Baydha
 Aerial photo (2018) of Islamic Baydha
Aerial photo (2018) of Islamic Baydha
APAAME - Robert Bewley
| Transliterated Name | Source | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Baydha | Arabic | بييدها |
| Beydha | Arabic | بييدها |
| Beidha | Arabic | بييدها |
| Khirbet at-Baydha | Arabic | كهيربيت اتءبايدها |
| Khirbet Beidha | Arabic | |
| Islamic Baydha |
Sinibaldi (2015) offers the following
description of Baydha: “Islamic Bayda is located about 7 km
north of the Petra old city centre, immediately east of
Siq el-Barid and west of the modern Ammarin village.” She
adds that “the site is a rural village whose most evident
remains consist of several clusters of built habitations
and rock-cut features; the village has been settled over a
long time during the Islamic period (Early Islamic to
Ottoman periods).” Earlier phases are also attested: “there
had been settlement at the site during the Nabataean and
Byzantine periods; frequentation or settlement in the Iron
Age has been also recorded.”
Sinibaldi (2014:127) notes that “the
Islamic Baydha Project has conducted excavations here since
2014 and has recently dated the two village mosques to the
11th–14th centuries.” She added that “the mosques, so far the
only ones identified and excavated in the region, demonstrate
the presence of a village of a considerable size and
significance through the Middle Islamic period, a time during
which the Franks were also intensely occupying this area
(12th century), in which they had a great strategic and
economic interest.”
The Neolithic site of
Beidha is also located in the vicinity.
- Fig. 5.6 Location map from
Sinibaldi (2016)

 Fig. 5.6
Fig. 5.6
Location of the mentioned sites in the Wadi Musa and Jabal Shara areas
(reproduced and adapted from B. Beckers and B. Schutt, The Chronology of Ancient Agricultural Terraces in the Environs of Petra, in M. Mouton and S. Schmid, 2013)
Sinibaldi (2016) - Baydha in Google Earth
- Fig. 1 Plan of the western
part of the study area from Bikai et al (2020)

 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Plan of the western part of the study area at Beidha
Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2
Bikai et al (2020) - Fig. 68 Tentative reconstruction
of Mosque 2 (aka Western Mosque) from Sinibaldi (2018)

 Fig. 68
Fig. 68
A tentative reconstruction of Mosque 2 - from above
- the excavated structure
- a reconstruction of the upper part of the building
- a reconstruction of its exterior
(Reconstruction by Qais Tweissi on the basis of the team’s study of the structure’s walls)
Sinibaldi (2018) - Fig. 2 A mosque recorded
by the Photogrammetry survey of the Islamic Baydha Project in the 2023 season from Sinibaldi (2024)

 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
A mosque recorded by the survey of the Islamic Baydha Project in the 2023 season.
(Photogrammetry by Maksym Mackiewicz)
Sinibaldi (2024)
- Fig. 1 Plan of the western
part of the study area from Bikai et al (2020)

 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Plan of the western part of the study area at Beidha
Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2
Bikai et al (2020) - Fig. 68 Tentative reconstruction
of Mosque 2 (aka Western Mosque) from Sinibaldi (2018)

 Fig. 68
Fig. 68
A tentative reconstruction of Mosque 2 - from above
- the excavated structure
- a reconstruction of the upper part of the building
- a reconstruction of its exterior
(Reconstruction by Qais Tweissi on the basis of the team’s study of the structure’s walls)
Sinibaldi (2018) - Fig. 2 A mosque recorded
by the Photogrammetry survey of the Islamic Baydha Project in the 2023 season from Sinibaldi (2024)

 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
A mosque recorded by the survey of the Islamic Baydha Project in the 2023 season.
(Photogrammetry by Maksym Mackiewicz)
Sinibaldi (2024)
- Fig. 1 Photo of Mosque 1
from Sinibaldi (2023)

 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Mosque 1
Sinibaldi refers to the Eastern Mosque as Mosque 1
Photo by Micaela Sinibaldi
Sinibaldi (2023) - Fig. 2 Photo of Mosque 2
from Sinibaldi (2023)

 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
Mosque 2
Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2
Photo by Micaela Sinibaldi
Sinibaldi (2023)
- Fig. 1 Plan of the western
part of the study area from Bikai et al (2020)

 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Plan of the western part of the study area at Beidha
Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2
Bikai et al (2020) - Fig. 68 Tentative reconstruction
of Mosque 2 (aka Western Mosque) from Sinibaldi (2018)

 Fig. 68
Fig. 68
A tentative reconstruction of Mosque 2 - from above
- the excavated structure
- a reconstruction of the upper part of the building
- a reconstruction of its exterior
(Reconstruction by Qais Tweissi on the basis of the team’s study of the structure’s walls)
Sinibaldi (2018)
- Fig. 1 Plan of the western
part of the study area from Bikai et al (2020)

 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Plan of the western part of the study area at Beidha
Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2
Bikai et al (2020) - Fig. 68 Tentative reconstruction
of Mosque 2 (aka Western Mosque) from Sinibaldi (2018)

 Fig. 68
Fig. 68
A tentative reconstruction of Mosque 2 - from above
- the excavated structure
- a reconstruction of the upper part of the building
- a reconstruction of its exterior
(Reconstruction by Qais Tweissi on the basis of the team’s study of the structure’s walls)
Sinibaldi (2018)
| Effect | Location | Image(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| probably destroyed by an earthquake suggests collapsed walls | Mosque 2 (aka Western Mosque)
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1Plan of the western part of the study area at Beidha Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2 Bikai et al (2020) |

 Fig. 68
Fig. 68A tentative reconstruction of Mosque 2 - from above
(Reconstruction by Qais Tweissi on the basis of the team’s study of the structure’s walls) Sinibaldi (2018) 
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2Mosque 2 Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2 Photo by Micaela Sinibaldi Sinibaldi (2023) |
|
-
Earthquake Archeological Effects chart
of Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
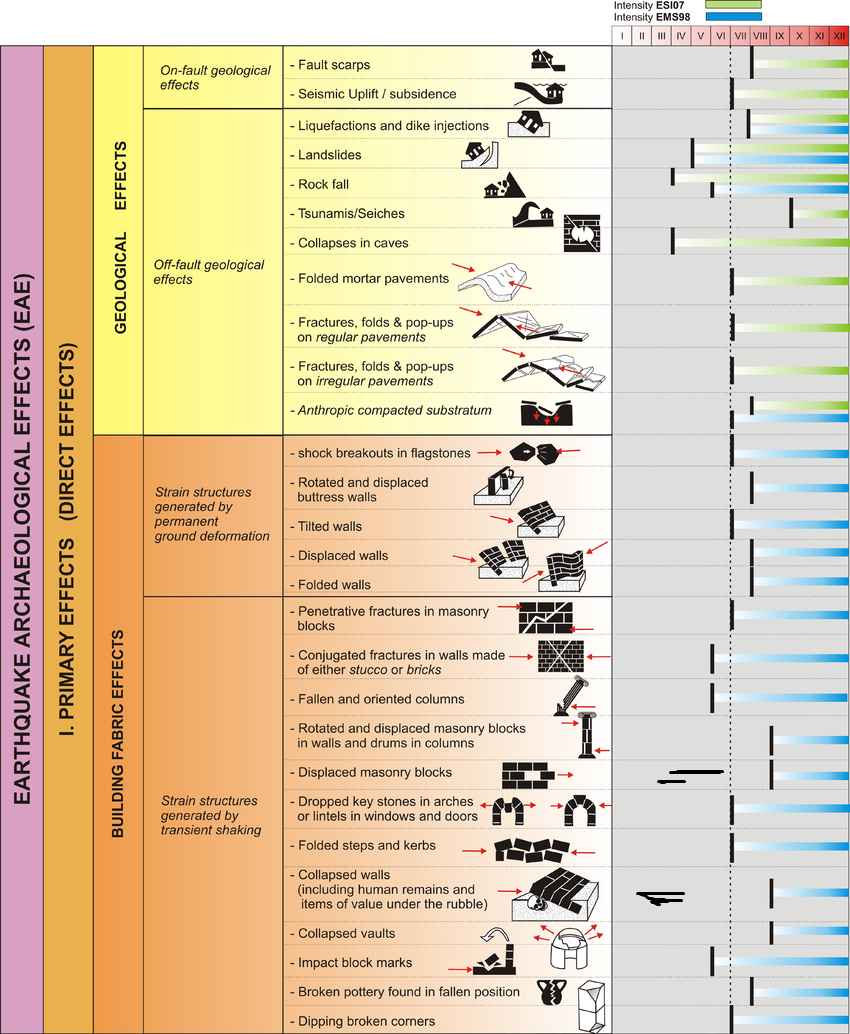
 Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Earthquake Archeological Effects (EAE)
Rodríguez-Pascua et al (2013: 221-224)
| Effect | Location | Image(s) | Description | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| probably destroyed by an earthquake suggests collapsed walls | Mosque 2 (aka Western Mosque)
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1Plan of the western part of the study area at Beidha Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2 Bikai et al (2020) |

 Fig. 68
Fig. 68A tentative reconstruction of Mosque 2 - from above
(Reconstruction by Qais Tweissi on the basis of the team’s study of the structure’s walls) Sinibaldi (2018) 
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2Mosque 2 Sinibaldi refers to the Western Mosque as Mosque 2 Photo by Micaela Sinibaldi Sinibaldi (2023) |
|
VIII+ |
Sinibaldi and Tuttle, 2011, THE BROWN UNIVERSITY PETRA ARCHAEOLOGICAL PROJECT:
2010 EXCAVATIONS AT ISLAMIC BAYḌĀ ADAJ 55
Sinibaldi, M. 2014. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2014. Report submitted to DOA, October 2014.
Sinibaldi, M. 2015. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2014. Palestine Exploration Quarterly 147.2 (2015), 160-164, Reports section.
Sinibaldi, M. 2016. Petra: Islamic Bayda Project, in G. Corbett et al., Archaeology in Jordan, 2014 and 2015 seasons, American Journal of Archaeology, 120.4, 660.
Sinibaldi, M. 2018. Islamic Baydha Project, seasons 2016 and 2017. In Archaeology in Jordan, edited by
J. Green, B. Porter and C. B. Shelton, the American Center of Oriental Research, Amman, pp. 74-75 (November 2018).
Sinibaldi, M. 2019. The Islamic Baydha Project, Baydha (Petra Region), season 2018, Palestine Exploration Quarterly, 151:3-4, 252-255.
Sinibaldi, M. 2020. Petra: Islamic Baydha Project, (2018-2019, Archaeology in Jordan 2:2018-2019
, the American Center of Oriental Research, Amman
Sinibaldi, M. 2015. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2015. Report submitted to DOA, October 2015.
Sinibaldi, M. 2016. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2016. Report submitted to DOA, September 2016.
Sinibaldi, M. 2017. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2017. Report submitted to DOA, November 2017.
Sinibaldi, M. 2019. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2019. Report submitted to DOA, November 2019.
Sinibaldi, M. 2018. Islamic Bayda Project, Bayda (Petra Region), season 2018. Report submitted to DOA, November 2018.
Sinibaldi, M. In preparation. Six Seasons of excavations of the Islamic Baydha Project (2014-2019), to be submitted to ADAJ
Sinibaldi, M. (2023). "Towards a Chronological Framing of the Two Mosques of Islamic Baydha."
Palestine exploration quarterly 155(4): 358-361.
Sinibaldi, M. (2024). Islamic Baydha Project season 2023
Archaeology in Jordan 2022-2023 Volume 4 2024. 127-129
Sinibaldi, M. 2018. Did Petra’s inhabitants really abandon the city? The British Academy blog (6 March 2018)
Sinibaldi, M. 2015. The Ceramic Assemblage from the Later phases at Tomb 303. Settlement in Wadi Ath-Thugrah in the Islamic Period,
Annual of the Department of Antiquities of Jordan 57, 167-178.
Sinibaldi, M. 2006. Crusader Archaeology in Southern Jordan. Newsletter of the American Center of Oriental Research 18.2: 4–6.
Sinibaldi, M. 2009. The Franks in Southern Transjordan and the contribution of ceramic studies. A preliminary report on the
pottery assemblages of Bayda and Wadi Farasa, Annual of the Department of Antiquities of Jordan 53: 449-464.
Sinibaldi, M. 2010. Villages of Crusader Transjordan: a survey of archaeological sources, Bulletin of Council for British Research in the Levant 2010: 60-63.
Sinibaldi, M. 2016. Settlement in the Petra Region During the Crusader Period: a Summary of the Historical and Archaeological Evidence,
in M. Sinibaldi K.Lewis, J. Thompson and B. Major (eds.), Crusader Landscapes in the Medieval Levant. The Archaeology and History of the Latin East, Cardiff, University of Wales Press, 2016, 81-102.
Sinibaldi, M. 2014. Settlement in Crusader Transjordan, 1100-1189. PhD thesis defended at Cardiff University, October 2014.
Byrd, B. F. (1989). The Natufian Encampment at Beidha: Late Pleistocene Adaptation in the Southern
Levant. Denmark: Jysk arkæologisk selskab.
Moore, A.M.T. (1978). The Neolithic of the Levant. Oxford University, Unpublished PhD Thesis. pp. 109–113, 243–256. - open access
Comer, D. (2003) Environmental History at an Early Prehistoric Village: An Application of Cultural Site Analysis at Beidha, in Southern Jordan
Journal of GIS in Archaeology, Volume I—April 2003 - open access
Byrd,(2005). Early Village Life at Beidha, Jordan : Neolithic Spatial
Organization and Vernacular Architecture: The Excavations of Mrs Diana Kirkbride-Helbæk.
United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Kirkbride, D. (1966). Five Seasons at the Pre-pottery Neolithic Village of Beidha in Jordan. United Kingdom: Palestine Exploration Fund.
- download these files into Google Earth on your phone, tablet, or computer
- Google Earth download page
| kmz | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Right Click to download | Master kmz file | various |
