–384 are folded or tilted up to 30° westward and lie in direct contact with the fault. These deformed units are truncated and overlain by undeformed lower channel-3 alluvium (unit 375), which also caps secondary fault strands. This contact marks the surface-rupturing event horizon for CH3-E2.
Evidence
Tilted and folded channel-3 alluvium, truncation by undeformed deposits, and fault-related deformation all indicate a discrete surface-rupturing event.
Quantification (Age Modeling)
Radiocarbon dating of detrital charcoal from trench units, modeled with OxCal, yields an age of 505–593 C.E. with peak probability around 551 C.E., expressed as 551 ± 42 C.E. (2σ uncertainty).
Conclusion
Event CH3-E2 represents a clear surface-rupturing earthquake that deformed lower channel-3 alluvium and is reliably dated to the mid-6th century C.E., consistent with regional historical earthquake records.
- from Chat GPT 5, 13 August 2025
- from Wechsler et al. (2014)
CH3-E1 is recognized on both trench walls as upward termination of fault strands capped by unit 305. In T45N, a large fissure along a secondary fault strand contains rotated blocks encased in fissure-fill material, capped by unit 305. Another western fault strand also ruptures to this same stratigraphic level; both features are overlain by unfaulted unit 305, while other strands cut higher deposits from later earthquakes.
On the south wall, a single fault strand ruptures to unit 305 and is similarly capped. These relationships indicate a discrete surface-rupturing event late in the lower Channel 3 sequence. The deformation likely caused uplift within the fault zone’s central block, potentially damming the channel and contributing to disruption of overlying upper Channel 3 deposits.
Radiocarbon modelling (OxCal, IntCal09) constrains CH3-E1 to 619–684 CE, with a peak probability at 653 ± 36 CE (2σ). This event predates the documented 1202 CE and 1759 CE ruptures and falls within a cluster of first-millennium earthquakes along the JGF.
Seismic effects at the site include:
- Fault rupture across multiple strands within a 1–2 m-wide zone
- Formation of a large fissure with rotated coherent blocks
- Local uplift of the central fault-zone block, possibly causing channel damming
Dating is based on stratigraphic relationships and 14C ages from detrital charcoal, using the youngest in-sequence ages from each unit to avoid old-wood bias. The event occurred during active deposition of Channel 3 and before avulsion to younger Channel 2 deposits, likely coinciding with a lake-level rise that influenced sedimentation.
We resolved displacement on buried stream channels that record the past 3400 years of slip history for the Jordan Gorge (JGF) section of the Dead Sea fault in Israel.
Based on three-dimensional (3D) trenching, slip in the past millennium amounts to only 2.7 m, similar to that determined in previous studies, whereas the previous millennium experienced two to three times this amount of displacement with nearly 8 m of cumulative slip, indicating substantial short term variations in slip rate.
The slip rate averaged over the past 3400 years, as determined from 3D trenching, is 4.1 mm/yr, which agrees well with geodetic estimates of strain accumulation, as well as with longer-term geologic slip rate estimates.
Our results indicate that:
- the past 1200 years appear to significantly lack slip, which may portend a significant increase in future seismic activity
- short-term slip rates for the past two millennia have varied by more than a factor of two and suggest that past behavior is best characterized by clustering of earthquakes.
The Dead Sea Transform is the plate boundary fault between the Arabian and African plates (Quennell, 1956; Fig. 1a). Average strain accumulation, at about 4–6 mm/yr, appears to be consistent at different time scales, from decadal measurements (Le Beon et al., 2008; McClusky et al., 2003; Reilinger et al., 2006) to geological time scales (Le Beon et al., 2010, Le Beon et al., 2012).
Motion on the DST is believed to have begun in early Miocene time, accruing about 105 km of total slip (Freund et al., 1968; Garfunkel, 1981; Garfunkel et al., 1981). Although seismically active and the source of several large and destructive earthquakes in the historical period (Ambraseys, 2009; Amiran et al., 1994; Guidoboni, 1994), the largest onshore instrumentally recorded earthquake is the 1927 M6.1 Jericho earthquake, for which no indication of surface deformation was found (Shapira et al., 1993).
The JVF section extends from the Dead Sea pull-apart basin to the Sea of Galilee and is a relatively straight and simple section of the DST (Fig. 1b). The northern-most part of the JVF appears to experience surficial creep at about 2 mm/yr in the top 2 km, with elastic loading accounting for the rest of the 4–6 mm/yr slip rate (Hamiel et al., 2016). The Sea of Galilee represents another pull-apart basin at a left step in the DST, although the 1 km width of the step is considerably smaller than that of the Dead Sea.
Some historical earthquakes north of the Sea of Galilee are inferred to have not ruptured into the Jordan Valley; the 1202 CE earthquake produced over 2 m of slip where it enters the Sea from the north (Marco et al., 2005) but there is no evidence that it propagated south of the Sea of Galilee, as there is a lack of damage to the contemporaneous crusader castle of Belvoir (Fig. 1b), situated only 13 km south of the lake (Shmuel Marco, personal comm.). The combination of the releasing step and a component of creep on the Jordan Valley section immediately south of the step may account for the termination of the 1202 earthquake at the step-over, in spite of its relatively small size. As several other notable historical earthquakes appear to have been limited to the Jordan Valley (1033, 747/749 and 363 CE; Ambraseys, 2009, Amiran et al., 1994, Guidoboni, 1994), we consider the Sea of Galilee to represent a resilient segment boundary.
In Beteiha Valley, the site of our investigation, the JGF is straight and simple through Jordan Gorge to the Hula Basin, where the main fault bends or steps left to the Yammouneh fault, which continues up through the Bekka Valley. In the vicinity of Hula Basin, the DST splays into at least three major fault strands; the Roum fault on the west, the Yammouneh fault in the middle, and the Rachaya (Si'on) fault on the east. Slip is partitioned among these three strands, although the majority of strain accumulation is interpreted to continue up the Yammouneh fault (Daëron et al., 2004). North of Lebanon, the slip rate at geologic and decadal time scales seems to diverge with the latter being significantly slower (Alchalbi et al., 2010). Notably, Hamiel et al. (2016) document the absence of creep along the DST in the region of our study. From this, we infer that all slip measurements that we document on offset fluvial channels in our 3D trenching study are the result of coseismic slip events during earthquakes.
The work presented in this paper adds to a body of work presented in Marco et al. (2005) and Wechsler et al. (2014). Marco et al. (2005) resolved the timing and displacement for three channels that were offset in the 1202 and 1759 earthquakes, with displacements of about 2.2 and 0.5 m of left lateral movement, respectively. Wechsler et al. (2014) extended the record of the timing of past earthquakes to the previous millennium, documenting up to eight additional surface ruptures at the Beteiha site. In this paper, we use the radiocarbon data from Wechsler et al. (2014) (Table 2) along with the 3D excavations of fluvial channels to refine the earthquake history in the previous millennium, as well as to resolve displacement for most of the earthquake ruptures.
Fig. 1c summarizes the overall trench layout at the site. For detailed site description, see the “site description” section and Fig. 2a in Wechsler et al. (2014). Whereas Wechsler et al. (2014) described the evidence for earthquake history based on cross-fault stratigraphy of buried channels at the Beteiha site, here we focus on the results of our 3D trenching that follows these buried channels across the fault. Hence, the following sections describe only geometric relations between channels and channel offset measurements. Most of the dating information relies on results included in Wechsler et al. (2014) that are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Additional dates for older channel forms that were not described by Wechsler et al. (2014) were modeled separately and will be discussed in the text.
The stratigraphy at the Beteiha paleoseismic site is characterized by massively bedded lacustrine clay deposited during high-stands of the Sea of Galilee, into which several incised channels filled with gravel and sand were later buried (Fig. 2). We mapped seven buried channels; their ages and general descriptions are summarized in Table 1 and they are numbered according to their relative age from Ch1 (youngest) to Ch7 (oldest). Collectively, offset of these channels and lake deposits record the nearly complete earthquake history for the past 2000 years, and the displacement history for the past 4000 years.
In order to reconstruct the original form of channel flow across the fault, prior to their being offset by the lateral fault movement, we used Petrel™, a software program originally used for seismic interpretation in the oil and gas industry. We first built a 3D model of the site in Petrel™ using the trench logs and DGPS coordinates from survey data presented in Wechsler et al. (2014). We then mapped the channel forms and distinct sub-channel units (when applicable) from the logs as horizons and used the picked horizons to reconstruct curved surfaces that fit those horizons and represent the channel outline, by using the surface generation toolbox, constraining it to horizons extent and choosing the convergent interpolation algorithm (least squares with Briggs biharmonic filter) with 0.5 m × 0.5 m grid cells. This choice of all-purpose algorithm ensures that the generated surface passes as close to the original points with less than a specified distance (in this case – 10 cm), and we did not further smooth the results. We then used those surfaces to reconstruct the horizontal movements and to measure the amount of slip for each channel form we could map. In some cases, the edges of channels or units could not be determined, either due to faulting or due to erosion by younger sediments. In that case, the thalweg form was used exclusively. Offset estimates were made by first choosing the best fit for each reconstructed feature (thalweg, channel margin, or the general modeled channel shape) and using that value as the estimated best guess, with uncertainty margins (error).

Table 1
The channels found at the Beteiha site, with ages and general descriptions. (Modified from Wechsler et al., 2014).
Wechsler at al. (2018)
General descriptions of the channels are summarized in Table 1. Detailed trench logs are available in the E. supp. of this paper, Fig. S1 and unit descriptions are in Table S2. In the following section, we describe the channel reconstructions along with the channel ages and their relationships to the offsets, and then follow with probable correlations to historical earthquakes.
We define the Channel 1 complex as a group of channels that were previously excavated and described as CH2, CH3 and CH4 by Marco et al. (2005), the margins or portions of which were exposed in trenches T30 through T34. These channels contained pieces of detrital charcoal that yielded dates ranging from the 9th century to at least as young as the 14th century CE, when the channel complex was buried by lake deposits during an historically high period in the lake level of the Sea of Galilee. We only dated one sample from the upper part and close to the north margin of Channel 1 in trench T30, which yielded an age range of 1036–1165 CE, consistent with earlier results. For our analysis, we base our interpretations for the age of the channel complex on the dates published in Marco et al. (2005). The dates all indicate a 12–13th century CE event, which is most likely the 1202 CE earthquake based on the historical and archaeological evidence from Ateret (Ellenblum et al., 1998).
The Channel 1 units were extensively excavated in the previous trenching campaign and therefore the only usable feature for offset reconstruction in our study was the channel complex's northern margin, which cuts into the sediments of Channel 3 (examples seen in trench logs T30, T34, and T38, Figs. 2 and S1).
Reconstruction of the northern margin of channel 1 by projection of the channel edge into the fault results in a horizontal offset of 2.6 ± 0.3 m (Fig. 3a, b), consistent with the 2.7 m that was previously estimated by Marco et al. (2005). We therefore are in agreement as to both the timing and the horizontal offset for the two most recent events at the site. Vertical offset could not be determined in our study due to lack of piercing points, but was apparently minor based on the Marco et al. (2005) study where the channel margins were mapped and showed about 30 cm of down-to-the-west displacement.
Channel 2 is 7–10 m wide and has a well-defined channel form. It was exposed in trenches T30, T31, T33, T34 and T38, all of them parallel to the fault. The channel fill is mostly sandy to silty in texture, with a middle layer of dark clay with a fire-oxidized burned appearance in places. The units associated with channel 2 are numbered 200–299 (Fig. S1, Table S2), with increasing numbers indicating increasing stratigraphic depth.
Channel 2 cuts the north edge of channel 3 in all exposures except the easternmost one (T30). West of the fault, the gravelly-pebbly lower units of channel 3 can be seen under channel 2 (T33). Near the fault zone, the north edge of channel 2 is cut by a fault (T38W log).
Most of the dates from channel 2 infill fall within a short, 100-year time period centered around 700–720 CE, indicating that this channel represents a fairly short period of flow (for a discussion concerning inheritance in 14C ages, see Wechsler et al., 2014). We did not trench within channel 2 across the fault, but from cross-cutting relations, we inferred that channel 2 is younger than channel 3, as it cuts and erodes channel 3's northern edge.
Reconstruction of the shape and thalweg of channel 2 indicates a horizontal offset of 4.0 ± 0.6 m and a vertical displacement of about 0.6 m (Fig. 3c). We interpret the ~1.3 m of additional offset over that of the channel 1 complex to represent slip from at least one additional earthquake. However, as we have no exposure of channel 2 across the fault, we cannot preclude that this offset may represent slip from two events of smaller magnitude, similar to that which occurred with the 1759 earthquake.
Channel 3 is a gravelly-sandy channel complex that was exposed in several fault-parallel trenches (T30, T33, T34 and T38) and in one fault crossing trench (T45). The sub-units in channel 3 were numbered 300–399 for reference, with increasing numbers indicating increasing stratigraphic depth. The fault-crossing trench (T45, Figs. 3 and S1a, b in Wechsler et al., 2014) exposed the longitudinal profile of Channel 3, and faulted sediments in this exposure were used to study the earthquake history while channel 3 was an active stream (Wechsler et al., 2014). Channel 3 was divided into lower and upper units based on channel morphology, with the upper units (units 310–329) cutting into and eroding the lower units (units 330–399) east of the fault (Fig. 3 in Wechsler et al., 2014). The upper strata were not observed in fault contact on the west side of the fault. The youngest units (300–309) cap the faults on the west side and appear unrelated to the other upper channel 3 units. The strata in channel 3 vary in composition from large, rounded pebbles and cobbles at the base of individual sub-channels in the lower part of the section, to foreset-bedded gravelly sand and silty clay in the upper part. Furthermore, the upper part of channel 3 exhibits an anomalous trend on the east side of the fault zone, with indications of a local along-fault flow direction (N to S) (Fig. 3).
There are two event horizons recorded in Channel 3 sediments, named CH3-E1 and CH3-E2 by Wechsler et al. (2014). The older event, CH3-E2, occurs within lower Channel 3 sediments, and its age is well constrained by 14C ages that date the event to the sixth century CE. The younger event, CH3-E1, is capped by sandy units 300–309 and while we previously assumed that sample 99 from unit 323 represented an upper age bound for this event (Wechsler et al., 2014), a re-examination of the unit relations, and based on the measured reconstructed offset of upper channel 3 deposits, we now think that units 300–309 are in fact a much younger capping stratum, possibly even younger than Channel 2. Therefore, we conclude that unit 323 is below the event horizon of CH3-E1, and the event age is younger than previously inferred, as discussed below.
The shape of the upper units of Channel 3 forms a well-defined thalweg west of the fault, with distinctive cross-bedded sands and gravels (units 320–325). East of the fault, the channel form is not as well-defined, perhaps due to ponding and an avulsion of the channel in the fault-zone due to a slip event. The units are mapped in T30, T31, T33, T34, T38 and T45. The estimated horizontal offset is 4.0+0.5/−1.3 m (Fig. 3d) and the vertical offset is about 1 m. The only 14C sample that we dated from those units is the aforementioned sample 99, with an un-modeled calibrated age of 658–766 CE. This falls within the age range of Channel 2 and suggests that the upper strata in Channel 3 also cap the strata in Channel 2. The unit age along with the nearly identical horizontal offset of Channel 2 and upper Channel 3, made us re-evaluate the timing of event CH3-E1, or at least regard it as a much smaller event with insignificant horizontal offset. The channel avulsion to the north (from Channel 3 to Channel 2) and some difference in the amount of vertical offset between the two channels may indicate an additional event. However, the avulsion could have been caused by up-stream changes and the vertical separation may be partially apparent, due to stronger channelization of upper Channel 3. Consequently we modified the OxCal model of Wechsler et al. (2014) and add event CH2-E1, which post-dates Channel 2 and pre-dates Channel 1. This event is inferred from the difference in offsets between Channels 1 and 2, without cross-fault evidence of an event horizon, unless CH3-E1 is actually the same event. This proposition cannot be resolved due to the lack of dates from the capping units 300–309. We therefore consider CH3-E1 as a marginally possible small event that is dated post-Channel 3 but pre-Channel 2. The revised OxCal model for channels 2 and 3 is presented and compared with Wechsler et al. (2014) in Table 2 and a visual comparison in Fig. 4.
The thalweg of the lower units (390–399) was mapped in T30, T31, T33, and T38. These units are characterized by mud-supported gravel and rounded pebbles. Parts of the lower channel 3 deposits were eroded by Channel 2 but the channel form and thalweg could be reconstructed. The estimated horizontal offset for the thalweg gravel is 5.2+0.9/−0.3 m (Fig. 3e) and the vertical offset is about 1 m. Most of the vertical displacement occurs between trenches T34 and T38, which are only a meter apart. Those trenches are east of the main fault zone, and there is evidence of secondary faulting in those trenches that explains the vertical separation across a short distance, which is also observed in trench T45. Radiocarbon dates from those units yield mid-5th to mid-6th century CE ages. Based on the dates and stratigraphic relationships, we attribute the additional offset of the lower Channel 3 units to event CH3-E2, with about 1.2 m of horizontal slip.
The stratigraphic units in Channel 4 are numbered 400–499, from youngest to oldest, and represent nearly continuous deposition of sand, gravel and clayey sandy silt across the fault for several hundred years, as exposed in trenches T30, T31, T33, T34, T37, T39, T41, and T42. Captured within the strata of Channel 4, Wechsler et al. (2014) documented evidence for up to six paleo-earthquakes based on upward fault terminations, folding and angular unconformities. Channel 4 crossed the fault in an area where a long, linear and narrow pressure ridge is interpreted to have caused localized uplift east of the main fault, while west of the main fault, local subsidence caused the thickening of sediments (see logs for T37 and T39, Figs. 6 and 8 in Wechsler et al., 2014). There is a locally significant, down-to-the-west component of vertical motion across the entire fault zone, and local uplift along the long, linear pressure ridge within the fault zone, resulting in an apparent but lesser down-to-the-east component of vertical slip on the east side of the pressure ridge.
Channel 4 sediments range in age from at least as early as the 1st century CE up through the 4th century CE, although the lowermost sandy gravel of Channel 4 remains undated. Lower strata of Channel 4 may extend back into the latest part of the 3rd millennium BP, as its age is only constrained by one sample taken from an older channel below Channel 4 that dates to the middle of the 3rd millennium BP. In fault-parallel exposures, the strata are progressively older to the south on the west side of the fault based on off-lapping stratigraphic relationships revealed in fault-parallel trenches T33 and T41a. This is consistent with a model where the fault’s left-lateral motion during the period of channel flow created a progression of overlapping sub-channels west of the fault, from the oldest in the south to the youngest in the north (see Figs. 7 and S1c in Wechsler et al., 2014 which describe the log of T33E, and Fig. S1k).
East of the fault, Channel 4 units are divided into two different subchannels, located about 3 to 5 m apart. The southern channel corresponds to the older sandy-gravelly units of Channel 4 (units 490–499), which are intensely faulted, tilted and possibly eroded by younger units above them. The amount of horizontal offset for this package of sediments is difficult to determine due to their limited appearance west of the fault. We can estimate a horizontal offset of about 6.3 m based on channel reconstruction, but this should be considered a minimum value because of post-channel deformation and erosion (Fig. 5).
The northern channel corresponds to the whitish gravelly sand of units 430–439 west of the fault that are present above event CH4-E3 (Wechsler et al., 2014). This unit package is exposed in trench T39 across the fault, where it is faulted in several places, and in trenches T34 and T41, where it is tilted to the north. In trench T31, the westernmost exposure, the channel does not display any apparent tilting or folding. In order to reconstruct the flow of this sub-channel across the fault, we used both the thalweg shape based on the contact between the unit package and the sediments below it, and the thickness of the sediment package (isopach mapping), assuming that the thickest part of the channel represents the thalweg geometry before it was tilted or folded (Fig. 6). The location of the channel as inferred from the shape reconstruction yields a horizontal offset estimate of 7 ± 0.8 m, and the one inferred from the isopach reconstruction yields a larger offset estimate of 8.8 ± 0.8 m. The shape reconstruction may underestimate the amount of offset because of the tilting of the sediments west of the fault. On the other hand, the isopach reconstruction may be affected by erosion from the deposition of overlying units composed of sandy-gravelly clays, which will change the apparent thickness of the mapped sediments. Due to these uncertainties we assign a horizontal offset estimate of 7.9 ± 1.7 m (the large uncertainty reflects the large difference between the upper and lower offset estimates). The vertical offset for both sub-channels is about 1.5 m.
The offset estimate for the younger units of Channel 4 is larger than the estimate for the older units, which is untenable, especially given the evidence for four surface rupturing events between the two unit packages (Wechsler et al., 2014). This inconsistency is most likely due to the underestimation of offset (6.2 m) from the lower units due to erosion of units 490–499 west of the fault. The difference in horizontal offset between Channel 3 (4.0 +0.5/−1.3 m upper Ch3, 5.2 +0.9/−0.3 m lower Ch3) and Channel 4 (7.9 ± 1.7 m) is attributed to the two youngest events recorded in Channel 4 sediments, both dated to the mid-3rd to mid-4th century CE. There may be a younger event between CH4-E1 and CH3-E2, for which we do not see evidence in the trenches. This difference of 2.7 +2/−2.5 m of lateral offset could be divided between two or three surface ruptures.
Channel 5 was crossed by one trench (T30) east of the fault. It is gravel-filled, has a v-shaped form and is possibly man-made, as v-shaped excavations were common forms for early drainage canals. The channel fill was dated to the 1st–3rd century CE. We did not expose this channel west of the fault and do not discuss this channel further.
In many trenches (T30, T31, T33, T34, and T41) we encountered distinctive red-clay horizons, rich in burned organic material, which we speculate were caused by massive brush fires. East of the fault, trenches exposed a channel form filled with white gravel overlain by one or two burn horizons and separated by a clean purple-brown clay unit (for example, see log of trench T34 in Fig. S1g) but we could not find a corresponding well-defined channel west of the fault. This could be explained because of the limited depth of the western trenches. We did encounter a burned horizon (red layer) west of the fault, about 2 m deeper than its likely counterpart on the east side, but the lower gravels confined to a distinct channel form were apparently too deep and were not exposed in the trenches. The burned horizon appeared to be more of a surface rather than associated with a distinct channel. Consequently, we couldn't resolve a good piercing point to follow across the fault so we do not make an estimate of lateral displacement. The burned horizon did yield several charcoal samples, and the dates yielded ages that ranged between 2840 and 2330 years BP.
Channel 7 is located farther south with respect to channels 1 to 4, and was exposed in trenches T30, T46, T47, T48, T49 and T51. Its upper part was previously excavated by Marco et al. (2005) and dated to about 5 ka BP based on bulk carbon dating. We excavated a deeper, and therefore older, part of the same channel across the fault. The channel that we mapped flows in a different direction to that described by Marco et al. (2005) and we therefore assume that its flow was interrupted, possibly by an earthquake, and changed its course from a northwest-flow direction to a southwest flow direction. Reconstruction of the channel form yielded a well-constrained horizontal offset of 14.3 ± 1.3 m (Fig. 7). The vertical offset was only about 1 m, a lower value than for most of the other younger channels, and indeed in this locality the overall fault scarp was lower and consistent with a smaller vertical component. We attribute this to lateral variations in vertical slip along strike, although we cannot preclude the effects of erosion within the channel during successive displacements.

Tying the offsets to event ages. The events that were recognized by Wechsler et al. (2014) are represented by their age probability density functions (pdfs) as generated by Oxcal, and color coded by channel. For each event, an associated offset is attached. Colored boxes at the top represent the age extent of each channel's sediments. Historically known earthquakes are marked by grey lines. There is an age uncertainty as to the age of the oldest units in channel 4 (units 490–499) marked by a dashed rectangle. Inset – the result of the CVt calculation for the earthquake ages.
JW: Shape of events at 1202 and 1759 on this plot understate uncertainty and present unrealistic probability distributions - because these two events came from older work where such a probability density vs. time plot wasn't generated. Event E.H. 1 dates to between 1020 and 1280 CE and very likely reflects the 1202 CE earthquake. Event E.H.2 struck after 1415 CE but it is not known how long after. It could have been a result of a number of different earthquakes such as the 1546, 1759, and 1837 earthquakes. Marco et al (2005) favored the 1759 CE earthquake but considered the possibility of other earthquakes.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
Table 3 and Fig. 8 summarize the event ages and the offsets attributed to each event. The earthquake ages were used for calculating the mean recurrence time between events and the corresponding coefficient of variation on timing (CVt), using a Monte-Carlo approach: the probability density functions (pdfs) of event ages are sampled thousands of times and the mean μ, standard deviation σ and CVt are calculated on the sampled set (Biasi, 2013; Zielke et al., 2015). The resulting mean recurrence time is 190 years and the CVt is 1.05 (Fig. 8b), which implies elevated periods of seismic activity followed by periods of quiescence, or clustered behavior. In the following section we discuss our results in light of the historical record of earthquakes and the known paleoseismic record on neighboring faults.

Table 3
Modeled earthquake dates and offset estimates for each. Historical candidate earthquakes that could have caused the offset are listed based on modeled age.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
The 1759 CE and 1202 earthquakes have 0.5 and 2.2 m of horizontal displacement attributed to them, respectively; the 1202 offset is the largest slip-per-event recorded at the site. The pre-1202 offset of Channel 2 of about 1.3 m is interpreted to represent slip in one moderately large earthquake. Channel 3 records one moderately large slip event of about 1.2 m, and possibly one additional small earthquake based on the cross-fault stratigraphy (Wechsler et al., 2014), although the displacement is virtually the same as that of Channel 2 suggesting that events CH2-E1 and CH3-E1 are the same event as indicated by their nearly identical ages.
Deposits in Channel 4 record evidence for six earthquakes in addition to those of Channels 1 through 3 (Wechsler et al., 2014); two of them affected the upper units with resolved additional cumulative slip 2.7 +2/−2.5 m. Likely both are moderate in size, each with about 1.3 m of horizontal slip, although it is possible that one of the two events may have significantly larger offset, as in 1202 CE, while the other may be a smaller, 1759-style event. We cannot rule out the possibility that there may be >2 events that contributed to the difference in offset between channels 3 and 4, but we lack records for such events due to a disconformity in the deposition sequence.
From historical records and paleoseismology, the Yammouneh segment ruptured in 1202, between 405 and 945 CE and between 30 BCE and 469 CE (Daëron et al., 2007; Fig. 8). The penultimate Yammouneh rupture could be one of the mid-8th century earthquakes (CH2-E1 or CH3-E1, which are probably the same event). During that period, three distinct earthquakes occurred in the region and were felt from Syria in the north to Petra in the south (Fig. 1a): the first around 746 CE, the second in 749 CE and the third around 757 CE, and while the second of which most likely ruptured the Jordan Valley segment, the first or the third could have been associated with the Yammouneh fault (Ambraseys, 2005, 2009).
The JVF is interpreted to have ruptured in the earthquakes of 1033 CE, 749 and 363 based on both paleoseismic and historical records (Alfonsi et al., 2013, Ambraseys, 2009, Ferry et al., 2011, Fig. 8). Thus, the events with resolved offset at the Beteiha site could have from local earthquakes on the Jordan Gorge segment of the DST. This does not mean that the Jordan Gorge fault ruptured at precisely the same time, as historical records often refer to an earthquake as lasting for weeks or months and a large aftershock on the Jordan Gorge fault could have been amalgamated into the main-shock event. Thus, the observed displacements that we document here (CH2-E1) could have been coseismic with a well-known historical event or they could have been separate events that were induced or triggered by the larger regional events, although in this case the displacement may be smaller than the detection threshold of this study.
The first event documented by Wechsler et al. (2014) in channel 3 sediments (CH3-E1) is considered either quite small (less than 0.5 m offset) or the same as CH2-E1, as discussed above. The lack of datable material from the capping units prevents dating the CH3-E1 event horizon more accurately and distinguishing between it and CH2-E1. To resolve, we use the dates from Channel 2 as the upper bound and date it to the mid-7th to mid-8th century CE (Table 2, Fig. 4). The two candidate historical earthquakes for that period are the 632/634 CE and the 659/660 CE events. The 634 earthquake occurred concurrently with the appearance of a comet, causing great consternation yet little damage in the area (Ambraseys, 2009; Guidoboni, 1994). The 660 earthquake caused extensive damage in the Jordan valley and damage in settlements throughout the region. The earthquake most likely ruptured at least part of the JVF and had documented strong aftershocks (Ambraseys, 2009).
The second event seen in channel 3 sediments (CH3-E2) dates to the 6th century CE. During that period of time several earthquakes are known to have caused damage in the region, including the 502 CE and 551 earthquakes. Both earthquakes caused damage mostly on the Lebanese and Palestinian coast, and according to damage reports, the 551 event was the stronger of the two earthquakes (Ambraseys, 2009). Paleoseismic studies point to the offshore Lebanese thrust system as the most likely source of the 551 earthquake (Elias et al., 2007), and it is possible that such a large event (estimated magnitude 7.5, Ben-Menahem, 1979) may have triggered movement on the JGF via the Roum fault, where paleoseismic evidence places the most recent event sometime after 84–239 CE (Nemer and Meghraoui, 2006). The 4th–8th century period is relatively well documented historically, so a historically “missing” event with >1 m of slip is not likely (Zohar et al., 2016), so we interpret CH3-E2 as either associated with the 502 CE or 551 earthquakes.
The two youngest events in channel 4 sediments, CH4-E1 and E2, are associated with 2.7 +2/−2.5 m of offset. This amount may represent two events of comparable magnitude, similar to the channel 3 and channel 2 offsets, or it may represent one larger and one smaller event, similar to the 1202 and 1759 CE offsets. There may even be an additional event between channel 4 and channel 3, which contributes slip to the overall measured offset, although evidence for such an event is lacking due to a gap in the sediment record (Fig. 8). Candidate earthquakes that caused the offset include historical events in the 303, 347 and 363 CE. The 303 earthquake caused damage mostly along the southern Lebanese coast whereas the 347 earthquake caused local damage that is only reported from Beirut, Lebanon. The 363 event was actually 2 earthquakes that caused extensive damage in the region, from Aqaba and Petra, Jordan, south of the Dead-Sea (Klinger et al., 2015) all the way to Paneas, north of the Sea of Galilee, and most likely one of them ruptured the Jordan Valley segment. Archaeological excavations in Sussita, east of the Sea of Galilee, revealed major destruction of an Odeion and Roman basilica, where coins found beneath the collapsed structures are dated to as late as 362 CE (Wechsler and Marco, 2017). It is reasonable to assume that the 363 earthquake rupture reached as far north as the Beteiha valley and that it is part of the measured 2.7 +2/−2.5 m offset of the youngest two events in channel 4.
In order to quantify the variability of slip per earthquake, we used the measured offset estimates and error margins for the past 6 events (excluding the doubtful CH3-E1) to calculate the coefficient of variation on displacement (CVs), using the same approach we used for the CVt calculations. The slip in events CH4-E1 and CH4-E2 together was assumed to sum up to a total of 2.7 m, but in one sampling run we set one event with 2.2 m of slip and the other with only 0.5 m, while in the second run we set both events to have 1.3 m of slip each. Lastly, we also calculated CVs for the last 4 events only. In all cases, the calculated mean slip-per-event was 1.2–1.3 m, with a CVs of 0.5–0.65, which implies fairly characteristically-sized slip events. Zielke et al. (2015) attribute the low variability of slip to the nature of the dataset they examined (offset geomorphic structures along the fault) and its inability to record offsets that are smaller than some threshold (approx. 1 m).
The higher values of CVs in this study may represent a difference in resolving power, and because we were able to resolve smaller offsets and attribute them to single events our dataset includes more variability. The observation of Zielke et al. (2015) that CVs is smaller than CVt is valid for this study as well. This likely reflects a fundamental characteristic of the JGF, which is seemingly unable to produce large offsets per event such as recorded on neighboring faults such as the Yammouneh fault to the north.
The variability in the amount of slip associated with the different events at the Beteiha site, most of which are about 1.2–1.3 m but which range from 0.5 m to > 2 m, may reflect the different sources of earthquakes on different segments. Based on the historical record combined with the paleoseismic data, the JGF segment appears capable of rupturing in conjunction with its northern and southern neighbors as well as by itself. For example, the 1202 CE earthquake that ruptured primarily the Yammouneh segment in the Bekka Valley (Daëron et al., 2007) also produced slip as far south as the Sea of Galilee, with 2.2 m at the Beteiha site. The 1759 CE earthquake of October (M6.6) ruptured along the Jordan Gorge and the Rachaya faults, and its epicenter was probably located south of the Hula basin (Ambraseys et al., 1994; Gomez et al., 2003; Gomez et al., 2001; Nemer et al., 2008; Sbeinati et al., 2005), and produced 0.5 m of slip at both the Beteiha site (Marco et al., 2005) and the Ateret fortress (Ellenblum et al., 1998).
We interpret the ~1.3 m of offset of Channel 2 and upper Channel 3 to have occurred in the mid-8th century CE. To the south, the 749 CE earthquake is interpreted to have ruptured the Jordan Valley segment based on historical reports of damage and paleoseismology (Ferry et al., 2011). Our mid-8th century event could be synchronous with the large (M7.5) 749 Jordan Valley earthquake, which extends the northern limit for this event, or it could have ruptured as a triggered event and been amalgamated into the 749 CE event, or it may represent rupture in the 746 CE or 757 CE events, both of which are interpreted to have ruptured faults north of the Beteiha Valley (Ambraseys, 2009).

Figure 9
Coulomb Stress modeling (using Coulomb 3.3, Toda et al., 2011) of the area using a simplified fault model of the DST from the Jordan Valley segment to the Lebanese restraining bend (not including the Mt. Lebanon thrust).
In each model, an earthquake was applied on one fault (marked in dashed red line), based on rupture estimates for the last earthquake on that fault (left-lateral strike slip). The resulting Coulomb Stress change on the neighboring faults was calculated.
See Table S1 for model parameters of each run.
Wechsler at al. (2018)
In order to test the feasibility of multi-segment ruptures on the JGF, a simplified model of the DST from the Jordan Valley segment to the Lebanese restraining bend (not including the Mt. Lebanon thrust) was constructed for Coulomb stress modeling. Fault orientations, dips and locking depths were taken from the literature or assumed based on surface geometry and topography (Table S1). The kinematics of the fault movement were estimated based on existing literature and fault geometry (see Table S1). We did not incorporate a creeping section along the northern JVF, to keep the model simple. In each model run, a rupture was initiated on one fault, based on displacement estimates for the last earthquake on that fault. The resulting Coulomb Stress change on the neighboring faults was calculated using Coulomb 3.3 code (Toda et al., 2011). For comparison, the typical stress drop in a surface-rupturing earthquake can range between 0.5 and 50 MPa (Allmann and Shearer, 2009), and an increase of as little as 0.1 MPa (1 Bar) in the Coulomb stress is considered in the literature as effective for triggering earthquakes (King et al., 1994).
It was found that the stress increases by at least 0.1–0.2 MPa on the JGF in all cases of rupture on nearby faults, and most strongly for large events originating on the Yammouneh or Jordan Valley faults (Fig. 9). Additionally, the model demonstrated that a large earthquake on the Yammouneh fault would un-stress and therefore delay the other Lebanese faults. The coulomb stress transfer model, while being very simple, still shows how the JGF location makes it primed for offset in the event of rupture of a nearby fault, which explains the relatively large number of moderate events observed from the trench data.
Ellenblum et al. (1998, 2015) excavated the archaeological site of Ateret (Vadum Iacub), which was constructed across the JGF about 12 km north of our paleoseismic site. They found an early Hellenistic (333–143 BCE) wall that was offset 6 m, and another late Hellenistic (143–63 BCE) wall that was estimated to be offset only 3.5 m. At our site, the cumulative offset for the last 1700 years is at least 7 m, and based on the overall slip rate it should be about 8–9 m for Hellenistic period features. It would be expected that the two sites would have similar amounts of displacement for similar amounts of time, yet the Ateret site appears to accommodate a lesser amount of cumulative slip, even ignoring the extremely low estimated offset of the late Hellenistic wall. This is also true for the 1202 CE rupture offset, estimated to be 1.5 m at Ateret, versus 2.2 m at the Beteiha site.
This difference of ~30% less slip at the Ateret site may be explained by its location astride a branch of the JGF which is near a trifurcation point and some of the offset is taken by other branches (Fig. 9). A normal fault branches to the north-west immediately south of the archaeological site, causing a left bend in the Jordan River and offsetting Pleistocene strata. Additionally, a fault strand parallel to the Ateret branch and marked as the main continuation of the JGF northward is mapped just north of the junction, east of the site (Fig. 10). Those faults and perhaps other unknown fault(s) that are immediately adjacent to the archaeological site may accommodate some of the offset. This is supported by GPS campaign data across the JGF south of the Ateret site and the branching point, which indicate a locked fault with a slip rate of 4.1 ± 0.8 mm/yr (Hamiel et al., 2016), in agreement with the paleoseismic slip estimates from the Beteiha site (this study).
We resolved slip per event for the past six surface ruptures at the Beteiha paleoseismic site, with slip estimates ranging from 0.5 to 2.2 m, a factor of more than four (Table 3) and a corresponding CVs value of 0.5–0.6. Although at first glance, this range of offsets argues against the characteristic earthquake model (Schwartz and Coppersmith, 1984), when local and regional structure is considered, the model may still apply in some cases. For instance, the largest displacement is associated with the 1202 earthquake, which is known to have ruptured the Bekka Valley with several meters of displacement (Daëron et al., 2007).
The Beteiha site may be near the southern terminus of the 1202 rupture, although it is not known whether the rupture terminated in the Sea of Galilee or propagated as far south as the Jordan Valley. As mentioned earlier, the crusader fortress of Belvoir, located only 13 km south of the Sea of Galilee, was not damaged in the 1202 earthquake indicating that rupture did likely stop at the Galilee releasing step. In contrast, damage from the October 1759 earthquake rupture is centered on the Jordan Gorge fault (Ambraseys and Barazangi, 1989; Sieberg, 1932), and 50 cm of offset at Ateret is attributed to this event, suggesting that this event ruptured only the short, 40 km-long segment of the DST that includes the Jordan Gorge and the east side of the Hula Valley until the NE-bend in the fault, or perhaps even only the 20 km long JGF.
Potentially, this earthquake may have also ruptured the Rachaya fault in Lebanon (Daëron et al., 2005), although conversely, it is possible that the Rachaya ruptured together with the Serghaya fault in the larger November 1759 event (Gomez et al., 2003). Thus, one plausible model is that small, half-meter events may represent rupture of only the 20 km-long JGF, whereas the large 1.2–2.2 offsets represent displacement in larger earthquakes that ruptured either to the north (1202 CE) or south (749, 363 CE).
In transition zones between simple and complex sections of plate boundary faults, repeating earthquakes with similar displacement and rupture extent (i.e., characteristic earthquakes) may be an over-simplified model that should not really be expected to conform to reality. It should be noted that resolving 0.5 m of slip is generally beyond the accuracy limits of this study, so while there may be other 1759-style rupture events, they have not been detected. It is possible that one or more of the channel 4 events are of the smaller 1759-offset type.
We estimate a moderate-term slip rate for this section of the DST from the offset of Channel 7. Calibrated ages for Channel 7 are between 4200 and 3400 years BP (Table 2). Sample 463 is from the bottom of the channel and does not represent the age of the channel deposits (T49E trench log, Fig. S2). We cannot distinguish between the offset of lower and upper units, but assuming that the youngest channel units are offset the same amount as the channel's thalweg, the calculated slip-rate on the fault for the last four millennia is 4.1+0.4/−1.0 mm/yr. This rate assumes that the offset mostly postdates the younger units, which is reasonable as there is no evidence of flow along the fault indicating that the channel had already been abandoned when it was offset. This rate is faster than the estimated 3 mm/yr of Marco et al. (2005), but they used bulk dating which was likely affected by the inheritance problem at the site (see discussion in Wechsler et al., 2014), yielding older apparent ages, and therefore slower apparent rates.
To assess short-term variations in slip rate, we used a Monte-Carlo based slip rate calculator (Styron, 2015) to estimate the overall slip-rate, and to explore the slip rate over different periods of time (Fig. 11). The overall slip-rate came out 4.0 mm/yr, in agreement with our estimate based on the offset of Channel 7 alone. Examining the 1st and 2nd millennia separately revealed a marked difference in strain release, so much so that had we inspected the site a thousand years ago we would have calculated a rate of over 8 mm/yr for the previous millennium. Thus, the slip rate determined at the Beteiha site depends on the duration over which it is averaged, because it is based on a series of discrete offsets associated with individual earthquakes. Hence, one study may underestimate the slip-rate on a fault, while another might overestimate it, depending on whether that fault had recently undergone a hiatus or a spurt of activity. For example, Marco et al. (2005) inferred a 3 mm/yr rate for the past 800 years at the site, which we confirm, whereas we also document slip rates of 4.7 mm/yr and 4.1 mm/yr for the past 1700 and 3400 years, respectively. Conversely, both the regional decadal GPS rate (Hamiel et al., 2016) and the geologic rate (Daëron et al., 2004) are consistent with our longest-term rate, as observed in most cases along strike-slip faults (Meade et al., 2013). Similar short-period discrepancies between slip rates based on only a few discrete offsets versus rates averaged over longer time periods and/or at regional scale have been observed elsewhere (Dolan et al., 2016; Onderdonk et al., 2015; Rockwell et al., 2015; Weldon et al., 2004), suggesting that the general relation between the amount of stress released by a single event and the average stress release is not necessarily straightforward.
As a thought experiment, one should wonder if a regional GPS rate established during the last 800 years would necessarily be different from a regional GPS rate established for the previous millennium, although rates established from earthquake offsets are different. A positive answer would imply significant changes over short periods of time for the deeper processes that drive long-term plate tectonics deformation rates, which seems unlikely. Eventually, this raises the question of how long should a record be in order to best estimate the long-term fault behavior, and how does that affect fault risk assessment for slow and intermediate faults, where long-term records can be difficult to obtain. Site location can also be an important factor, as seen by the tendency of the JGF to rupture in conjunction with its neighboring segments. Moreover, the interval from which a short record is sampled may bias the interpretation of average recurrence interval to be as much as a factor of two too high or too low, as seen in the Hog Lake record on the San Jacinto fault in California during the 1st millennium vs. the 2nd millennium (Rockwell et al., 2015). These observations support the notion that slip rates, as well as recurrence intervals, determined from a series of singular earthquakes should be considered with large uncertainty unless the cumulative offset has been produced by a large number of events, and supported by multiple sites.
There are several major observations resulting from this study that deserve discussion. First, despite the agreement between GPS and the longer-term geological slip rates on the DST, the past 800 years appear deficient in strain release everywhere from the Gulf of Aqaba to Lebanon. Thus, in terms of moment release, most of the DST appears to have remained locked and is accumulating elastic strain. In contrast, the preceding 1200 years or so at the Beteiha site experienced a spate of slip between about 300 and 750 CE (Fig. 12). During this 450 year “cluster”, about 5 m of slip was released along the Jordan Gorge fault at the Beteiha site, yielding a short-term slip rate that exceeds a cm/yr. Thus, the slip rate on the JGF, as well as the return period, appears to have varied by a factor of two to four during the historical period, yielding a coefficient of variation (CVt) of 1.05 on the recurrence interval, which reflects that variability. This isn't to say that the far-field strain loading has varied, but rather, that strain release in the form of fault slip has varied by a factor of two to four. This behavior is expected when the CVt is significantly above zero, as in California where Onderdonk et al. (2015) document a factor of two variabilities in short-term slip rate for the northern San Jacinto fault, which expresses a CVt of about 0.6.
The CVt is a common measure of the variability in earthquake recurrence, and in California, the CVt derived from long (> 8 events) records on sections of the San Andreas fault system yield values in the 0.4 to 0.8 range, with an average close to 0.6 (Biasi and Scharer, 2015). The value of the CVt can vary from 0 to CVt > 1, with specific ranges of CVt values corresponding to different timing behaviors for earthquake series, from fully periodic to random to clustered (Zielke et al., 2015). The CVt tends to be in the range of about 0.4 to 0.7 on major transform faults (Biasi et al., 2002, 2015; Biasi, 2013; Biasi and Scharer, 2015; Rockwell et al., 2001, 2009, 2015), which is still a quasi-periodic behavior but implies a nonperiodic component. In contrast, a study of the activity of the Alpine fault in the central part of New-Zealand yielded a low CVt value of 0.33 attributed to its simple geometry and high slip-rate (Berryman et al., 2012).
The CVt is important because it affects our ability to forecast future earthquakes based on the timing of occurrence of past events (Field et al., 2009, 2015, WGCEP, 2007). In some regions, the relatively high CVt of ~0.6–0.7 may be explained by Coulomb stress loading, where a large earthquake on one fault advances or retards the timing of earthquakes on nearby faults in a complex fault array. It could also be (partly) explained by the uncertainties in dating, as paleoseismology rarely can determine the timing of a past earthquake to better than a century, so what may appear as randomly distributed earthquakes on a fault system may mask a more clustered or ordered sequence of events. This is particularly a problem on fast-moving faults, such as the San Andreas in California and the North Anatolian fault in Turkey, as the probability distributions of events ages commonly overlap because of short time intervals between successive earthquakes, dating uncertainties, and the 14C calibration curve.
We interpret the high CVs and CVt values as a result of the JGF interacting with its northern and southern neighboring segments, so that earthquakes nucleating to the south or to the north can either propagate into or trigger a smaller event on the JGF; the first case may have occurred in the 1202 and 1759 earthquakes and possibly also in the 551 earthquake, whereas the second case may be represented by the 363 and 749 earthquakes. This effect may result from the fact that the Beteiha site lies along a short, straight section of the DST, with relatively simple fault segments separated by releasing steps to the south and north. The northern Jordan Valley section of the DST, just south of the Sea of Galilee, exhibits some surficial creep at about half of the long-term slip rate, which suggests that the combination of the relatively small (~1 km) step in the DST at the Sea combined with the partially creeping section at the north end of the Jordan Valley may, together, be considered a potentially weak segment boundary.
To the north of our site, the DST splays into at least three major faults, each of which have produced historical earthquakes (1202 on the Yammouneh fault, 1759 on the Jordan Gorge-Rachaya-Sergaya fault system, and 1837 on the Roum fault; Fig. 1b). This factor, combined with the releasing bend that produced Hula Basin north of Jordan Gorge (Fig. 1b), suggests that the Jordan Gorge section of the DST may fail on its own in moderate earthquakes, as apparently happened in October 1759.
The model that best fits the observed data for the Jordan Gorge fault is a “weak segment model”, where the relatively short (20 km) JGF is bound by releasing steps (one with a component of creep) that fails on its own in moderate earthquakes or ruptures with adjacent segments. The outcome is irregular earthquake recurrence with varying amounts of displacement, resulting in significant short-term variations in slip rate. Over many earthquake cycles (8–10 or more), however, the slip rate averages out and agrees well with the geodetic and long-term geologic rates. This behavior is neither characteristic nor predictable and makes seismic hazard assessment in northern Israel more difficult. Nevertheless, as it has been over 800 years since the last large rupture, and the average recurrence interval for the past 2000 years is on the order of 250–300 years, it appears that the DST from the JGF southward to perhaps the Arava Valley is ripe for failure and should be considered as a likely source for a damaging earthquake in the geologic near-term.
Hamiel, Y., Piatibratova, O., & Mizrahi, Y. (2016). Creep along the northern Jordan Valley section of the Dead Sea Fault
. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(6), 2494–2501. - open access
Marco, S., et al. (2005). "Late Holocene activity of the Dead Sea Transform revealed in 3D palaeoseismic trenches on the Jordan Gorge segment." Earth and Planetary Science Letters 234(1-2): 189-205.
Wechsler, N. (2005). Paleoseismology in the Eastern Kinnarot Basin, Dead Sea Transform, Tel Aviv University.
Wechsler, N., et al. (2014). "A Paleoseismic Record of Earthquakes for the Dead Sea Transform Fault between the
First and Seventh Centuries C.E.: Nonperiodic Behavior of a Plate Boundary Fault." Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. - open access at academia.edu
Electronic Supplement to
Wechsler, N., et al. (2014). "A Paleoseismic Record of Earthquakes for the Dead Sea Transform Fault between the
First and Seventh Centuries C.E.: Nonperiodic Behavior of a Plate Boundary Fault." Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. - at BSSA
Wechsler, N., et al. (2018). "Variable slip-rate and slip-per-event on a plate boundary fault: The Dead Sea fault in northern Israel." Tectonophysics 722.
Tom Rockwell (personal correspondence, 2022) relates the following:
In our 2014 paper, we show a map of the site, which includes our original locator trench - T30 - in which we searched for channels. For Neta's post-doc work, we focused on the northern set of channels, but look at the ages of the southern several channels - they fill in time periods that we didn't investigate. I believe that area is still open for study - was a bit salty for the farmers.
T30 Trench Log
from Tom Rockwell (email 30 March 2022)
- download these files into Google Earth on your phone, tablet, or computer
- Google Earth download page
| kmz | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Right Click to download | Bet Zeyda Paleoseismic file | various |







