Horbat Be'er Shema
| Transliterated Name | Source | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Horbat Be'er Shema | Hebrew | |
| Be'er Shema | Hebrew | |
| Birsama | Greek | Βιρσαμίς |
| Castellum Versaminum | Latin | |
| Berzama | Greek | Βερζαμμα |
ChatGPT Introduction
- from Chat GPT 5, 31 August 2025
- sources: Wikipedia – Be’er Shema, Jewish Virtual Library – Archaeology in Israel: Be’er Shema - Church of St. Stephen
Excavations have uncovered remains of houses, public buildings, agricultural installations, and especially a large Byzantine synagogue dated to the 4th–5th century CE. The synagogue’s mosaic floor, decorated with geometric patterns, menorahs, and dedicatory inscriptions, is one of the most important Jewish mosaics of the region. It provides valuable evidence of Jewish community life in the southern frontier during Byzantine rule.
The settlement appears to have been abandoned by the early Islamic period, possibly due to changing economic and political conditions in the Negev. Today, Horbat Be’er Shema stands as an important example of the cultural and religious landscape of Byzantine Palestine, illustrating both regional trade networks and the vitality of Jewish life in the late antique Negev.
Birsama in the Notitia Dignitatum
- from Chat GPT 5, 31 August 2025
- sources: Erickson-Gini, Dolinka & Shilov (2015), Dolinka (2015)
The presence of Birsama in this high-level military register underscores its importance as more than a local settlement. It was integrated into the Roman imperial infrastructure, tied to both taxation and regional security. Together with corroborating sources such as the *Codex Theodosianus* and ecclesiastical writings, the entry in the *Notitia Dignitatum* reveals that Be’er Shema functioned simultaneously as a fortified station, an administrative hub, and eventually a thriving Christian diocese in the Late Antique period.
Maps, Aerial Views, Plans, and Photos
Maps
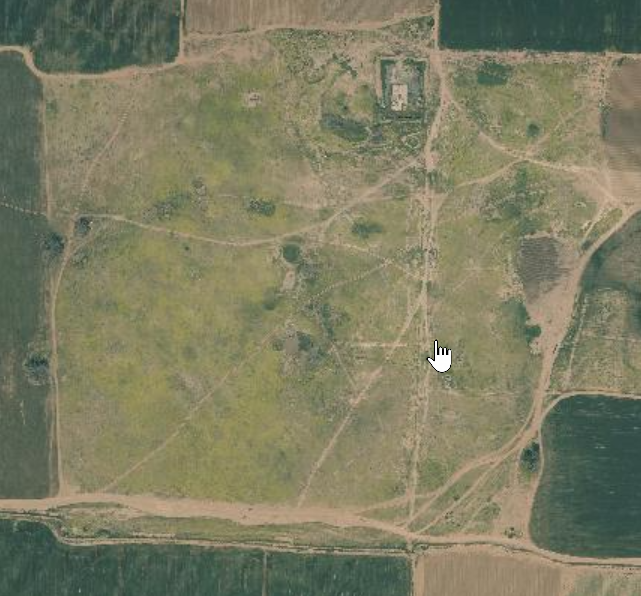
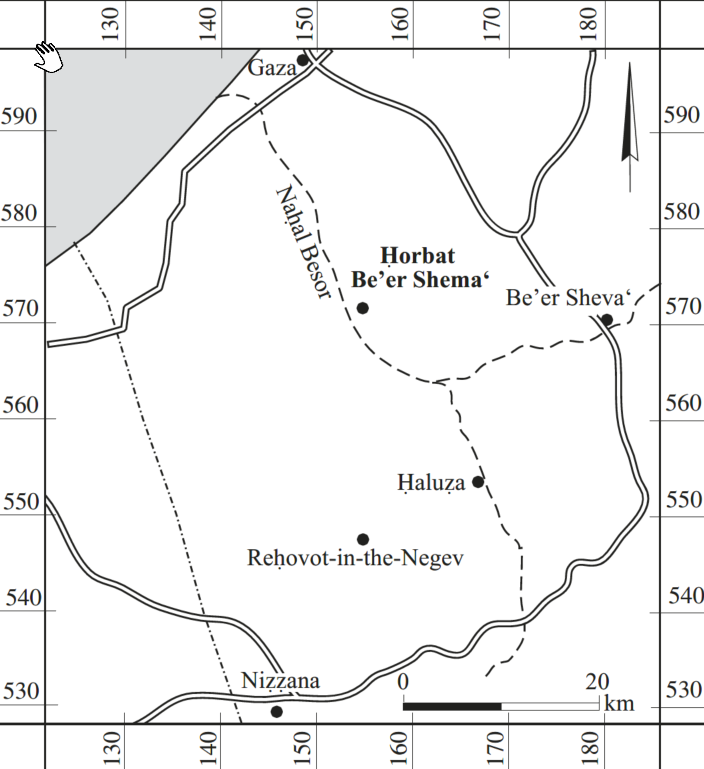
- Fig. 1 Location map
from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
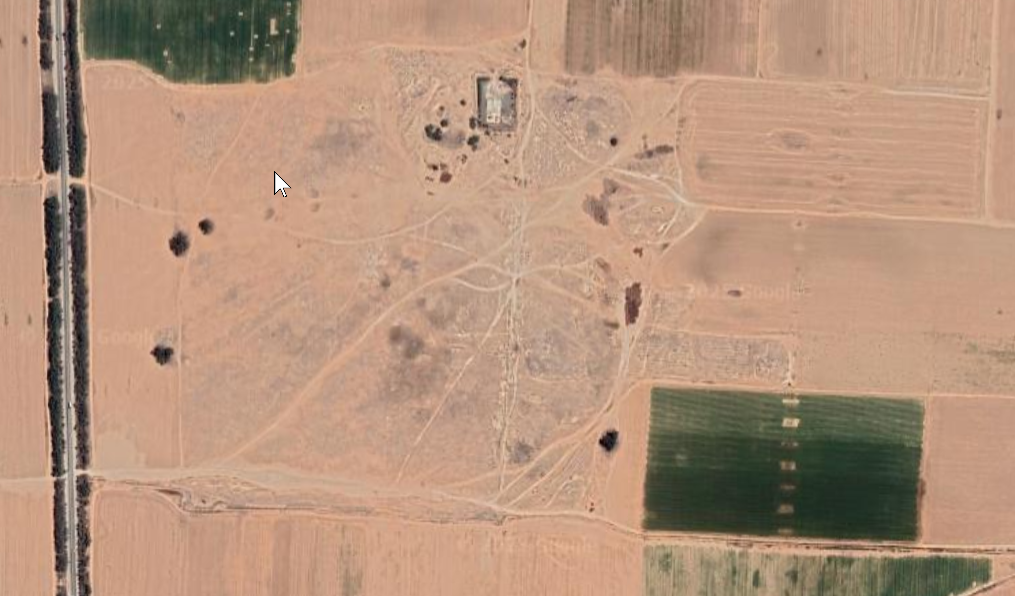
Aerial Views
Plans
Site Plans
Normal Size
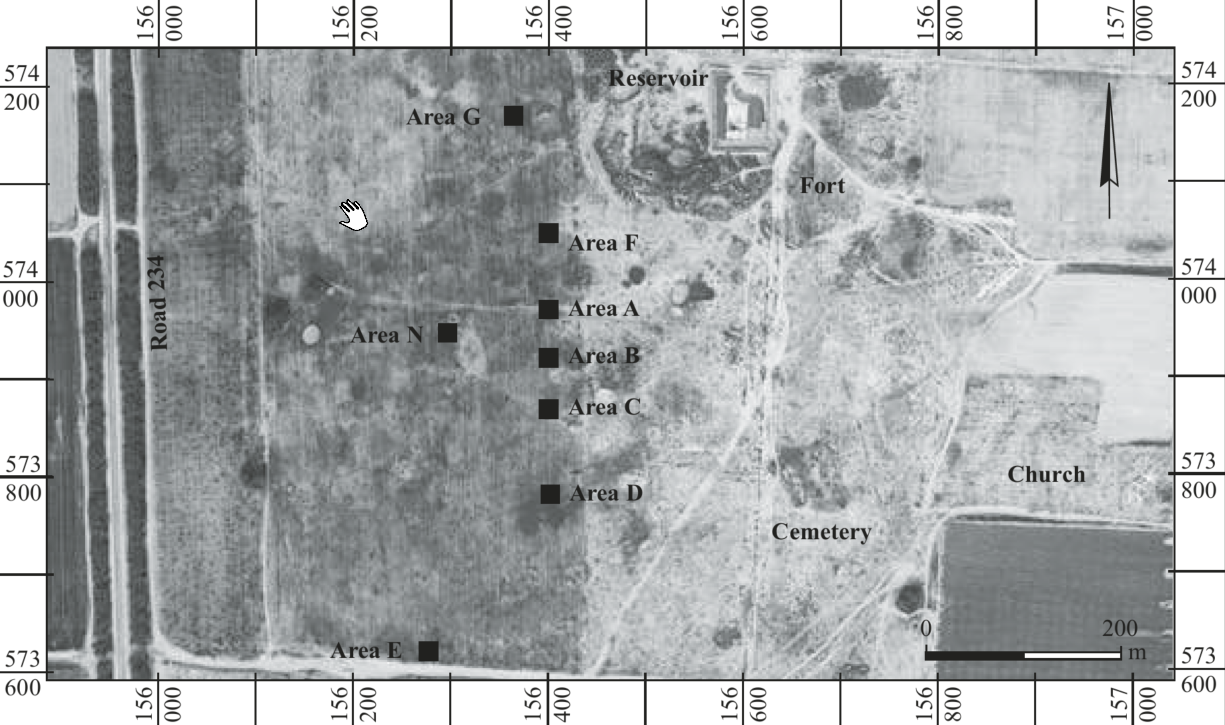
- Fig. 2 Excavation areas
from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
Magnified
- Fig. 2 Excavation areas
from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
Photos
Normal Size
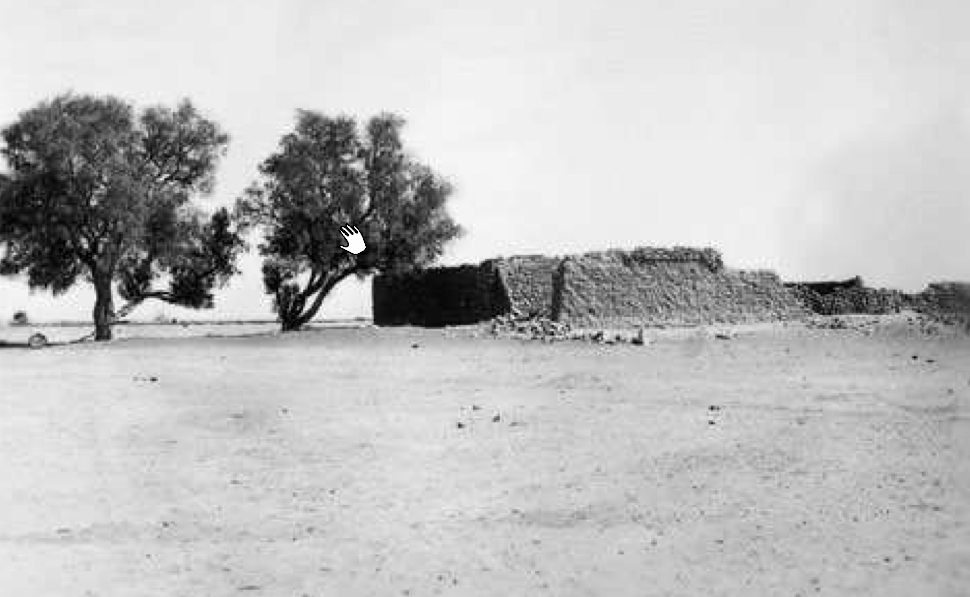
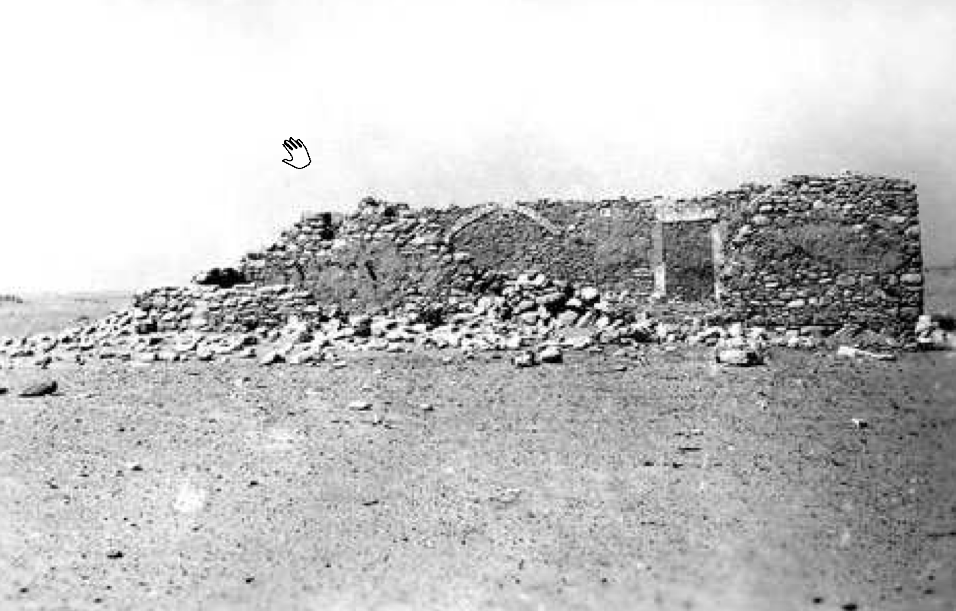
- Fig. 3 Mud-brick structure
at Horbat Be’er Shema‘ in the 1950s from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
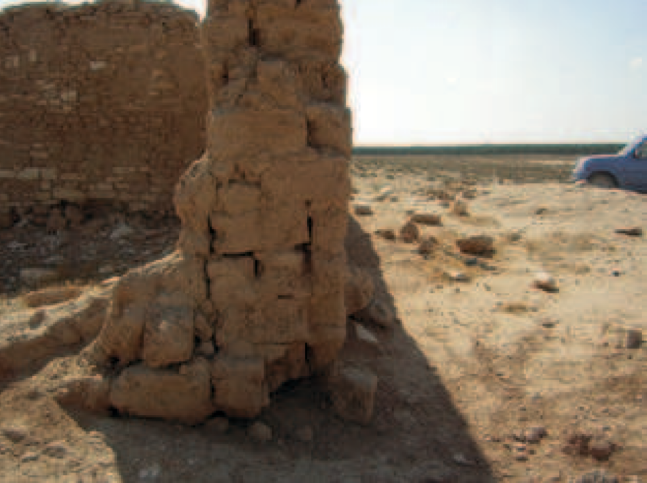
- Fig. 4 Stone and mud-brick
structure at Horbat Be’er Shema‘ in the 1950s from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
- Fig. 21 Mud-brick structure
at Horbat Kasif from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
Magnified
- Fig. 3 Mud-brick structure
at Horbat Be’er Shema‘ in the 1950s from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
- Fig. 4 Stone and mud-brick
structure at Horbat Be’er Shema‘ in the 1950s from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
- Fig. 21 Mud-brick structure
at Horbat Kasif from Erickson-Gini et al. (2015)
Stratigraphy
Entire Site
- from Chat GPT 5, 31 August 2025
- from Erickson-Gini, Dolinka & Shilov (2015)
| Phase | Period | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Byzantine (Late Antique) | 5th–early 7th c. CE | Industrial quarter with winepress (Area C), storage facilities (Area A), and a structure with cellar (Area H). Associated with Gaza wine jar production and large-scale viticulture. |
| II | Early Islamic | 8th–9th c. CE | Domestic occupation in Area F, with field walls, rooms, a clay tabun, and associated ceramics. Represents continued settlement after Byzantine decline. |
| III | Modern (British Mandate) | Early 20th c. CE | Mud-brick houses on stone foundations (Areas D, E, N), built by local fellahin. Occupied until 1948, later dismantled or abandoned. |
Potential Archaeoseismic Evidence at Horbat Be’er Shema‘
- from Chat GPT 5, 31 August 2025
- from Erickson-Gini, Dolinka & Shilov (2015) and Brantmayer (pers. comm, 2025)
| Area / Structure | Seismic Effects | Dating Evidence | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fort's Walls | "While we did find some evidence that the fort's walls may have collapsed at the end of the Byzantine Period (probably late 7th c CE, though we haven't had anything intensively dated!), there's been no direct evidence of seismic activity at the site." - Erin Brantmayer, personal communication, 8/31/2025 | probably late 7th c CE, though we haven't had anything intensively dated! | |
| Area A – Storage facility | No explicit seismic damage reported. Robbing of floors and stones noted; mud-slurry foundations could indicate structural instability. | Associated ceramics and storage jars, mainly 5th–7th c. CE. | Stripping and stone removal in modern times complicate evidence. Earthquake damage cannot be confirmed. |
| Area C – Winepress | Robbing of pavement stones and damage to water tank reported. No clear seismic collapse layers identified. | Coins of Anastasius I (512–517 CE) and Justin I (518–527 CE) in overlying debris; pottery dated to 5th–6th c. CE. | Industrial facility remained in use until at least the early 6th c. CE. Disturbance attributed to stone robbing rather than seismic destruction. |
| Area H – Storage building with cellar | Well-built cellar preserved intact. No collapsed earthquake destruction layers observed. Domestic traces (cooking fires, vessels) found in situ. | Vessels dated 6th–7th c. CE, with some later Byzantine forms extending into the Early Islamic period. | High ceramic preservation suggests intentional discard rather than sudden seismic destruction. |
| Area F – Early Islamic occupation | No seismic destruction noted. Features include tabun, walls, and fire pits. Structures modest and lightly built. | Pottery dated to 8th–9th c. CE; Arabic-inscribed sherd. | Occupation evidence continuous after Byzantine decline; no signs of earthquake-induced abandonment. |
| Areas D, E, N – Modern houses | Collapse of mud-brick walls documented, but attributed to abandonment and dismantling rather than seismic damage. | Modern Black Gaza Ware and metal finds; structures dated to early 20th c. | Modern houses abandoned in 1948. No archaeoseismic relevance. |
References
Articles and Books
Wikipedia pages
Notitia Dignitatum