Tell Ya'amun
| Transliterated Name | Source | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Tell Ya'amun | Arabic | تل ياعَمون |
- from Chat GPT 5.2, 1 March 2026
- Sources: Rose et al. (2007)
- Location Map from
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website

 Location Map
Location Map
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website
- Location Map from
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website

 Location Map
Location Map
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website
- Church Plan from
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website

 Location Map
Location Map
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website
- Church Plan from
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website

 Location Map
Location Map
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website
To the south of the previously excavated Byzantine church, we uncovered two rooms with walls surviving to a height of 2 m. Each room has a door opening onto the flat stone pavement that separates these rooms from the church. The mosaic floors are preserved along with the bases of archways for ceiling supports. Coins, architectural stratigraphy, and style of mosaic decoration all indicate contemporaneity between the sixth-century church and rooms. The rooms were modified during the Umayyad period when the mosaic floor was repaired with flat paving stones along the damaged edges and some walls were reconstructed with differently sized stones. Further modification and re-use occurred during the Ayyubid-Mamluk period when new walls were built directly on top of the mosaic floors. The mosaic floor of the east room is extensively dented by collapsed wall stones, which suggests that use ended with destruction caused by an earthquake.
| Effect | Location | Figure | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dented Floor suggesting wall collapse | East room of Byzantine church
 Location Map
Location MapTell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website |
|
- Earthquake Archeological Effects chart
of Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
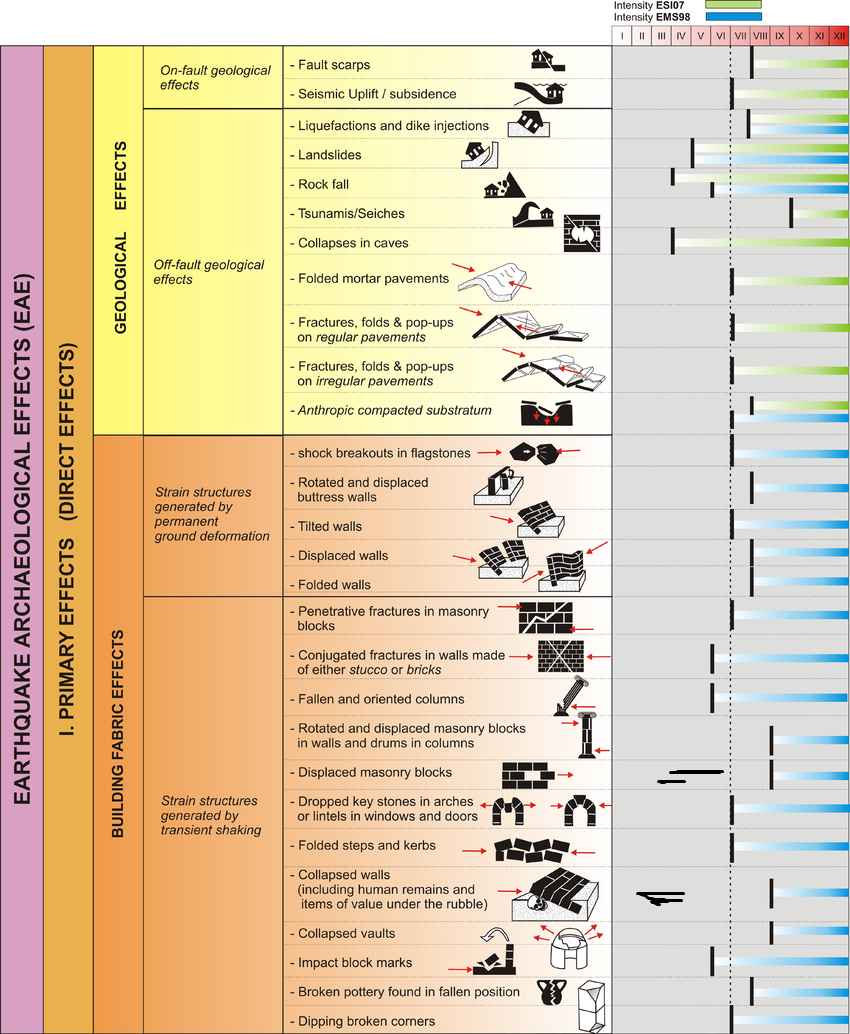
 Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
| Effect | Location | Figure | Comments | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dented Floor suggesting wall collapse | East room of Byzantine church
 Location Map
Location MapTell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations website |
|
VIII+ |
Rose, J. et al. (2007) Trade and the Acquisition of Wealth in Rural Late Antique North Jordan, SHAJ 9 – mentions Tell Ya'amun but does not discuss earthquakes
Savage, S., Zamora, K., and Keller, D. (2003) Archaeology in Jordan, 2002 Season, American Journal of Archaeology 107: 449–475
Turshan, Y. and Nassar, M. (2011) A Mosaic of the Book of Daniel in the Ya'amun Church, Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies 51: 340–349 – no discussion of earthquakes
Jordan Excavations including Tell Ya'amun, Dr. Jordan Rose
Tell Ya'amun 2002 Excavations, Dr. Jordan Rose
Tell Ya'amun 2004 Excavations, Dr. Jordan Rose – notes that the wine-press “seems to have been destroyed by earthquakes” but provides no associated dates
- download these files into Google Earth on your phone, tablet, or computer
- Google Earth download page
| kmz | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Right Click to download | Master kmz file | various |
